Have you ever looked into a mirror and seen yourself exactly as you are? That’s because a plane mirror creates an image that looks just like the real object! In this guide, we will explore how images are formed by plane mirrors, their properties, and important concepts for SSC, Banking, RRB NTPC, UPSC, and other state-level exams.
A plane mirror is a flat, smooth mirror that reflects light in a straight line. The image formed by a plane mirror is virtual, upright, laterally inverted (left-right reversed), and of the same size as the object. Understanding these properties is essential for general science (physics) preparation in competitive exams.
By the end of this guide, you will learn:
✔️ How light reflects from a plane mirror
✔️ Key characteristics of the image formed
✔️ Important laws of reflection
✔️ Real-life applications of plane mirrors
✔️ Previous year questions (PYQs) for practice
This topic is frequently asked in SSC CGL, CHSL, Railway Exams, Banking Exams, UPSC Prelims, and other state-level exams. Let’s dive in and master the concept of image formation by plane mirrors! 🚀
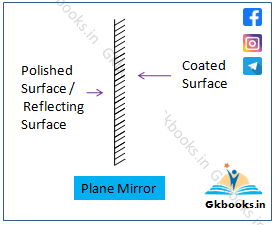
What is a Mirror?
A mirror is a light-reflecting surface typically made of polished glass. It reflects almost all light that strikes its surface, creating an image. The polished surface of the glass is coated with a reflective layer to improve the mirror’s efficiency in reflecting light.
Key Features of a Mirror
- Reflects light: Mirrors reflect almost all incident light.
- Polished surface: The smooth surface is essential for clear image formation.
- Reflective coating: Mirrors have a thin reflective layer applied to the back of the glass.
Coating of Mirrors
The coating of mirrors refers to the process of applying a thin reflective layer of metal onto the surface of a glass. This coating enhances the mirror’s ability to reflect light, ensuring high-quality image formation.
Coating Process
- A thin metal layer is applied to the mirror’s surface.
- Metal plating techniques are commonly used to give the glass a reflective coating.
Metals Used in Coating Mirrors
- Silver
- Aluminum
- Gold
- Zinc
- Copper
- Platinum
- Tin
Among these metals, silver and aluminum are the most commonly used metals for coating mirrors due to their high reflective properties and cost-effectiveness.
Silvering of Mirrors
What is Silvering of Mirrors?
Silvering is the process of applying a thin layer of silver to a glass surface to create a mirror. This process ensures that most of the light incident on the surface is reflected, providing high-quality image formation.
Silvering Process
The silver layer helps enhance the mirror’s reflective efficiency, making it suitable for various applications like household mirrors, optical instruments, and more.
Glucose is commonly used in the silvering process to deposit a thin layer of silver onto the glass.
Types of Mirrors
Mirrors are classified based on their shape into two major types:
- Plane Mirror
- Spherical Mirror
1. Plane Mirror
A plane mirror is a mirror with a flat reflecting surface, not curved. It is the most common type of mirror used in everyday life, such as in bathroom mirrors, dressing mirrors, and vehicle side mirrors.
Properties of Plane Mirror
- Equal Angles of Reflection and Incidence
In a plane mirror, the angle of reflection is equal to the angle of incidence, which is a fundamental law of reflection.
- Image Type
The image formed by a plane mirror is always virtual (it cannot be projected onto a screen) and erect (upright).
- Size of Image
The image size is always equal to the size of the object. This means the image appears the same size as the actual object.
- Equal Distances
The distance between the image and the mirror is the same as the distance between the object and the mirror.
- Linear Magnification
The linear magnification produced by a plane mirror is 1, meaning the size of the image is exactly the same as the size of the object.
- Minimum Size of Mirror
To view the full image of an object, the minimum size of the mirror required is half of the object’s height.
- Focal Length
The focal length of a plane mirror is infinity, meaning the power of a plane mirror is zero.
2. Spherical Mirror
A spherical mirror is a mirror that is a cut-out portion of a reflecting sphere. These mirrors are commonly used in applications such as optical instruments, flashlights, makeup mirrors, and telescope mirrors.
