What is the Pituitary Gland?
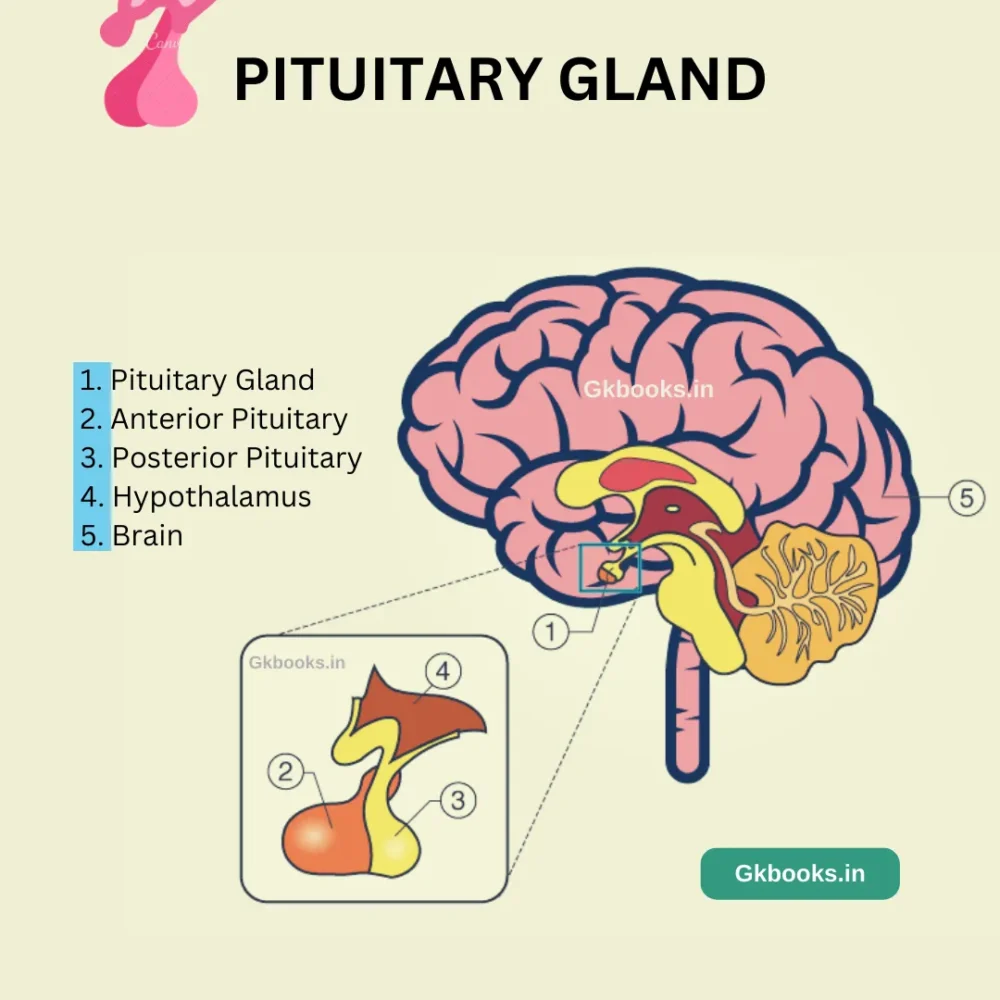
The Pituitary gland, also known as the hypophysis, is a small endocrine gland about the size of a pea located at the base of our brain.
Often called the ‘Master Gland,’ it plays a crucial role in producing essential hormones in our body.
Nestled in a bony structure known as the Pituitary fossa, just beneath the hypothalamus and near the optic nerve.
This gland is divided into three parts, referred to as lobes:
- Anterior pituitary
- Intermediate pituitary (Absent in adult human beings)
- Posterior pituitary
Also Read: What are Hormones? Types, Functions, Important Hormones
What are the Functions of Pituitary Gland?
The pituitary gland, often called the “master gland,” is a tiny but mighty organ located at the base of the brain. It plays a crucial role in regulating numerous bodily functions through the hormones it produces.
In adults, the pituitary gland is divided into two sections: the Anterior and the Posterior parts. The Intermediate pituitary diminishes during pregnancy and is not present in grown-up humans.
The anterior and posterior parts of the master gland secrete various essential hormones. Those hormones regulate and control various functions in our body.
Let’s discuss the function of the hormones produced by the Anterior and the Posterior parts of the pituitary glands.
