Understanding the atomic number is essential for mastering chemistry. It plays a key role in identifying elements and helps in organizing the periodic table. In this blog post, we will explore the meaning, significance, and application of atomic numbers in a simple and engaging way.
What is an Atomic Number?
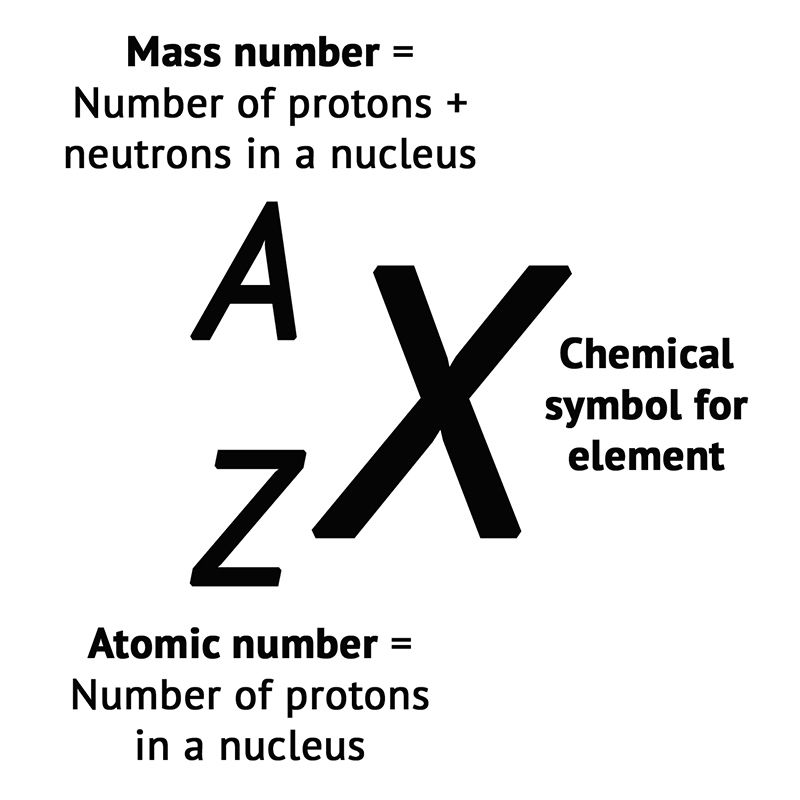
- The atomic number of an element is the number of protons present in the nucleus of an atom.
- It is represented by the symbol Z.
- Example: Hydrogen (H) has 1 proton, so its atomic number is 1. Oxygen (O) has 8 protons, so its atomic number is 8.
◾Atomic Number – Know Atomic Mass Number, Isotopes, Isobars & Understand with Examples
Key Points
- Every element has a unique atomic number.
- It determines the identity of an element.
- The atomic number is found in the periodic table.
- It helps in classifying elements into groups and periods.
Example
- The atomic number of Hydrogen (H) is 1, which means it has one proton.
- The atomic number of Oxygen (O) is 8, meaning it has eight protons.
Key Points to Remember
✅ The atomic number is unique for each element.
✅ It determines the identity of an element.
✅ Elements in the Periodic Table are arranged in increasing order of atomic number.
✅ It is always a whole number (not a fraction or decimal).
Importance of Atomic Number
The atomic number is crucial for understanding the structure and behavior of elements. Here’s why:
🔺Defines the Element: No two elements can have the same atomic number. Changing the atomic number means changing the element itself.
🔺Determines the Position in the Periodic Table: Elements in the periodic table are arranged in increasing order of atomic number.
🔺Identifies the Number of Electrons in a Neutral Atom: In a neutral atom, the number of electrons is equal to the atomic number.
Example: Carbon (C) has an atomic number of 6, so it has 6 protons and 6 electrons in its neutral state.
🔺Determines the element’s chemical properties: Since the number of electrons (in a neutral atom) is equal to the atomic number, it affects how an atom reacts.
🔺Helps differentiate elements: Even if two atoms have the same mass number, they are different elements if they have different atomic numbers.
🔺Plays a role in chemical bonding: The atomic number decides the valency (combining capacity) of an element.
Atomic Number and the Periodic Table
The periodic table is arranged based on atomic numbers, not atomic mass.
| Element | Atomic Number | Number of Protons | Number of Electrons (Neutral Atom) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hydrogen (H) | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Helium (He) | 2 | 2 | 2 |
| Lithium (Li) | 3 | 3 | 3 |
| Oxygen (O) | 8 | 8 | 8 |
| Sodium (Na) | 11 | 11 | 11 |
Atomic Number vs. Atomic Mass
| Property | Atomic Number (Z) | Atomic Mass (A) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Number of protons in an atom | The Sum of protons + neutrons in an atom |
| Representation | Denoted by Z | Denoted by A |
| Unique for Each Element? | Yes | No (Isotopes have the same Z but different A) |
Example:
- Carbon-12 has an atomic number Z = 6 and an atomic mass A = 12.
- Carbon-14 has the same atomic number, Z = 6, but a different atomic mass, A = 14.
Mnemonic to Remember Atomic Numbers of First 10 Elements
You can use this funny sentence to remember the first 10 elements:
“Hi He Likes Beer But Could Not Offer Full Nice Neon”
- H – Hydrogen (1)
- He – Helium (2)
- Li – Lithium (3)
- Be – Beryllium (4)
- B – Boron (5)
- C – Carbon (6)
- N – Nitrogen (7)
- O – Oxygen (8)
- F – Fluorine (9)
- Ne – Neon (10)
Real-Life Examples of Atomic Number
- Gold (Au) – Atomic Number 79: Used in making jewelry.
- Iron (Fe) – Atomic Number 26: Found in construction and our red blood cells (as hemoglobin).
- Oxygen (O) – Atomic Number 8: Essential for breathing.
- Carbon (C) – Atomic Number 6: Found in all living things.
Exam-Oriented Tips
- Always memorize the atomic numbers of common elements like H, O, C, Fe, Na, Cl.
- The atomic number increases from left to right in the periodic table.
- The Atomic number determines the number of electrons in a neutral atom, which affects chemical behavior.
- Remember that elements with the same atomic number but different mass numbers are called isotopes.
- Practice Periodic Table charts to get familiar with atomic numbers quickly.
Practice Questions
Fill in the Blanks
- The atomic number of Oxygen is ___.
- The atomic number is equal to the number of ___ in an atom.
- Sodium (Na) has ___ protons.
- The element with atomic number 1 is ___.
- The atomic number helps in identifying an element’s ___.
Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs)
Q1: What is the atomic number of Carbon?
a) 4
b) 5
c) 6
d) 7
Q2: Which of the following elements has an atomic number of 11?
a) Oxygen
b) Sodium
c) Magnesium
d) Hydrogen
Q3: What does the atomic number represent?
a) Number of neutrons
b) Number of protons
c) Number of molecules
d) Number of compounds
Answers:
Fill in the Blanks:
- 8
- Protons
- 11
- Hydrogen
- Identity
MCQs:
- (c) 6
- (b) Sodium
- (b) Number of protons
Conclusion
The atomic number is a fundamental concept in chemistry that helps us understand elements and their properties. By knowing an element’s atomic number, we can determine its identity, electron arrangement, and position in the periodic table.
By understanding atomic numbers, you now have a strong foundation in chemistry! Keep practicing, and soon, you will master even more advanced concepts. Happy Learning! 🚀





