The cell membrane, also known as the plasma membrane, is one of the most important parts of a cell. It acts like a protective barrier, controlling what enters and exits the cell. Think of it as the security guard of the cell, ensuring that only the right materials go in and out. Understanding the cell membrane is essential for competitive exams like SSC, RRB NTPC, UPSC, and state-level exams.
Structure of the Cell Membrane
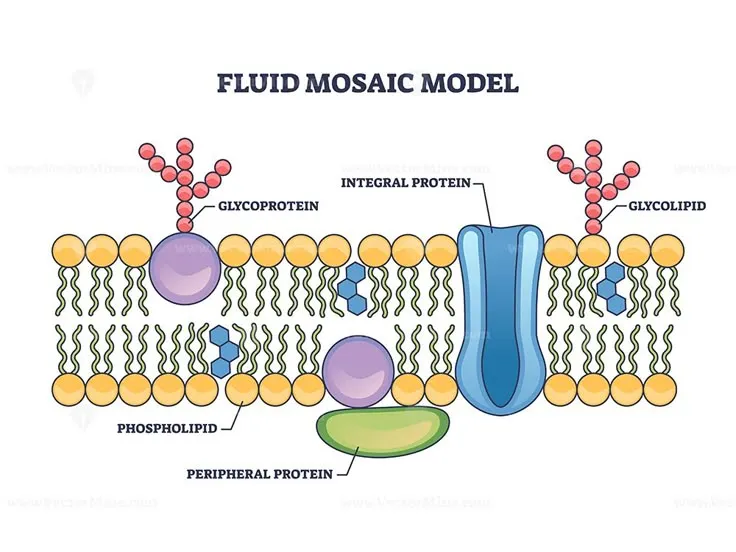
The cell membrane is made up of:
Phospholipid Bilayer
- The main structure of the membrane.
- Composed of two layers of phospholipids (fats with a water-loving head and a water-hating tail).
- Each phospholipid has a hydrophilic (water-attracting) head and a hydrophobic (water-repelling) tail.
- This arrangement provides structural integrity and flexibility.
Proteins
- Embedded within or attached to the membrane.
- Functions include transportation, signaling, and cell recognition.
- Types:
- Integral proteins: Span the entire membrane.
- Peripheral proteins: Attach to the surface.
Carbohydrates
- Found on the outer surface.
- Carbohydrates aid in cell recognition and communication.
- Cholesterol maintains the fluidity and stability of the membrane.
Cholesterol
- Maintains the fluidity of the membrane.
- Prevents it from becoming too rigid or too flexible.
📌 Mnemonic: “PPC – Phospholipids, Proteins, Carbohydrates & Cholesterol”
Diagram of a Cell Membrane
A simple representation of a cell membrane structure:
To stay updated with the latest GK and Current Affairs infographics, follow our official Instagram and Facebook page and prepare for exams easily.
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Phospholipid Bilayer | Forms the basic structure, controls permeability |
| Proteins | Help in transport and communication |
| Carbohydrates | Assist in cell recognition |
| Cholesterol | Provides stability and flexibility |
Functions of the Cell Membrane
The cell membrane performs several important functions:
- Selective Permeability: It allows only specific substances to enter and exit the cell.
- Protection: Acts as a shield, preventing harmful substances from entering.
- Communication: Sends and receives signals from other cells.
- Transport of Materials: Moves nutrients, gases, and waste in and out of the cell.
- Maintaining Cell Shape: Helps in maintaining the structure of the cell.
Types of Transport Across the Cell Membrane
There are two main types of transport:
1. Passive Transport (No Energy Required)
- Diffusion: Movement of molecules from high to low concentration (e.g., oxygen, carbon dioxide).
- Osmosis: Movement of water molecules across a membrane.
- Facilitated Diffusion: Transport of substances with the help of proteins.
2. Active Transport (Requires Energy)
- Uses ATP (Adenosine Triphosphate) to transport substances.
- Moves molecules from low to high concentration (opposite of diffusion).
- Example: Sodium-Potassium Pump in nerve cells.
| Transport Type | Energy Required? | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Diffusion | No | Oxygen, Carbon dioxide |
| Osmosis | No | Water movement |
| Facilitated Diffusion | No | Glucose transport |
| Active Transport | Yes | Sodium-Potassium Pump |
| Transport Type | Energy Required? | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Passive Transport | ❌ No | Moves molecules from high to low concentration. |
| Active Transport | ✅ Yes | Moves molecules from low to high concentration using ATP. |
📌 Mnemonic: “DOF-E” (Diffusion, Osmosis, Facilitated diffusion – Endocytosis, Exocytosis)
Fun Fact 🌟
Did you know? The cell membrane is like a soap bubble! Just like a bubble’s outer layer is made of a thin film of water and soap molecules, the cell membrane is made of a thin layer of lipids and proteins that keep the cell safe and functional!
Real-Life Examples of Cell Membrane Function
🔸 Security Gate: Allows only specific molecules, like a security checkpoint.
🔸 Tea Bag & Water: Tea diffuses out, similar to diffusion.
🔸 Water Absorption by Plants: Roots absorb water via osmosis.
Exam Tips for Cell Membrane
✔ Learn key terms like diffusion, osmosis, and active transport.
✔ Use mnemonics to simplify memorization.
✔ Study diagrams and tables for quick revision.
✔ Relate concepts to real-world examples.
✔ Practice previous exam questions.
Quick Revision:
✅ The cell membrane is also called the plasma membrane.
✅ It is made of phospholipids, proteins, carbohydrates, and cholesterol.
✅ It allows selective permeability—only certain substances can pass.
✅ There are two types of transport: Passive (No energy) and Active (Uses energy).
Keep learning, stay curious, and ace your exams! 🚀💡
Practice Questions
Q1: What is the primary function of the cell membrane?
A. Producing energy
B. Controlling what enters and leaves the cell
C. Storing genetic material
D. Making proteins
Q2: Which part of the cell membrane helps with cell recognition?
A. Phospholipids
B. Proteins
C. Carbohydrates
D. Cholesterol
Q3: Osmosis is the movement of:
A. Proteins
B. Oxygen
C. Water
D. Glucose
True or False
- Facilitated diffusion requires energy. (True/False)
- Endocytosis is a type of passive transport. (True/False)
💡 Bonus Challenge: Draw and label the cell membrane structure!
Conclusion
The cell membrane is an essential part of a cell, acting as a protective barrier and selective filter. Understanding its structure, functions, and transport mechanisms is crucial for mastering biology concepts in competitive exams. Use mnemonics, diagrams, and real-life examples to enhance your learning! 🚀
📢 Stay tuned for more interesting biology topics! Keep learning, and keep growing! 🌱

