Sound is a type of energy that travels in waves. But have you ever wondered how fast sound moves? The speed of sound is how quickly sound waves travel through different materials like air, water, or metal. It depends on factors like temperature, pressure, and the medium through which it travels.
In general, sound moves fastest in solids, slower in liquids, and slowest in gases. For example, in dry air at 20°C, the speed of sound is about 343 m/s (meters per second). But in water, it travels faster, around 1,480 m/s, and in steel, it can go up to 5,960 m/s!
The speed of sound is an important topic for SSC, Banking, RRB NTPC, UPSC, and state-level exams. Questions about this concept often appear in Physics, General Science, and GK sections. In this article, we will explore key details about the speed of sound along with important MCQs (Multiple Choice Questions) to help you prepare better.
What is Sound?
Sound is a form of energy that travels in the form of waves. These waves need a medium like air, water, or solid objects to travel.
Unlike light, which can travel in space, sound cannot travel in a vacuum (empty space) because there are no particles to carry the vibrations.
What is the Speed of Sound?
The speed of sound is how fast sound waves travel through a medium (like air, water, or solid objects). Sound needs a medium to travel because it moves in the form of vibrations. It cannot travel through a vacuum (like outer space) since there are no particles to carry the sound. It depends on three main factors:
- The Medium (Air, Water, or Solid)
- Temperature
- Pressure (less important compared to the medium and temperature)
The formula for speed of sound in a medium is:
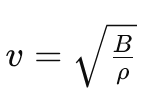
Where:
- v = speed of sound
- B = Bulk modulus (stiffness of the medium)
- ρ = Density of the medium
Speed of Sound in Different Mediums
Sound travels at different speeds in different materials. The denser and more rigid the material, the faster sound can travel.
| Medium | Speed of Sound (m/s) |
|---|---|
| Air (at 20°C) | 343 m/s |
| Water | 1,480 m/s |
| Steel | 5,960 m/s |
| Glass | 5,000 m/s |
| Wood | 3,300 m/s |
Key Takeaway:
🔹Sound travels slowest in gases (like air).
🔹Sound is faster in liquids than in gases.
🔹Sound travels fastest in solids because particles are closely packed together.
Factors Affecting the Speed of Sound
1. Medium
- Sound moves faster in solids than in liquids, and faster in liquids than in gases.
- Example: Sound travels faster through metal than through air.
2. Temperature
- When temperature increases, particles move faster, allowing sound to travel more quickly.
- Example: On a hot day, sound travels faster in the air than on a cold day.
3. Humidity (Moisture in Air)
- Higher humidity means more water vapor in the air, which makes sound travel faster.
- Example: Sound travels faster on a rainy day than on a dry day.
4. Altitude (Height Above Sea Level)
At higher altitudes, air is less dense, but the effect on sound speed is minimal compared to temperature changes.
Real-Life Examples of Speed of Sound
- Echo: When sound bounces back from a solid surface, it creates an echo. The time taken for an echo depends on the speed of sound.
- Sonar (Sound Navigation and Ranging): Ships and submarines use sound waves to measure the depth of the ocean.
- Supersonic Jets: Some jets travel faster than the speed of sound, creating a sonic boom.
- Musical Instruments: The speed of sound affects how different musical instruments produce sound.
Fun Fact!
When an object moves faster than the speed of sound, it breaks the sound barrier, creating a loud sonic boom. The first person to break the sound barrier in an aircraft was Chuck Yeager in 1947.
Quick Revision Points
✅ Sound needs a medium to travel. It cannot move in a vacuum.
✅ The speed of sound is 343 m/s in air (at 20°C).
✅ Sound moves fastest in solids, slower in liquids, and slowest in gases.
✅ Higher temperature and humidity increase the speed of sound.
✅ Supersonic jets travel faster than sound and create a sonic boom.
Practice Quiz
Q1: What is the speed of sound in air at 20°C?
a) 300 m/s
b) 343 m/s
c) 5100 m/s
d) 1482 m/s
Q2: In which medium does sound travel the fastest?
a) Air
b) Water
c) Steel
d) Helium
Q3: Which factor does NOT affect the speed of sound?
a) Medium
b) Temperature
c) Humidity
d) Pressure (at constant temperature)
Q4: Why do we see lightning before we hear thunder?
a) Because our ears are slow
b) Because sound cannot travel in air
c) Because light travels faster than sound
d) Because sound does not travel at night
Q5: What is the approximate speed of sound in distilled water at 25°C (77°F)? [CHSL 2020]
(a) 1498 m/s
(b) 1284 m/s
(c) 3980 m/s
(d) 1598 m/s
(Answers: 1-b, 2-c, 3-d, 4-c, 5-a)
Final Words
The speed of sound is an important concept in science and technology. It helps us understand everything from weather forecasting to aircraft engineering. By knowing how sound behaves in different materials, we can better understand the world around us. Keep exploring and keep learning!
Happy Learning! 🚀

