Dear Aspirants,
Check out the brief notes on “Reserve Bank of India functions & facts”. The Reserve Bank of India, mostly known as RBI, is India’s primary central bank responsible for regulating and supervising the Indian banking system.
Its functions encompass a wide range of financial activities, including managing monetary policy, maintaining financial stability, regulating the banking sector, and issuing currency. RBI is recognized as an important institution that ensures the smooth functioning of the Indian economy and is widely respected for its contribution to the country’s growth and development.
About Reserve Bank of India
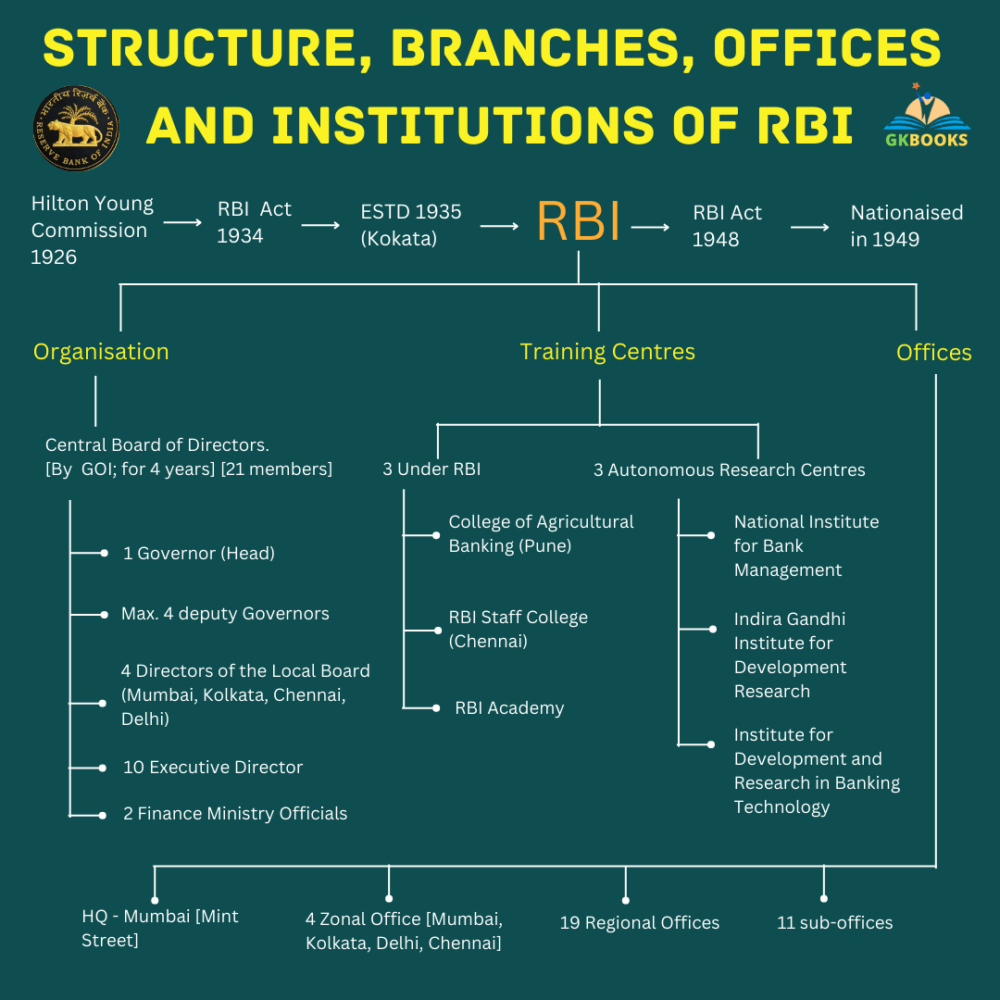
▪ RBI was Set up on 1 April 1935 Under the Reserve Bank of India Act, of 1934.
▪ It was nationalized on 1 January 1949.
▪ The Reserve bank of India is a member bank of the Asian Clearing Union.
▪ The RBI served as the central bank of Burma (now Myanmar) until April 1947.
▪ The RBI also served as the central bank of Pakistan until June.
▪ Initially, RBI was headquartered in Kolkata. In 1937 the headquarters of RBI was shifted to Mumbai.
▪ The Reserve Bank of India sets up the 1926 Hilton–Young Commission recommendations.
▪ The original choice for the seal of RBI was The East India Company Double Mohur, with the Lion and Palm Tree sketch.
▪ It was decided to replace the lion with the tiger, the national animal of India.
▪ The bank is often referred to by the name Mint Street.
▪ RBI is also known as a banker’s bank.
▪ RBI was conceptualized as per the guidelines, working style, and outlook presented by Dr. B. R. Ambedkar in his book “The Problem of the Rupee – Its Origin.
Also, See Regional Rural Banks of India
Composition of the central board of directors of RBI
▪ RBI is entrusted with a 21-member central board of directors. They are:
- The governor
- 4 deputy governors
- 2 finance ministry representatives
- 10 government-nominated directors
- 4 directors to represent local boards, located in Mumbai, Kolkata, Chennai, and Delhi.