There are two main types of spherical mirrors:
- Concave Mirror
- Convex Mirror
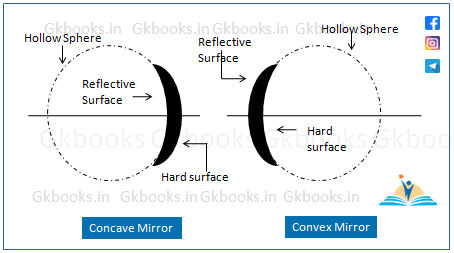
1. Concave Mirror
A concave mirror is a type of spherical mirror where the inner surface of the sphere is the reflecting surface, while the outer surface is polished.
- Another Name: The concave mirror is also known as a converging mirror because it converges light rays after reflection, meaning the reflected rays meet at a single point.
- Applications: Concave mirrors are used in flashlights, shaving mirrors, satellite dishes, and telescopes because they can focus light at a specific point.
2. Convex Mirror
A convex mirror is a type of spherical mirror where the outer surface is the reflecting surface, and the inner surface is polished.
- Applications: Convex mirrors are widely used in vehicle side mirrors, security mirrors, and street corners because they provide a wider field of view and reduce blind spots.
- Another Name: The convex mirror is also known as a diverging mirror because it diverges (separates) light rays after reflection. This means the reflected rays appear to come from a single point behind the mirror.
Characteristics of the image formed by a Plane Mirror
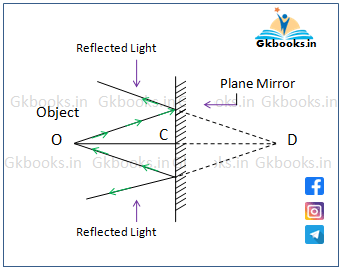
- A plane mirror formed an erect (Upright), virtual image. And the size of the image is the same as the object.
- The image formed by a plane mirror is at the same distance inside the mirror as the object in front of it.
- In the below image, OC = CD
‘OC’ is the distance between the object and the mirror and CD is the distance between the image and the mirror.
- To view an object’s entire image, the plane mirror’s minimum length should be half of the object’s length.
- For example, if your height is 5 feet and you want to see your full image in a plane mirror, then the length of the mirror should be 5/2 or 2.5 feet.
Number of images formed by two Plane Mirrors placed at a certain angle
When two plane mirrors are placed at a certain angle (θ) facing each other, and an object is placed between them, multiple images are formed due to multiple reflections.
Formula for Number of Images Formed by Two Plane Mirrors
The total number of images (n) formed by two mirrors depends on the angle (θ) between them and the position of the object.
1️⃣ If (m = 360° / θ) is EVEN:
- The number of images, n = (m – 1)
- This holds regardless of whether the object is placed symmetrically or asymmetrically.
2️⃣ If (m = 360° / θ) is ODD:
- Case I (Symmetrical Placement of Object):
- Number of images, n = (m – 1)
- Case II (Asymmetrical Placement of Object):
- Number of images, n = m
Simplified Steps to Calculate the Number of Images
1️⃣ Calculate m → Use the formula m = 360° / θ
2️⃣ Check if m is Even or Odd:
- If Even: Number of images n = (m – 1)
- If Odd:
- For a symmetrical object placement, n = (m – 1)
- For an asymmetrical object placement, n = m
🔰If m is even, then (m -1) is the total number of images, irrespective of the position of the objects. (Symmetrical or Unsymmetrical)
🔰 If m is odd then consider the following 2 cases.
✅ Case I
- If the object is placed symmetrically, then (m-1) is the actual number (n) of images.
✅Case II
- If the object is placed asymmetrically, then n itself is the number (n=m) of images.
