Know details about the 6 classical languages of India with important questions. Arts and Culture is an inevitable part of the most competitive exams in India such as WBCS, UPSC IAS Prelims, SSC, and RRB NTPC Exams. So, Read this article to learn more about the classical languages of India.
The official language of India
• India has the fourth highest number of languages (447) in the world after Papua New Guinea (840), Indonesia (710), and Nigeria (524).
• The Eighth Schedule of the Indian Constitution lists 22 languages.
• According to Article 343, the official language of India should be Hindi in the Devanagari script.
• In 2004, the Government of India decided to grant the status of “classical languages” to certain languages that have rich traditions and independent origins.
• The concept of “classical language” originated in Europe. In 2004, the Government of India declared Tamil as a classical language.
✅ 8 classical dance forms of India UPSC
Criteria for Declaring Classical Languages of India
• The government follows the following criteria for determining the eligibility of a language to be considered for classification as a “classical language”:
• Extraordinary antiquity of its early transcripts or verified history from 1500 to 2000 years.
• A body of ancient literature or texts, which is considered a valuable heritage by generations of speakers.
• The literary tradition should be original and unique, and certainly not hired from another language community.
• Classical language and literature are diverse from modern literature, and there may also be a discontinuity among the classical languages and their later forms or sprouts.
Classical Languages of India
• Tamil was the first classical language of India, which was declared by the government of India in 2004.
• In 2005, the government of India declared Sanskrit as a Classical Language of India.
• The two languages, Tamil and Sanskrit, are undoubtedly the parent source for several languages belonging to the Indo-European family and the Dravidian family of languages.
• The government gave the status of classical language to Kannada and Telugu in 2008.
• Malayalam was declared a classical language in 2013.
• In 2014, Odia was also given the status of the Classical language.
✅ Famous Temples in India GK: Complete Details
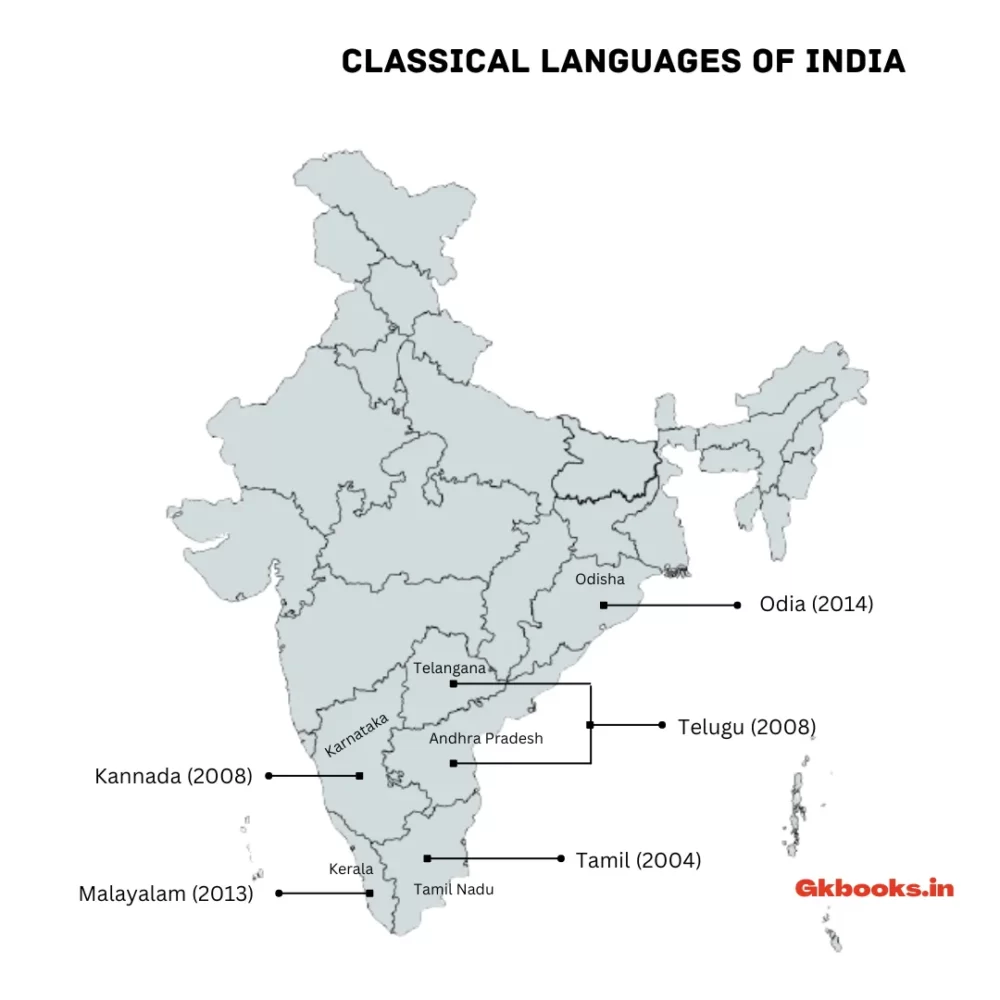
6 Classical Languages of India with Year of Declaration
| Sl.No | Classical language | Year |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Tamil | 2004 |
| 2 | Sanskrit | 2005 |
| 3 | Telugu | 2008 |
| 4 | Kannada | 2008 |
| 5 | Malayalam | 2013 |
| 6 | Odia | 2014 |
Top One-liners on classical languages of India
Question 1. When was Tamil declared a classical language?
Answer: 2004
Question 2. When was Sanskrit declared as a classical language?
Answer: 2005
Question 3. When was Kannada declared as a classical language?
Answer: 2008
Question 4. When was Telugu declared as a classical language?
Answer: 2008
Question 5. When was Malayalam declared as a classical language?
Answer: 2013
Question 6. When was Odia declared as a classical language?
Answer: 2014
Question 7. Which state is Malayalam the official language of?
Answer: Kerala
Question 8. In which script are most of the classical languages written?
Answer: Brahmi-derived scripts such as Devanagari, and Eastern Nagari.
Question 9. Recently, which language has been claimed to have the status of classical language?
Answer: Marathi language
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) on classical languages of India
Answer: Brahmi-derived scripts such as Devanagari, and Eastern Nagari.
• Languages belonging to the Devanagari script are Tamil, Telugu, Kannada, Odia, and Sanskrit.
• Languages belonging to Eastern Nagari script – Assamese and Bengali, etc.
Answer: Tamil(2004), Sanskrit (2005), Telugu(2008), Kannada (2008), Malayalam (2013), Odia (2014)
Answer: India currently has 6 classical languages.
Answer: Tamil (2004)
Answer: Odia (2014)