Function of Anterior Pituitary Hormones
The front part of the pituitary gland plays a crucial role in creating and releasing several important hormones in the body. These hormones include:
Human Growth Hormone (HGH)
- This hormone is like your body’s maintenance manager. It helps cells grow and repairs them.
Thyroid Stimulating Hormone (TSH)
- Think of TSH as a messenger for your thyroid gland. It tells the thyroid to release thyroxine, which is kind of like a thyroid superhero hormone. Another name for TSH is Thyrotropin.
Adrenocorticotropic Hormone (ACTH)
- ACTH is like the conductor of the stress orchestra. It signals your adrenal gland to release Cortisol, the stress hormone. You might also hear it called corticotropin.
Luteinising Hormone (LH) and Follicle-Stimulating Hormone (FSH)
- LH and FSH are like the directors of the body’s reproductive show. They control the male and female characteristics in terms of sex and reproduction. Together, they’re known as Gonadotropins.
Prolactin (PRL)
- PRL is like the milk producer. It plays a role in making milk in the breast. It’s there all the time, but its job kicks into high gear during and after pregnancy.
Melanocyte-stimulating hormone (MSH)
- MSH is in charge of color! It tells your skin and hair to produce melanin, the pigment that gives color. It’s like the artist of your body.
Posterior Pituitary Hormones
This part is like the storage room for two important hormones.
Antidiuretic Hormone (ADH)
- ADH is the water manager. It tells your kidneys to reabsorb water, helping to balance the amount of water in your body.
Oxytocin
- Oxytocin is the pregnancy and childbirth helper. It’s in charge of things like making the uterus contract and producing milk. Think of it as the superhero for moms during this special time.
Also Read: Learn More about Oxytocin [clevelandclinic.org]
Pituitary disorders
Let’s talk about what happens when the pituitary gland faces some issues:
Sometimes, the pituitary gland doesn’t work as it should. This can happen because of a non-cancerous tumor called a pituitary adenoma.
Increase or Decrease in Hormones
- When the pituitary gland isn’t happy, it might release too much or too little of certain hormones, messing up the balance.
Pituitary Macroadenoma
- Imagine a bigger-than-normal pituitary tumor, more than 10 mm in size. This big guy can mess with the blood supply to the gland.
Pituitary Apoplexy
- This is when things get serious. The large tumor can mess with the blood flow, causing either too much or not enough. It’s like a traffic jam for the blood going to the pituitary gland, and it’s called pituitary apoplexy.
Q&A about Pituitary Gland
Q1. What is the role of the pituitary gland in height increase?
The pituitary gland influences growth hormone secretion, and its activation can play a role in height increase, especially during the growth years.
Q2. How to stimulate the pituitary gland?
Practices like meditation, adequate sleep, and a balanced diet with essential nutrients may contribute to stimulating the pituitary gland.
Q3. Where would you find the pituitary gland in the human body?
The pituitary gland is located in a small bony cavity at the base of the brain called the sella turcica.
Q4. What hormones does the pituitary gland release?
The pituitary gland releases hormones such as growth hormone, thyroid-stimulating hormone, adrenocorticotropic hormone, and more.
Q5. Is the pituitary gland affected by tumors?
Yes, non-cancerous tumors known as pituitary adenomas can disrupt the normal functioning of the pituitary gland, leading to hormone imbalances.
FAQs about Functions of Pituitary Gland
The pituitary gland is a petite, pea-sized endocrine organ positioned at the bottom of the brain, beneath the hypothalamus. It resides within a hollow in the sphenoid bone known as the sella turcica.
The pituitary gland acts as a master control center, regulating various hormones that influence growth, reproduction, and other essential bodily functions.
Natural methods to potentially activate the pituitary gland include regular exercise, sufficient sleep, and stress management.
It earns the title “master gland” because it controls the activity of other endocrine glands by releasing hormones that trigger their functions.
The pituitary gland secretes various hormones, including growth hormone, thyroid-stimulating hormone, and oxytocin.
More Topics on Biology:
Heart Chambers: Anatomy, Functions, Diagram & Exam-Focused Notes
Vitamin Deficiency Diseases – Causes, Symptoms, Sources & Exam-Focused Notes
Function of the Stomach in the Human Body: Key Roles, Mechanisms & Importance
Composition of Lymph Fluid: Definition, Components, and Functions Explained
Composition of Serum: Components, Functions & Clinical Importance
Salivary Glands: Structure, Functions, and Clinical Importance
Zygote: Definition, Formation, Timeline, Totipotency, and Role in Human Development
