Have you ever wondered how a microscope helps us see tiny germs or how a telescope brings distant stars closer? These amazing devices are called optical instruments because they use light to help us see things more clearly. From eyeglasses to binoculars, these tools make our lives easier in many ways.
In this guide, we will learn about different optical instruments, their uses, and how they work. This topic is very important for competitive exams like SSC, Banking, RRB NTPC, UPSC, and state-level exams. Questions about microscopes, telescopes, periscopes, and other optical devices are common in General Science and General Awareness sections.
By the end of this guide, you will understand:
✅ What optical instruments are
✅ Their different types and functions
✅ How they help in daily life and scientific research
Let’s explore the world of optical instruments! 🌍🔬🔭
What are optical instruments?
An optical instrument is a device that uses light waves to enhance images or analyze their properties. These instruments help us see distant objects, magnify tiny structures, and even capture images.
Definition of Optical Instruments
An optical instrument is a tool that processes light waves to improve visibility or measure optical properties. These devices are widely used in science, medicine, photography, and astronomy.
Common Examples
Here are some widely used optical devices and their applications:
✅ Microscope – Magnifies tiny objects, used in biology and medical research.
✅ Telescope – Helps observe stars and planets, used in astronomy.
✅ Periscope – Allows viewing over obstacles, used in submarines and military.
✅ Camera – Captures images and videos, used in photography and surveillance.
✅ Magnifying Glass – Enlarges objects, commonly used for reading and inspection.
✅ Binoculars – Enhances distant views, useful in birdwatching and sports events.
✅ Spectrometer – Analyzes light properties, used in scientific research.
Uses of Optical Instruments
🔹 Scientific Research – Microscopes and spectrometers help in experiments and discoveries.
🔹 Medical Field – Optical tools are used in eye check-ups, surgeries, and diagnostics.
🔹 Photography & Videography – Cameras and lenses enhance image quality.
🔹 Astronomy & Space Exploration – Telescopes help us explore the universe.
🔹 Defense & Surveillance – Night vision goggles and periscopes assist in military operations.
The magnifying power of optical instruments
- The Magnifying power of an optical instrument is defined by the ratio of the angle subtended by the image at the eye (visual angle) to the angle subtended by the object seen directly when both lie at the least distance of distinct vision or nearest point. It is also called angular magnification and is denoted by M.
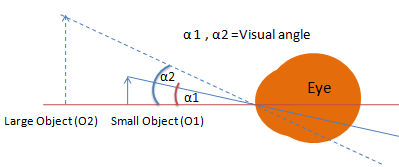
What is Visual Angle?
- Visual angle is the angle subtended by the object in the human eye. A larger Visual angle means a larger Object, and similarly, a Small visual angle means a smaller object.
- The optical instrument enhances the visual angle of the object, causing us to see it as larger than its actual size.
- In other words, the optical instrument creates a larger image of the object, and this final image creates a larger visual angle for our eyes.
α1 – Small visual angle = O1 – Smaller Object
α2 – Bigger visual angle = O2 – Larger Object
Types of Optical Instruments
Here is the major optical instruments list, which are commonly in use:
1. Camera
2. Simple Microscope or Magnifying Glass
3. Compound Microscope
4. Telescopes
5. Periscopes
6. Binoculars
7. Kaleidoscope
✅ Read Also: Image formed by Plane Mirror: Detaild Notes
Photographic Camera
- A camera is an optical instrument that captures a visual image. At a basic level, cameras’ bodies are sealed lightproof boxes with a small hole known as an aperture that allows light through to capture an image on a light-sensitive surface, usually photographic film or a digital sensor.
- Cameras have various mechanisms to control how the light falls onto the light-sensitive film.
- The amount of time the photosensitive surface is exposed to light is controlled by the shutter mechanism.
- Lenses focus the light entering the camera, and the aperture size can be widened or narrowed. The f-number represents the size of the aperture.
✔️ F-Number = Focal length of the lens / Diameter of lens
✔️ Generally, 2, 2.8, 8, 11, 22, and 32 are f-numbers.
- The amount of light entering the camera is directly proportional to the area of the aperture.
✔️ L ∝ A ∝ d2
✔️ The Brightness of an image ∝ d2/f2
✔️ Here, d=diameter of the lens and f=focal length of the lens
- Exposure time is when light is incident on photographic film.
- A real, inverted image of the object is formed on the film by the lens system.
Microscope
What are Microscopes?
- A Microscope is an optical instrument that forms a bigger or magnified image of a small nearby object by increasing the visual angle subtended by the image at the eye so that the object is seen to be bigger and distinct.
- The optical microscope, often referred to as the light microscope, uses visible light and a system of lenses to magnify images of small subjects.
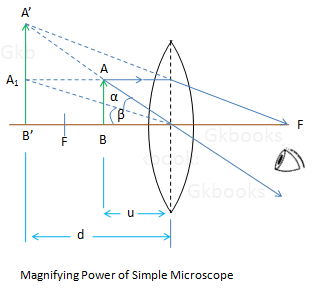
Magnifying Power of Microscope
- The magnification in a microscope is defined by the ratio of the visual angle formed by the final image (β) to the visual angle formed by the object kept at potion D (α).