Numerical Examples
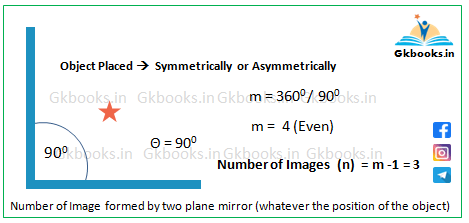
Example 1: Mirrors Placed at 90°
- Given: Angle (θ) = 90°
- Calculate m = 360° / 90° = 4
- Since 4 is EVEN, the number of images:
n = (4 – 1) = 3
✅ Final Answer: 3 images
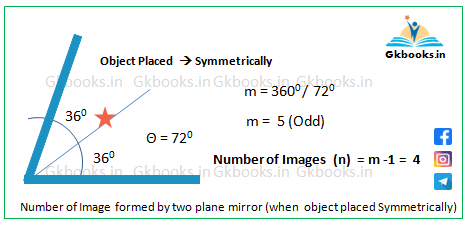
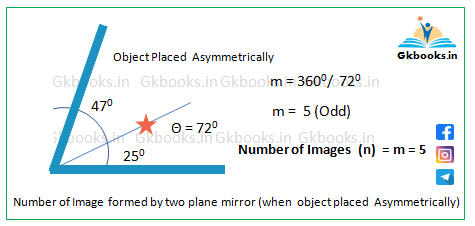
Example 2: Mirrors Placed at 72°
- Given: Angle (θ) = 72°
- Calculate m = 360° / 72° = 5
- Since 5 is ODD, consider:
- Symmetrical object placement → n = (5 – 1) = 4
- Asymmetrical object placement → n = m = 5
✅ Final Answer:
- 4 images (Symmetrical case)
- 5 images (Asymmetrical case)
Special Cases: Parallel Plane Mirrors (θ = 180°)
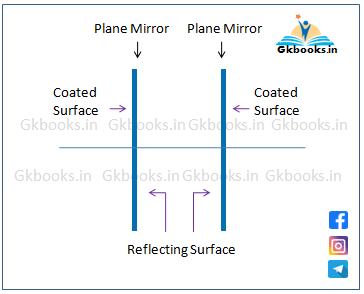
1️⃣ If Two Parallel Plane Mirrors Face Each Other:
- They form an INFINITE number of images.
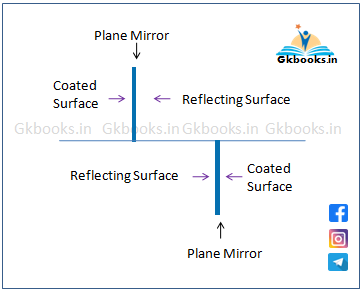
2️⃣ If Two Parallel Plane Mirrors Face in Opposite Directions:
- Only 2 images are formed.
🔶 Two parallel plane mirrors form only 2 images if the angle (θ) between them is 180 degrees and they face each other like the following image.
🔶Two parallel plane mirrors formed only 2 images if they are perpendicular to each other or the angle (θ) between them is 90 degrees and they are facing each other like the following image.
Uses of Mirrors: Plane, Concave, and Convex Mirrors
Mirrors are essential optical devices used in various applications, from daily life to scientific and industrial uses. Based on their shape and properties, mirrors are classified into Plane, Concave, and Convex Mirrors, each having unique applications.
1. Uses of Plane Mirrors
A plane mirror is a flat reflective surface that forms an upright, virtual image of the same size as the object. Some of its key uses include:
✔ As a looking glass – Used in households for grooming and dressing.
✔ In torch lights – Reflects light to direct beams efficiently.
✔ In solar cookers – Reflects and concentrates sunlight to generate heat.
✔ In periscopes – Two plane mirrors are used in periscopes to help view objects from hidden positions.
✔ In kaleidoscope toys – Creates beautiful symmetrical patterns using multiple reflections.
What is a Kaleidoscope?
- A kaleidoscope is an optical instrument that produces colorful patterns due to multiple reflections.
- It contains two or more reflecting mirrors placed at an angle, allowing them to form beautiful symmetrical designs.
2. Uses of Concave Mirrors
A concave mirror is a converging mirror that reflects light inward, making it useful for focusing light on a specific point. Some of its key applications are:
✔ In searchlights and headlights – Helps focus and direct strong beams of light.
✔ In shaving and makeup mirrors – Provides a magnified reflection for better visibility.
✔ In satellite dishes – Used to focus signals efficiently.
✔ In dental mirrors – Used by dentists for a magnified view of teeth and gums.
3. Uses of Convex Mirrors
A convex mirror is a diverging mirror that spreads light out, making it ideal for applications where a wider field of view is required.
✔ As rear-view mirrors in vehicles – Provides a wider angle of vision for drivers.
✔ As security mirrors in shops and parking areas – Used for surveillance to monitor blind spots.
✔ In interior design – Adds depth and aesthetic appeal to spaces.
Conclusion
Mirrors play an essential role in our daily lives, scientific applications, and industries. Whether it’s a plane mirror for simple reflections, a concave mirror for light focusing, or a convex mirror for a wider field of view, each type of mirror serves a unique purpose.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Answer: Erect, Virtual Image
Answer: 2 Plane Mirror
Answer: Concave mirror
Answer: Convex Mirror