Navigating the vast seas of Indian Geography is no easy feat, especially for aspirants gearing up for competitive exams like SSC, UPSC, Railway, and various state PSCs. Understanding the maritime infrastructure of our nation is not just a part of the syllabus; it’s a crucial component of our economic and strategic landscape. Welcome aboard as we embark on a comprehensive voyage through the Major Sea Ports in India, serving as your compass to success in the upcoming examinations.
India’s coastline covers a rich tapestry of ports, each playing a pivotal role in facilitating trade, commerce, and connectivity on both domestic and international fronts.
In this article, we’ll unravel the significance, locations, and operational nuances of these maritime gateways. From the bustling ports of Mumbai and Chennai to the lesser-known gems dotting our shores, we’ll delve into their historical significance, modern infrastructure, and strategic importance in the global trade network.
✅ View all articles on Indian Geography Covered by Gkbook
How many Seaports are there in India?
- India boasts 13 main ports and approximately 200 non-major ports, also known as minor ports, spread across its expansive coastline.
- Major Ports fall under the administrative umbrella of the Ministry of Shipping, while respective State Maritime Boards or state governments govern non-major ports.
- All 13 Major ports are fully operational, serving as vital nodes in India’s maritime infrastructure.
- Among the 200 non-major ports, approximately 65 handle cargo, while the remaining serve as “Port Limits,” primarily catering to fishing vessels and small ferries for passenger transportation across creeks.
- Maharashtra leads the tally with 53 ports, followed by Gujarat with 40, Tamil Nadu with 15, Karnataka with 10, and others accounting for 82 ports.
- Maritime transport plays a pivotal role in India’s trade, with around 95% of trading volume and 70% of value conducted through sea routes, according to the Ministry of Ports, Shipping, and Waterways.
- Previously, India had 14 major ports, including Port Blair Port, situated in the Andaman and Nicobar Islands, which lost its ‘major port’ status due to insufficient container traffic.
- To modernize and enhance port infrastructure, the Indian government has approved the Sagarmala project.
- In a bid to attract investment and foster development, the Indian government allows Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) up to 100% through the automatic route for port and harbour construction and maintenance projects.
List of Major Sea Ports in India
| S.No. | Seaports | States | Major export |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Kochi Port | Kerala | Tea, Coffee, Spices, etc |
| 2. | Ennore Port | Tamil Nadu | Iron ore, petroleum, coal, and chemicals |
| 3. | Haldia port | West Bengal | Jute, steel, iron ore, etc |
| 4. | Kolkata Port | West Bengal | Iron ore, tea, coal, steel, etc |
| 5. | Kandla Port | Gujarat | Textile, manganese, machinery, leather, chemical products, etc |
| 6. | Mangalore Port | Karnataka | Iron ore |
| 7. | Marmagoa | Goa | Iron ore |
| 8. | Mumbai Port | Maharashtra | Textile, manganese, machinery, leather, chemical products, etc |
| 9. | Jawaharlal Nehru port | Maharashtra | Textile, chemicals, pharmaceuticals, carpets, etc |
| 10. | Paradip Port | Odisha | Iron ore, iron, and aluminium |