- So, Magnification (M) = β / α
- Here D is the least distance of distinct vision.
What is meant by the least distance of distinct vision?
- It is the distance up to which the human eye can see the object clearly without any strain on it. For a normal human eye, this distance is generally taken to be 25 cm.
Types of Microscopes
There are two types of microscopes:
1. Simple microscopes
2. Compound microscopes.
Simple microscope
Simple Microscope Definition
- A simple microscope is a magnifying glass of a single convex lens with a short focal length. It magnifies the object through angular magnification, thus producing an erect virtual image of the object near the lens.
Magnifying Power
- Since a simple microscope uses only one objective lens, its magnification capability is greatly limited. Most simple microscopes have a 10x magnification power.
- The formula for calculating the magnifying power of a simple microscope is:
M = 1 + D/F
Where D is the least distance of distinct vision, and F is the focal length of the convex lens. The shorter the focal length of the lens, the higher the magnifying power of the microscope.
Compound Microscope
Compound Microscope Definition
- A compound microscope consists of two convex lenses. A lens of short aperture and short focal length faces the object and is called the objective. The eyepiece is another lens of short focal length but a large aperture facing the eye. The objective and eyepiece are placed coaxially at the two ends of a tube. The eyepiece lens is nothing but a simple microscope.
Magnification of compound microscope
- The Magnifying power of a compound microscope is defined as the ratio of the angle subtended by the final image at the eye to the angle subtended by the object at the unaided or naked eye.
- When the final image is formed at least a distance of distinct vision (D), then
M = v0 /u0 (1 + D/fe)
When, v0=distance of the image, formed by the objective lens
u0=distance of objects from the objective lens.
- When the final image is formed at infinity, then
M=v0 /u0 (D/fe)

Telescopes
- Telescopes are used to see distant objects not visible to the naked eye, such as celestial bodies or heavenly bodies like the sun, moon, planets, and stars, and terrestrial bodies such as distant objects on the earth’s surface.
- In the naked or unaided eye, the distant objects are not seen properly due to the small visual angle subtended by the distant objects at the eye.
- The use of a telescope increases the visual angle and brings the image nearer to the eye.
Types of Telescope
Mainly two types of telescopes are in common use:
1. Refracting telescope and
2. Reflecting telescope.
The refracting telescopes are also of two types:
1. Astronomical telescopes
2. Terrestrial telescopes
Astronomical Telescope
- It is also a combination of two convex lenses, called an objective lens and an eyepiece, separated by a distance. It is used for observing distinct images of heavenly bodies like stars and planets.
- The objective lens has a large aperture and large focal lengths (fo), and it faces towards the object.
- The eyepiece is the lens facing the eye. It has a small aperture and a short focal length (fe).
- The objective and eyepiece are mounted coaxially in two metal tubes.
- An astronomical telescope produces a virtual and erect image.
Magnifying Power
- When the final image is formed at least a distance of distinct vision (D), then
M = – fo/fe (1+fe/D)
- Where, fo and fe focal lengths of objective and eyepiece, respectively.
- Length of the Telescope (L) = (fo +fe)
- When the final image is formed at infinity, then M = – fo/fe
- Length of the Telescope (L) = (fo +fe)
- For telescope’s magnifying power should be large, and fe should be small.
- For large magnifying power of a microscope; fo < fe but fe should be small
Periscope
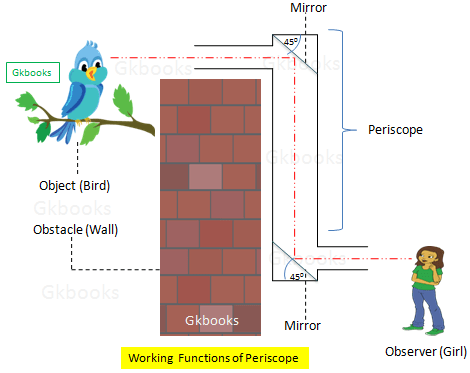
- A periscope is an instrument for observation over, around, or through an object, obstacle, or condition that prevents direct line-of-sight observation from an observer’s current position.
- A Periscope is a simple optical instrument that consists of an outer case with two plan mirrors that are set parallel to each other at a 45° angle.
- This form of periscope, with the addition of two simple lenses, served for observation purposes in the trenches during World War I.
- The earliest periscope was known as the “polemoscope” which was developed by Johannes Hevelius.
- Hippolyte Marié-Davy invented the first naval periscope.
Binoculars
- Binoculars or field glasses are two refracting telescopes mounted side-by-side and aligned to a point in the same direction. They allow the viewer to use both eyes (binocular vision) when viewing distant objects.
- Unlike a (monocular) telescope, binoculars give users a three-dimensional image.
- This optical system of a Binocular consisted of an objective lens and the ocular lens (eyepiece), which had two facing, right-angle prisms arranged to invert and correct the orientation of the image.
