Flowers are one of the most beautiful parts of a plant. But have you ever noticed how flowers are arranged on a plant? This arrangement is called inflorescence. In this blog, we will explore the types of inflorescence in a simple and easy-to-understand way!
What is Inflorescence?
Inflorescence refers to the way flowers are arranged on a plant’s stem or branch. Some plants bear flowers singly, while others bear them in clusters.
A flower is a modified shoot, where the shoot apical meristem changes into a floral meristem. In this transformation:
- Internodes do not elongate, and the axis gets condensed.
- Instead of leaves, the apex produces different floral appendages at successive nodes.
- When a shoot tip transforms into a flower, it is always solitary.
- The arrangement of flowers on the floral axis is called inflorescence.
Depending on whether the apex develops into a flower or continues to grow, two major types of inflorescences are defined:
- Racemose Inflorescence (Indeterminate)
- Cymose Inflorescence (Determinate)
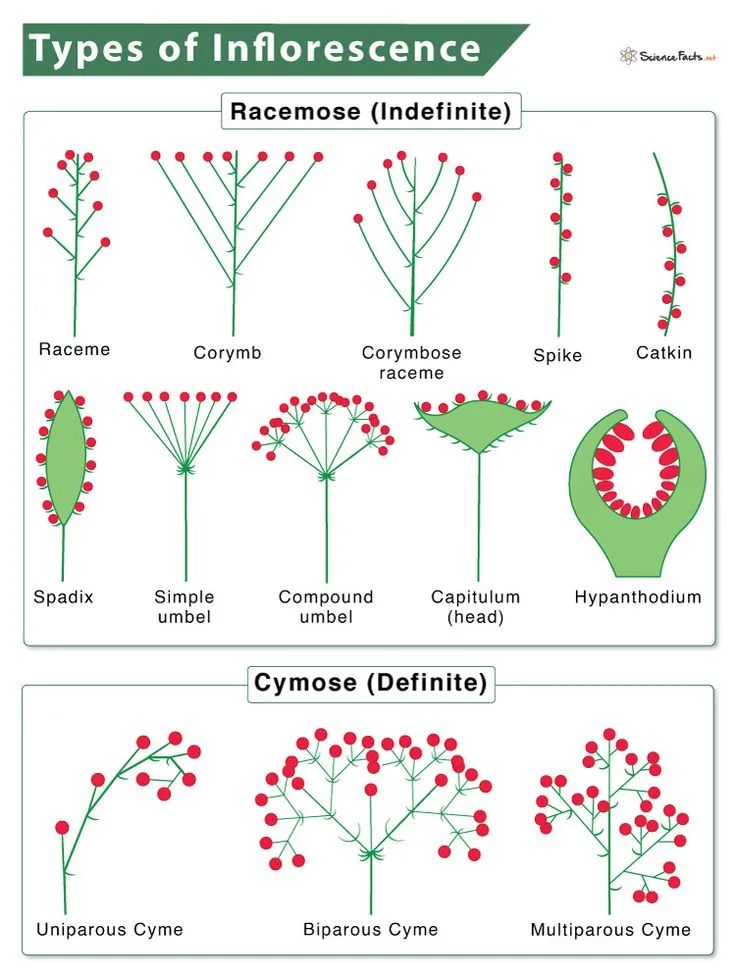
Types of Inflorescence
1️⃣ Racemose Inflorescence (Indeterminate)
In racemose inflorescence, the main axis continues to grow, and flowers bloom in an orderly manner from the bottom to the top. This is called acropetal succession.
✨ Characteristics
- The Main stem keeps growing.
- Flowers bloom from the base to the tip (oldest at the bottom, youngest at the top).
- Continuous flowering.
🔹 Types of Racemose Inflorescence:
| Type | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Raceme | Flowers are arranged on an elongated main axis | Mustard, Radish |
| Spike | Flowers are attached directly to the stem | Wheat, Barley |
| Catkin | Hanging spike-like flowers | Willow, Mulberry |
| Spadix | Fleshy spike covered by a large leaf-like structure (spathe) | Banana, Maize |
| Umbel | All flower stalks originate from a single point | Onion, Carrot |
| Head/Capitulum | Small flowers arranged in a dense, rounded structure | Sunflower, Marigold |
2️⃣ Cymose Inflorescence (Determinate)
In cymose inflorescence, the main axis ends in a flower, meaning it stops growing once a flower blooms. This is called basipetal succession.
✨ Characteristics
- The Main stem stops growing after producing a flower.
- Flowers bloom from the top to the base (youngest at the bottom, oldest at the top).
- Limited flowering.
🔹 Types of Cymose Inflorescence:
| Type | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Uniparous (Monochasial) Cyme | A single branch grows below each flower | Sunflower, Cotton |
| Biparous (Dichasial) Cyme | Two branches arise below each flower | Jasmine, Ixora |
| Multiparous (Polychasial) Cyme | More than two branches arise below each flower | Alstonia |
Special Types of Inflorescence
Some plants have unique flower arrangements that do not fall into Racemose or Cymose. These include:
- Corymb – Unequal flower stalks, making all flowers appear at the same level (e.g., Cauliflower).
- Verticillaster – Flowers in whorls around the stem (e.g., Tulsi, Mint).
- Hypanthodium – Cup-shaped structure with small flowers inside (e.g., Ficus, Peepal tree).
Key Differences Between Racemose and Cymose Inflorescence
| Feature | Racemose | Cymose |
|---|---|---|
| Growth of Main Stem | Continues Growing | Stops growing after flowering |
| Flowering Order | From base to tip | From tip to base |
| Example Plants | Sunflower, Mustard | Jasmine, Ixora |
🎯 Exam Tips & Tricks!
✅ Remember: Racemose = Continuous growth, Cymose = Limited growth.
✅ Use mnemonic: “Racemose Rises, Cymose Closes” (Racemose keeps growing, Cymose stops growing).
✅ Practice by observing different flowers around you and identifying their inflorescence type.
Conclusion
Inflorescence plays a vital role in the reproduction and beauty of plants. By understanding its types and characteristics, you can easily identify different plants and enhance your knowledge for competitive exams like SSC, RRB NTPC, UPSC, and more!
🌟 Keep learning and keep growing! 🌟