| 11. | Tuticorin Port | Tamil Nadu | Salt, fertilizer, petroleum, coal, etc |
| 12. | Vishakhapatnam Port | Andhra Pradesh | Coal, alumina, oil, and coals |
| 13. | Chennai port | Tamil Nadu | Rice, textile, leather, goods, etc |
Major Ports in India Map
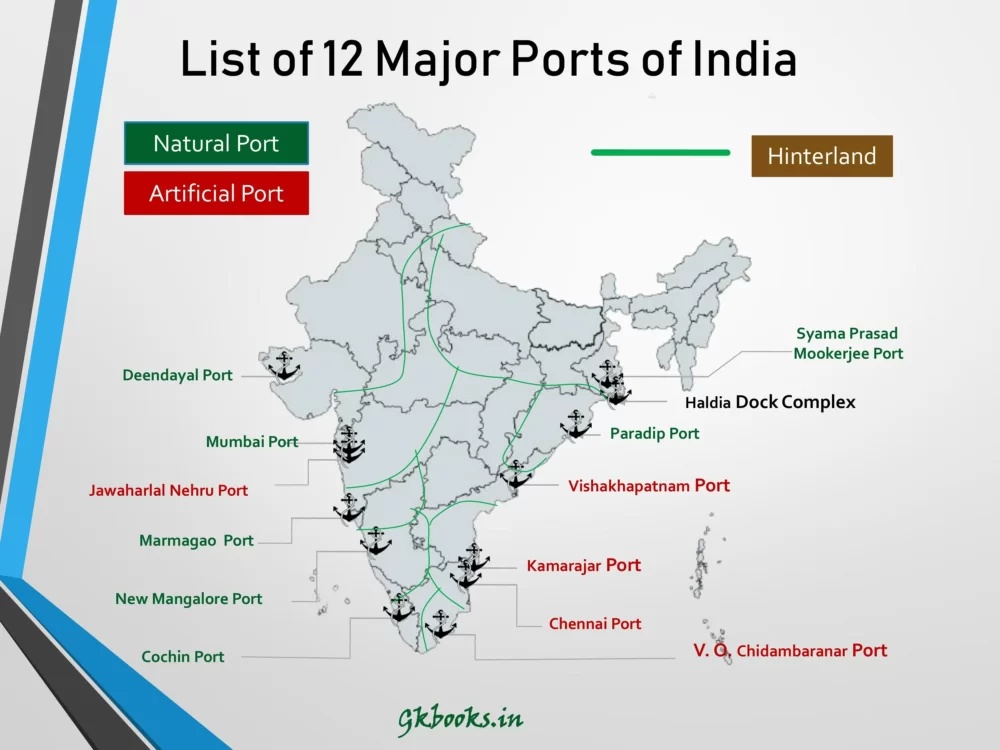
List of Ports in India: State-Wise
Ports hold a significant place in the historical context of international trade and have played a crucial role in connecting countries via sea routes. Knowing the names and locations of these ports in India can be quite challenging in the context of exams and studies. To make this information easier to recall, we have organized a comprehensive list of Indian ports categorized by the states they are located in. This will aid in better memorization and understanding of their significance.
Here is the List of State Wise Ports in India
| State | Ports |
|---|---|
| Gujarat | Kandla Port Trust or Deendayal Port (Kutch District) |
| Odisha | Paradip Port (Jagatsinghpur District) |
| Maharashtra | Jawaharlal Nehru Port/ Nhava Sheva (Mumbai) Mumbai Port Trust (Mumbai) |
| Andhra Pradesh | Visakhapatnam Port (Visakhapatnam) Krishnapatnam Port (Nellore District) |
| Tamil Nadu | Chennai Port (Chennai) V.O.Chidambaranar Port (Thoothukudi) Ennore Port (Chennai) |
| West Bengal | Syama Prasad Mookerjee Port (Kolkata) |
| Karnataka | New Mangalore Port (Mangalore) |
| Kerala | Cochin Port (Kochi) |
| Goa | Mormugao port |
Important Ports in India Zone-wise
| Zone | State | Port Name | Features |
| Eastern Coast | Tamil Nadu | Chennai | It is an artificial port and the Second busiest port. |
| Western Coast | Kerala | Kochi | It is a natural harbour. Deals with the export of iron and aluminium. |
| Eastern Coast | Tamil Nadu | Ennore | It is India’s First corporatized port. |
| Eastern Coast | West Bengal | Kolkata | It is known as Tidal Port and is acknowledged as Trade Free Zone. It is the largest port in terms of the volume of cargo handled. |
| Western Coast | Gujarat | Kandla | It is the largest Natural Port and harbour In India. It is the busiest port in India. |
| Western Coast | Karnataka | Mangalore | It deals with the iron ore exports |
| Western Coast | Goa | Mormugao | It is situated on the estuary of the river Zuari |
| Western Coast | Maharashtra | Mumbai Port Trust | It is the largest artificial port, and it is the largest container port in India. |
| Western Coast | Maharashtra | Jawaharlal Nehru Port Trust (JNPT) also known as Nhava Sheva, Navi Mumbai | It is the largest Artificial PortIt is the largest Container Port in India. |
| Eastern Coast | Odisha | Paradip | It is a significant port in southern India that handles petrochemical and fertilizer products. |
| Eastern Coast | Tamil Nadu | Tuticorin | It is a significant port in southern India that handles petrochemical and fertiliser products. |
| Eastern Coast | Andhra Pradesh | Visakhapatnam | It is the largest artificial port, and it is the largest container port in India. |
| Bay of Bengal | Andaman & Nicobar Islands | Port Blair | The port was connected to the Indian subcontinent by ship and air. This port is located between the Saudi Arabian and US Singaporean shipping lanes. |
Main Sea Ports in India: Key Facts
Syama Prasad Mookerjee Port
▪ Kolkata Port is officially known as Syama Prasad Mookerjee Port.
