Imagine your body as an orchestra, with countless instruments playing in harmony. The conductor, ensuring everything flows smoothly? That’s your nervous system! This intricate network of nerves and specialized cells is like the body’s electrical wiring, constantly buzzing with messages that control everything from the flutter of your heartbeat to the spark of a creative thought. ⚡️
You can also Imagine the Human Nervous System as a high-tech communication network, comprising the brain, spinal cord, and nerves, all working together to ensure seamless interactions within our body.
Explore its functions, diagnostic tools, and some intriguing facts that might just blow your mind! Are you ready to discover the conductor within you?
What is the Human Nervous system?
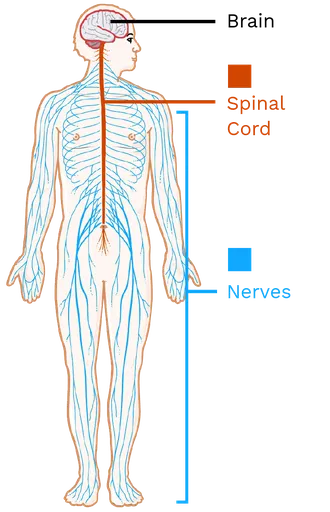
- Our body’s control hub, the nervous system, comprises the brain, spinal cord, and nerves.
- Through the transmission of electrical signals, this intricate network conveys messages between the brain and various body parts, directing essential functions such as breathing, movement, speech, and vision.
- Not only does the nervous system monitor internal and external stimuli, but it also determines appropriate responses to different situations.
- Apart from consciously controlled actions, the nervous system governs involuntary processes like thoughts and memory.
- It also plays a pivotal role in overseeing unconscious bodily activities such as blushing, sweating, and blinking.
Function
What does the nervous system do?
The primary role of your nervous system revolves around the exchange of messages between different body parts and the brain. This complicated communication system oversees various aspects of your well-being, influencing:
Cognitive Functions
- Thoughts, memory, learning, and feelings are intricately regulated by the nervous system.
Physical Coordination
- Governing movements, balance, and coordination to ensure smooth bodily functions.
Sensory Interpretation
- Influencing how your brain interprets stimuli, including sight, hearing, taste, touch, and overall sensory experiences.
Healing Processes
- Playing a crucial role in wound healing and overall recovery mechanisms.
Sleep Regulation
- Impacting your sleep patterns and ensuring a balanced and restorative rest.
Cardiovascular and Respiratory Control
- Overseeing heartbeat and breathing patterns to maintain optimal physiological conditions.
Stress Response
- Managing your response to stressful situations, including the production of sweat.
Digestive Harmony
- Regulating digestion for efficient nutrient absorption and overall well-being.
Life Stages and Aging
- Contributing to essential body processes such as puberty and aging, shaping the various stages of life.
Delve into the intricate web of your nervous system’s functions, understanding its pivotal role in maintaining a harmonious balance in both mind and body.
How does the nervous system work?
In the complicated network of our nervous system, specialized nerve cells known as neurons act as messengers, transmitting electrical signals throughout your body.
These signals navigate through the brain, skin, organs, glands, and muscles, contributing to various essential functions.
Communication Pathways
- Electrical signals travel seamlessly between the brain, skin, organs, glands, and muscles, orchestrating coordinated responses.
Limb Movement and Sensations
- Neuronal messages facilitate limb movement and sensory perceptions, allowing you to interact with your environment and experience sensations like pain.
Sensory Input and Information Processing
- Your eyes, ears, tongue, nose, and body’s nerves collaborate to collect information about the surroundings. Nerves then convey this data to and from the brain, enabling a comprehensive understanding of the environment.
Neuronal Diversity
- Different types of neurons serve distinct purposes in the nervous system.
Motor Neurons
- Transmit signals from the brain and spinal cord to muscles, facilitating movement, breathing, swallowing, and speaking.
Sensory Neurons
- Convey information from your senses (sight, touch, taste, etc.) to the brain, forming the basis of your sensory experiences.
Interneurons
- Act as communicators between motor and sensory neurons, regulating movements in response to sensory input. They also contribute to learning, thinking, and memory processes.

What tests examine the well-being of our nervous system?
A healthcare professional might use one of the following tests to assess the health of your nervous system:
- Computed Tomography (CT) Scan: This imaging test provides detailed pictures of the inside of your body.
- Electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG): This measures the electrical activity of your heart to evaluate its function.
- Electroencephalogram (EEG): This test records brain activity and helps identify any abnormalities.
- Lumbar Puncture (Spinal Tap): A procedure involving the collection of cerebrospinal fluid to check for potential issues.
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) Scans: These scans use magnetic fields and radio waves to create detailed images of your body’s internal structures.
Note: Knowing the full forms of medical acronyms like MRI, ECG, CT Scan, and EEG is crucial for competitive exams.
Key Takeaways for Competitive Exams
- The nervous system, comprising the brain, spinal cord, and nerves, controls body functions through the transmission of electrical signals.
- It governs both conscious actions and involuntary processes, impacting everything from movement to emotions.
- The nervous system regulates cognitive functions, physical coordination, sensory interpretation, and sleep patterns.
- Neurons, the specialized nerve cells, transmit electrical signals, orchestrating communication between the brain and various body parts.
- Motor neurons transmit signals for movement, while sensory neurons convey information from the senses to the brain.
- Interneurons act as communicators, regulating movements and contributing to learning and memory processes.
- Diagnostic tests for nervous system health include CT scans, ECG/EKG, EEG, lumbar puncture, and MRI scans.
Interesting Facts about the Nervous System
- The nervous system is so complex that it contains around 300 billion cells in African elephants, the largest number of any animal.
- Neurons can send signals at speeds of up to 200 miles per hour, which is faster than the fastest bullet train.
- The brain uses about 20% of the body’s energy, even though it only makes up about 2% of the body’s weight.
- We only use about 10% of our brain, but this is still enough to perform complex tasks like thinking, feeling, and moving.
- The human brain is capable of generating about 100 watts of electrical power, which is enough to power a small light bulb.
- The nervous system is constantly changing and adapting, even in adulthood.
- There are more neurons in the human brain than there are stars in the Milky Way galaxy.
- The nervous system is responsible for everything we do, from thinking and feeling to moving and breathing.
- Nervous tissue originated in wormlike organisms approximately 550 to 600 million years ago.
- Sponges, placozoans, and mesozoans are the only multicellular animals without a nervous system.
- Ctenophores and cnidarians possess a diffuse nerve net rather than a centralized nervous system.
- Worms may have a simple nervous system with a few hundred cells.
- Comb jellies and cnidarians exhibit radially symmetric nervous systems.
- Malfunctions in the nervous system can result from genetic defects, trauma, toxicity, infection, or aging.
- Neurology is the medical specialty dedicated to studying and addressing disorders of the nervous system.
- Diabetic neuropathy is a common peripheral nervous system problem associated with diabetes.
Sources:
- forteelements.com/nervous-system/
- brainly.ph/question/30482533
- en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Nerve
- en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Nervous_system
✅ More Recommended Posts on Biology 👇