Reserve Bank of India logo / Symbol
▪ The original choice for RBI’s seal was the East India Company’s Double Mohur, which featured a sketch of a lion and a palm tree. Later, it was replaced by the national animal of India, the Tiger.

Reserve Bank of India Headquarters
▪ The Reserve Bank of India was established on April 1, 1935, under the provisions of the Reserve Bank of India Act, 1934.
▪ Initially, the headquarters or central office of the Reserve Bank of India was established in Kolkata but in 1937 it was permanently shifted to Mumbai.
Reserve Bank of India (RBI) – Major Timeline
| Year | Event |
|---|---|
| 1934 | The British enacted the Reserve Bank of India Act |
| 1 April 1935 | Reserve Bank of India was established in Calcutta (Kolkata) |
| October, 1935 | London Office of the RBI set up. ( closed on September 30, 1963) |
| 1937 | RBI acts as banker to the Government of Burma |
| 1937 | The headquarters of the Reserve Bank of India is permanently shifted from Kolkata to Mumbai |
| January, 1938 | First Reserve Bank notes issued |
| 11 March, 1940 | RBI Accounting Year changed from Jan-Dec to July-June. |
| 1 January, 1949 | RBI got nationalized after independence. Earlier the bank was in the hands of private stakeholders. |
Reserve Bank of India branches and supportive bodies
▪ There are also four zonal training centres in Mumbai, Chennai, Kolkata, and New Delhi.
▪ 19 regional offices and 11 sub-offices throughout India.
▪ 3 training colleges for its officers ___
- 1. Reserve Bank Staff College, Chennai
- 2. College of Agricultural Banking, Pune.
- 3. RBI Academy
▪ 3 autonomous institutions run by RBI namely ___
- 1. National Institute of Bank Management (NIBM)
- 2. Indira Gandhi Institute of Development Research (IGIDR)
- 3. Institute for Development and Research in Banking Technology (IDRBT).
Governor of Reserve Bank of India facts
▪ Current Governor of RBI: Shaktikanta Das (25th Governor)
▪ Other 4 Deputy Governor list: M.D. Patra, M. Rajeshwar Rao, T. Rabi Sankar, Mahesh Kumar Jain
▪ First governor of the Reserve Bank of India: Osborne Smith
▪ First Indian governor of the Reserve Bank of India: CD Deshmukh
▪ Longest serving governor of the Reserve Bank of India: Benegal Rama Rau (7 – years)
▪ Shortest serving governor of the Reserve Bank of India: Amitav Ghosh (20 – days)
▪ 15th Governor of Reserve Bank of India: Manmohan Singh (13th – Prime Minister)
▪ 24th Governor of Reserve Bank of India: Urjit Patel
▪ 23rd Governor of Reserve Bank of India: Raghuram Rajan
Functions of the Reserve Bank of India
Monetary Authority
▪ The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) is the central bank of India, which performs various crucial functions to promote economic growth and stability. One of the primary functions of the RBI is to formulate, implement, and monitor India’s monetary policy to maintain price stability and inflation while supporting growth.
Regulator and supervisor of the financial system
▪ The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) plays an important role in regulating and specifying various parameters of banking activities in India.
▪ By performing regulatory and supervisory functions, the RBI ensures that the banking and financial system operates within a framework that maintains public confidence, protects the interests of depositors, and provides affordable banking services to the public.
▪ The RBI follows guidelines and regulations for banks and financial institutions, covering aspects such as capital adequacy, lending practices, risk management, and financial reporting. These guidelines are designed to ensure that banks operate safely and soundly, reduce the risk of financial instability and protect the interests of depositors.
▪ Further, RBI’s supervisory functions include monitoring and evaluating the performance of banks and financial institutions, identifying potential risks and vulnerabilities in the system, and taking corrective action to mitigate them. This oversight ensures that the banking system operates transparently and accountable, which contributes to increasing public confidence in the system.
▪ By performing these regulatory and supervisory functions, RBI creates a stable and reliable banking and financial system that provides affordable banking services to the public, supports economic growth, and enhances financial inclusion.
Manager of Foreign Exchange
▪ The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) plays an important role in managing and maintaining foreign exchange in India under the Foreign Exchange Management Act (FEMA) of 1999.
▪ The primary objective of the RBI is to facilitate external trade and payments by ensuring that sufficient foreign exchange is available to meet the country’s import and export requirements.
▪ To achieve this objective, RBI carefully monitors foreign exchange inflows and outflows and intervenes in the foreign exchange market whenever necessary to maintain stability and liquidity.
Issuer of currency
▪ One of the important functions of the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) is to issue, exchange and destroy currency notes and coins in India. RBI plays an important role in maintaining an adequate supply of good quality currency notes and coins in circulation to meet public demand and support the country’s economic growth.
▪ RBI is responsible for designing, printing, and distributing currency notes of various denominations starting from Rs. 5 to Rs. 2000. These notes are produced under the strict supervision of RBI at four currency presses located in different parts of the country. The central bank controls the quality of currency notes to ensure they meet the required security and durability standards.
