Have you ever noticed how leaves are arranged on the branches of different plants? Some plants have leaves growing one by one, while others have leaves growing in pairs or clusters. This arrangement of leaves on a stem or branch is known as Phyllotaxy.
Phyllotaxy plays an important role in maximizing sunlight capture for photosynthesis. Understanding this concept is useful for students preparing for exams like SSC, RRB NTPC, UPSC, and state-level exams.
Types of Phyllotaxy
There are three main types of phyllotaxy:
- Alternate Phyllotaxy
- Opposite Phyllotaxy
- Whorled Phyllotaxy
Let’s understand each type with examples and diagrams.
1. Alternate Phyllotaxy
- In this type, a single leaf grows at each node, and the leaves are arranged alternately along the stem.
- This pattern ensures that leaves do not overlap and get maximum sunlight.
- Example: Sunflower, Mustard, China Rose (Hibiscus)
2. Opposite Phyllotaxy
- In this type, two leaves grow at each node, directly opposite to each other.
- This helps in balancing the plant and ensuring uniform light distribution.
- Example: Guava, Mint, Tulsi (Holy Basil)
3. Whorled Phyllotaxy
- In this type, more than two leaves grow at a single node, forming a whorl around the stem.
- This is commonly seen in certain flowering plants.
- Example: Alstonia, Nerium (Oleander)
| Phyllotaxy Type | Number of Leaves per Node | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Alternate | One | Sunflower, Mustard |
| Opposite | Two (opposite to each other) | Guava, Tulsi |
| Whorled | More than two | Alstonia, Nerium |
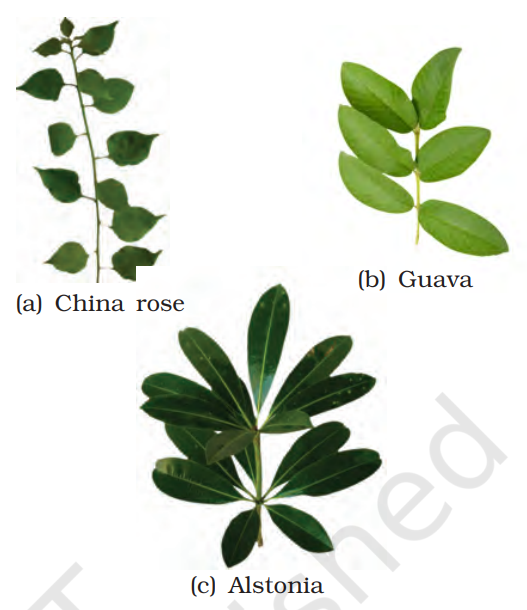
(a) Alternate (b) Opposite
(c) Whorled
Importance of Phyllotaxy
Phyllotaxy is important for plants because:
- It helps in maximum light absorption for photosynthesis.
- It prevents the overlapping of leaves to reduce shading.
- It ensures proper air circulation and minimizes fungal infections.
- It plays a role in water conservation by reducing excessive water loss.
Exam Tips and Tricks
To remember phyllotaxy easily, use these simple tricks:
- Alternate – Think of a zig-zag pattern, like in a sunflower.
- Opposite – Imagine two hands facing each other, like in a guava.
- Whorled – Think of a circular ring of leaves, like in Alstonia.
Mnemonic to Remember Examples:
- Alternate – Sunflower (A for Sunflower)
- Opposite – Guava (O for Guava)
- Whorled – Alstonia (W for Alstonia)
Conclusion
Phyllotaxy is an important topic in botany and competitive exams. Understanding how leaves are arranged on a stem helps in plant classification and studying their adaptations.
Keep observing different plants around you and identify their phyllotaxy! Happy learning! 🌿😊
Read More:
Important Days and Themes 2026: Month-wise Complete National & International List
Banking Current Affairs 2026 One-liners: Bank in News Latest Updates
Reserve Bank of India in News 2025: Latest Finance and Banking One-liners
International Financial Institutions in News 2025 [WB, IMF, ADB, NDB and More]