▪ It is the only riverine port of India located on the left bank of the Hooghly River.
▪ Kolkata port handles goods from South-East Asian countries, Australia and New Zealand.
▪ Kolkata port is called the ‘Gateway to Eastern India’.
▪ Major exporting items include Jute products, tea, coal, steel, iron ore, copper, leather, and leather products.
▪ Major import consists mainly of machinery, crude oil, paper, fertilizers, and chemical products.
▪ The port has two distinct dock systems _
- Kolkata Docks in Kolkata.
- It has a deep water dock complex at Haldia Dock Complex.
▪ It has a massive hinterland comprising the whole North East of India, including West Bengal, Bihar, Jharkhand, Uttar Pradesh, Madhya Pradesh, Assam, North East Hill States, and two landlocked neighbouring countries, Nepal and Bhutan.
Haldia Dock Complex
▪ Haldia Port was built at the confluence of rivers Hoogly and Haldi.
▪ Its main purpose is to release congestion at Kolkata port.
▪ The main items of trade are mineral oil and petroleum products.
Paradip Port
▪ Paradip Port was established by the late Biju Patnaik, the then Chief Minister of Odisha.
▪ Paradip Port is the sole Principal Port in the State of Odisha.
▪ It is a natural, deepwater port on the eastern coast of India, Jagatsinghpur district of Odisha.
▪ On 1st June 1965, the Government of India acquired the management of the Port of the Government of Odisha on 1st June 1965.
▪ On 18 April 1966, the government of India declared it the 8th major port of India.
▪ It has a vast hinterland covering the states of Odisha, Chhattisgarh, Madhya Pradesh, Jharkhand, Bihar, Uttar Pradesh, and West Bengal.
▪ Paradip Port has the advantage of soft underwater soil, which is why it can be operated at any depth by cutting out the soft soil easily according to need.
Visakhapatnam Port
▪ Visakhapatnam Port is the largest port on the eastern coast of India, Andhra Pradesh.
▪ By volume of cargo handled, It is India’s third-largest state-owned port and the largest in the
Eastern Coast.
▪ Visakhapatnam Port was an ancient Port city with trade relations with the Middle East and Rome.
Kamarajar Port
▪ It was formerly known as Ennore Port.
▪ Kamarajar Port located on the Coromandel Coast, Chennai
▪ Kamarajar Port is the 12th major port in India.
▪ It is the first public company port in India.
Chennai Port
▪ Chennai Port is the third oldest key port among the 13 major ports in India.
▪ Earlier the Chennai Port was known as Madras Port.
▪ After Mumbai’s Nhava Sheva port, It is India’s second largest container port.
▪ It is an all-weather artificial port with wet docks.
V. O. Chidambaram Port
▪ V. O. Chidambaram Port is the second-largest port in Tamil Nadu and the third-largest container terminal in India.
▪ It is an artificial port.
▪ Strategically located very close to the East-West International Sea Route.
▪ It services the USA, China, Europe, Sri Lanka, and Mediterranean countries.
Cochin Port
▪ It is also the first transhipment port in India.
▪ The harbour spans two islands in Lake Kochi, namely Willingdon Island and Vallarpadam Island.
New Mangalore Port
▪ The New Mangalore port is the only major port in the state of Karnataka.
▪ It was declared as the 9th Major Port on 4th May 1974.
▪ The major commodities imported through the Port are Cement, coal, fertilizer, edible oil,
liquid chemicals, containerized cargo, etc.
▪ The hinterland of New Mangalore Port lies in Karnataka and the northern part of Kerala.
▪ Its main importance lies in the export of iron ore from the Kudremykh mines.
Marmagao Port
▪ With the emergence of Iron ore mining as a major industry in Goa, the Portuguese developed a master plan for the development of Mormugao Port as an iron ore terminal.
▪ The port, is located at the entrance of the Zuvari estuary.
▪ Major exports are iron ore, Manganese, Coconut, and Cotton.