▪ RBI also exchanges old or damaged notes for new ones. It conducts regular “currency chest inspections” to check the stock and quality of notes held by banks and other financial institutions. This ensures that there is always an adequate supply of good quality notes available to the public.
▪ In addition, RBI is responsible for preventing the recirculation of damaged or unfit notes. It follows a strict protocol for the disposal of these notes, including shredding and burning, to maintain the integrity and security of the currency.
Developmental role
▪ The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) undertakes a wide spectrum of promotional functions aimed at supporting national objectives. These functions serve as important policy tools to achieve various economic and social goals of the country.
▪ RBI plays an active role in promoting financial inclusion and literacy to ensure every citizen can access banking services and financial resources. It also works towards promoting a stable and efficient financial system by regulating and supervising banks and other financial institutions.
▪ Furthermore, the RBI promotes the development of financial markets and infrastructure, including stock markets, bond markets, and payment systems. It helps mobilize savings and channel them toward productive investment, thereby supporting economic growth.
▪ RBI plays an important role in promoting agricultural and rural development by providing credit facilities and other financial services to farmers and rural communities. It supports various government schemes and initiatives to promote rural livelihoods and reduce poverty.
▪ Further, RBI undertakes measures for sustainable development, such as promoting green finance, implementing environmental and social safeguards, and encouraging responsible banking practices.
Regulator and Supervisor of Payment and Settlement Systems
▪ The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) also acts as the regulator and supervisor of the country’s payment and settlement system. RBI introduced various frameworks and guidelines to enhance the security and efficiency of payment systems by meeting the large-scale requirements of the public.
▪ It continuously monitors the performance of payment and settlement systems, ensures that they comply with established norms and standards, and takes corrective action when necessary.
▪ Through its regulatory and supervisory role, the RBI aims to maintain the integrity and stability of the payment and settlement system, thereby contributing to the overall financial welfare of the country.
Banker to the Government
▪ The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) not only acts as a regulatory authority for the banking sector but also serves as a vital merchant banking solution and banker for the central and state governments.
▪ As a banker, the RBI manages and maintains the financial transactions of the governments, such as managing their accounts, facilitating their borrowing and lending, and providing them with various financial services such as short-term loans.
▪ As a merchant banker, the RBI assists governments in managing their public debt, issuing government securities, and undertaking financial advisory services. This dual role of the RBI is crucial for maintaining financial stability and ensuring effective governance in the country.
Banker to Banks
▪ One of the prior functions of the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) is to maintain a cash reserve for all scheduled banks operating in the country. This cash reserve, known as the Cash Reserve Ratio (CRR), is a certain percentage of the total deposits held by banks that they are required to maintain with the RBI.
▪ By regulating the CRR, the RBI can control the amount of money available for lending by banks, thus maintaining the economy’s stability.
▪ Moreover, the RBI also provides loans to the scheduled banks. It acts as a lender of last resort for banks that face a shortage of funds and are unable to meet their financial obligations. By providing such facilities, the RBI ensures the smooth functioning of the banking system, thereby contributing to the overall financial stability of the country.

Previous year questions (Asked in SSC)
1. The symbol of the Reserve Bank of India is: [SSC CGL Prelim 2002]
Answer: Tiger before a Palm tree
2. Currency notes of Rs. 2 denomination and above are liabilities of : [SSC CGL Prelims 2004]
Answer: Reserve Bank of India
3. Which of the following functions as a controller of credit in India? [SSC Tax Assistant (Income Tax & Central Excise) 2004]
Answer: The Reserve Bank of India
4. What is the name of the electronic communication network of the Reserve Bank of India?
Answer: RBINET
[SSC Statistical Investigators Grade–IV 2006]
5. Which of the following has the sole right of issuing currency (except one rupee coins and notes)
in India? [SSC Section Officer (Commercial Audit) 2007]
Answer: The Reserve Bank of India
6. Reserve Bank of India was nationalized in: [SSC Section Officer (Audit) 2008]
Answer: 1949
7. The credit control operation in India is performed by__[SSC Combined Matric Level (PRE) 2001]
Answer: Reserve Bank of India
8. The Reserve Bank of India issues currency notes under
Answer: Minimum reserve system
[SSC Combined Matric Level (PRE) 2001]
9. Which bank in India performs the duties of the Central Bank?
[SSC Combined Matric Level (PRE) 2008]
Answer: Reserve Bank of India
10. Who amongst the following has never been the Governor of the Reserve Bank of India? [SSC (10+2) Level Data Entry Operator & LDC 2012]
A. D. Subbarao
B. C. Rangarajan
C. B.B. Bhattacharya
D. Y.V. Reddy
Answer: B.B. Bhattacharya
11. Which of the following announces The Monetary and Credit Policy? [SSC CGL Tier-I 2014]
Answer: Reserve Bank of India
12. Who was the first Indian governor of the Reserve Bank of India? [SSC CGL Tier-I (CBE) 2016]
Answer: C.D. Deshmukh
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Answer: 1 April 1935
Answer: 1st April
Answer: 1 January 1949
Answer: Osborne Smith
Answer: Shaktikanta Das (25th Governor)