▪ It has a comparatively small hinterland covering the whole of Goa and parts of north Karnataka and southern Maharashtra.
▪ This port is well connected through the Konkan Railway.
Mumbai Port
▪ Mumbai Port is a Natural harbour on the West Coast of India.
▪ It is considered the biggest port in India.
▪ It handles foreign trade with Western countries and East African countries.
▪ It has a vast hinterland covering the whole of Maharashtra and large parts of Madhya
Pradesh, Gujarat, Rajasthan, and Delhi.
Jawaharlal Nehru Port
▪ Jawaharlal Nehru Port was formerly known as Nhava Sheva Port.
▪ This new port has been built on an island named Nhava Sheva across the famous Elephanta caves.
▪ The main purpose of this port is to release pressure on the Mumbai Port.
▪ Nhava Sheva Port is considered the largest container port in India.
Deendayal Port
▪ Formerly known as Kandala Port.
▪ Deendayal is a seaport located on the Gulf of Kutch, Kutch district, Gujarat.
▪ The Kandla Port was built in 1950.
▪ It is a natural harbour in Kandala Creek.
▪ Kandla port was built to serve Western India, due to the partition of India leaving the port of
Karachi in Pakistan.
▪ The first special economic zone to be established in India and Asia is the Kandla port
Special Economic Zone (KASEZ).
▪ Kandla port is the first Export Processing region/ Zone in India.
▪ The hinterland of Kandala Port covers the maximum portion of Gujarat, Rajasthan, Haryana, Punjab,
Delhi, Himachal Pradesh, Jammu Kashmir, Uttarakhand, and Ladakh.
▪ Major imported products from Kandla Port are petroleum, chemical substances, and iron and steel and iron machinery, but it also handles salt, textiles, and grain.
Government Initiatives for the Port Sector
▪ The Union Budget 2021, taking cues from the government’s Blue Economy policy, has allocated funds for the expansion of shipping and inland waterways infrastructure, along with a budget of ₹2,000 crores for PPP models in major ports.
▪ The Make in India initiative is also being promoted, as the Ministry of Shipping has revised the Right of First Refusal (ROFR) licensing conditions, prioritising vessels built in India, flagged in the country, and owned by Indians for chartering.
▪ Additionally, a National Logistics Portal (Marine) will be developed to assist exporters, importers, and service providers, while the Ministry of Shipping has created a dispute redressal portal, SAROD-Ports’ (Society for Affordable Redressal of Disputes – Ports), for private players.
▪ Finally, the Parliament has passed the Major Port Authorities Bill 2020, which seeks to repeal the Major Ports Trust Act of 1963 and establish a Board of Major Port Authority for each major port.
Previous Year Questions on Major Sea Ports in India
1. Which of the following industries are the major beneficiaries of the Mumbai port? [SSC Tax Assistant 2006]
A. Iron and Steel industry
B. Sugar and Cotton textile industry
C. Cotton textile and Petrochemical industry
D. Engineering and Fertilizer industry
Answer –C. Cotton textile and Petrochemical industry
Explanation-
2. Which two ports is Kudremukh Iron-ore exported from? [SSC Combined Matric Level (PRE) 2002]
A. Kandla and Mumbai
B. Marmugoa and Mangalore
C. Kochi and Tuticorin
D. Paradip and Kolkata
Answer –B. Marmugoa and Mangalore
Explanation-
3. Which port in India has a free trade zone? [SSC Combined Matric Level (PRE) 2002]
A. Kochi
B. Paradip
C. Kandla
D. Tuticorin
Answer –C. Kandla
Explanation-
4. Which of the following ports has the largest hinterland? [SSC Section Officer (Commercial Audit) 2007]
A. Kandla
B. Kochi
C. Mumbai
D. Visakhapatnam
Answer –C. Mumbai
Explanation-
5. Which of the following is a major port on the East Coast of India? [SSC CPO 2011]
A. Kandla
B. Vishakhapatnam
C. Karikal
D. Pondicherry (Puducherry)
Answer –B. Vishakhapatnam
Explanation-
6. Which one of the following ports is located on the eastern coast of India? [SSC Combined Matric Level (PRE) 2001]
A. Kandla
B. Kochi
C. Mormugao
D. Paradeep
Answer –D. Paradeep
Explanation-
7. Which of the following is an inland river port? [SSC Combined Matric Level (PRE) 2002]
A. Kolkata
B. Mumbai
C. Chennai
D. Tuticorin
Answer –A. Kolkata
Explanation-
8. The ports located along the eastern coast of India are: [SSC Stenographer (Grade ‘C’ & ‘D’) 2010]
A. Kandla and Haldia
B. Haldia arid Cochin
C. Paradeep and Kandla
D. Paradeep and Haldia
Answer –D. Paradeep and Haldia
Explanation-
9. Which is the artificial port of India? [SSC (10+2) Level Data Entry Operator & LDC 2011]
A. Kandla
B. Mangalore
C. Chennai or Madras
D. Haldia
Answer –C. Chennai or Madras
Explanation-
10. How many major sea ports are there in India? [(SSC (10+2) 2011)]
A. 6
B. 12
C. 10
D. 13
Answer –D. 13
Explanation-
Key Features of Major Sea Ports in India
India’s major ports are pivotal gateways facilitating global trade and economic activities. These ports are strategically positioned along the expansive Indian coastline, significantly impacting the nation’s economic progress. Here are the noteworthy characteristics of these major ports:
Diverse Coastal Locations: Major ports are strategically distributed across India’s coastal regions, encompassing states like Kerala, Tamil Nadu, West Bengal, Gujarat, Karnataka, Goa, Maharashtra, Odisha, and Andhra Pradesh.
Variety of Port Types: The major ports include various port types, such as natural ports, artificial ports, and tidal ports, each designed for specific functions and purposes.
Cargo Handling Expertise: Major ports efficiently manage a substantial volume of cargo, encompassing a wide spectrum of goods, from vital resources like iron ore, coal, and steel to exquisite commodities like spices, tea, and coffee.
State-of-the-Art Infrastructure: These ports boast cutting-edge infrastructure, equipped with modern facilities, advanced docks, and sophisticated handling systems, ensuring the smooth operation of cargo activities.
Container Handling Proficiency: Several major ports, including the Jawaharlal Nehru Port, are prominent container ports that handle a substantial portion of India’s container traffic.
Economic Significance: Major ports play an indispensable role in bolstering India’s import-export trade and contributing substantially to the country’s Gross Domestic Product (GDP).
Employment Opportunities: These ports serve as significant employment centres, offering a multitude of job opportunities across sectors like shipping, logistics, and warehousing.
Efficient Connectivity: Major ports are seamlessly connected to the hinterland through well-established road and rail networks, ensuring the efficient movement of goods to and from the port areas.
Government Oversight: Most major ports in India are under government ownership and operation, ensuring effective management and regulation of port activities.
Enhanced Trade Relations: Major ports are vital links between India and its numerous international trade partners, strengthening trade relations and expanding global connectivity.
India’s major ports are pivotal components of the nation’s maritime infrastructure, playing an indispensable role in various industries and contributing significantly to the country’s economic growth and global trade relations.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Answer: Mumbai Port (Maharashtra)
Answer: Kolkata Port or Syama Prasad Mookerjee Port (It was commissioned in 1870)
Answer: Nhava Sheva Port (built in 1989)
Answer: Visakhapatnam port in Andhra Pradesh (16.5 meters deep)
Answer: Vadhavan Port, Maharashtra
Answer: At present, there are 13 major ports in India.
The nearest major seaport to Delhi is the Jawaharlal Nehru Port, also known as Nhava Sheva, located in the state of Maharashtra. It serves as a crucial gateway for maritime trade and is approximately.
File Details ▪ File Name- Main Sea Ports in India Map PDF ▪ File Size - 925KB ▪ Quality - Good ▪ No. of Page - 9 ▪ Category - Indian Geography
More Posts on Indian Geography
- Important Water Reservoirs in India with Key Facts: Complete Guide
- 10 Major River of Tripura: Complete Notes
- Vembanad Lake: Must-Know Facts for Competitive Exams
- Renuka Lake: Key Details about Smallest Ramsar Wetland Sites of India
- Hydroelectric Power Plants in India 2025: Complete Notes
- Keibul Lamjao National Park: The World’s Only Floating National Park
- Brahmaputra River System, Tributaries, Map, Origin, Length: Complete Notes
- Eastern Ghats – Indian Geography Easy Notes
- Ganga River System: Complete Notes
- Master the Western Ghats: Exam-Focused Notes