- The most common configuration is that invented in 1849 by Carl Kellner.
Kaleidoscope
- A kaleidoscope is an optical instrument that creates beautiful patterns.
- It consists of two or more reflecting surfaces (or mirrors) tilted to each other at an angle so that one or more (parts of) objects on one end of the mirrors are seen as a regular symmetrical pattern when viewed from the other end due to repeated reflection.
- The reflectors are usually enclosed in a tube, often containing on one end a cell with loose, coloured pieces of glass or other transparent (and/or opaque) materials to be reflected into the viewed pattern.
- Rotation of the cell causes motion of the materials, resulting in an ever-changing view being presented.
Note: There are many Kaleidoscope photo apps on play store you can download and try them out. In the above image, Kaleidoscope patterns applied on two detergent bubbles through mobile app.
Optical instruments previous year MCQs
Question 1: What is an endoscope?
A. It is an optical instrument used to see inside the alimentary canal
B. It is a device that is fitted into the chest of the patient to regularise the irregular heartbeats
C. It is an instrument used for examining ear disorders
D. It is an instrument for recording electrical signals produced by human muscles
Answer: A. It is an optical instrument used to see inside the alimentary
canal
Question 2: A periscope works on the principle of _
(SSC Combined Matric Level (PRE) Exam. 30.03.2008 (Ist Sitting)
A. refraction
B. total internal reflection
C. diffraction
D. reflection
Answer: D. reflection
Question 3. A microscope used in pathological laboratories forms _
(SSC Combined Matric Level (PRE) Exam. 13.05.2001 (Ist Sitting)
A. magnified, virtual, erect image
B. diminished, real and erect image
C. magnified, virtual and inverted image
D. diminished, virtual and erect image
Answer: C. magnified, virtual and inverted image
Question 4: The final image in a simple microscope is
(SSC Combined Matric Level (PRE) Exam. 16.06.2002 (Re-Exam)
A. real, diminished and inverted
B. real, magnified and erect
C. virtual, magnified and erect
D. virtual, diminished and erect
Answer: C. virtual, magnified and erect
Question 5: What is a compound microscope?
(SSC Constable (GD) Exam. 12.05.2013)
A. A microscope that has one lens.
B. A microscope has two sets of lenses: an ocular lens and an eyepiece.
C. A microscope whose lenses are concave.
D. A microscope whose lenses are convex.
Answer: A microscope with two sets of lenses: an ocular lens and an eyepiece.
Question 6: An electron microscope gives higher magnifications than an optical microscope because :
(SSC CAPFs SI, CISF ASI & Delhi Police SI Exam, 21.06.2015 (Ist Sitting)
A. The velocity of electrons is smaller than that of light
B. The wavelength of electrons is smaller as compared to the wavelength of visible light
C. The electrons have more energy than the light particulars
D. The electron microscope uses more powerful lenses
Answer: The wavelength of electrons is smaller as compared to the wavelength of visible light
Question 7: Which country is in the process of building the largest single Aperture Radio Telescope – FAST
(SSC CGL Tier-I (CBE) Exam. 31.08.2016 (Ist Sitting))
A. Japan
B. China
C. USA
D. Russia
Answer: B. China
Note:
• The world’s largest radio telescope, the Five-hundred-metre Aperture Spherical Telescope or FAST, was installed in Pingtang in China’s Guizhou province.
Question 8: The instrument used to see the distant objects on the Earth is _
(SSC Tax Assistant (Income Tax &Central Excise) Exam. 29.03.2009
A. Terrestrial telescope
B. Astronomical telescope
C. Compound microscope
D. Simple microscope
Answer: A. Terrestrial telescope
Question 9: One can distinguish a telescope from a microscope by observing _
(SSC CPO(SI, ASI & Intelligence Officer) Exam. 28.08.2011 (Paper-1)
A. length
B. colour
C. size of the lens
D. length and size of the lens
Answer: D. Length and size of the lens
Question 10: The magnifying power of an astronomical telescope can be decreased by _
(SSC Combined Matric Level (PRE) Exam. 27.05.2001 (IInd Sitting (East Zone)
A. decreasing the focal length of the eyepiece
B. increasing the focal length of the eyepiece
C. increasing the focal length of the objective
D. None of these
Answer: B. Increasing the focal length of the eyepiece
Question 11: Where is the largest reflecting telescope in Asia?
(SSC Tax Assistant (Income Tax &
Central Excise) Exam. 25.11.2007)
A. Kodaikanal
B. Ooty
C. Kavalur
D. Nainital
Answer: D. Naini Tal
Note:
• A reflecting telescope is able to collect light from outer space using a highly reflective surface or a mirror. A reflecting or reflector telescope uses a single mirror or a series of curved mirrors to collect and focus light in order to make an image.
• The largest reflecting telescope in Asia is located in the Devasthal Observatory at Nainital, Uttarakhand, India. The 3.6m Devasthal Observatory Telescope (DOT) is currently the largest reflecting telescope in Asia.
FAQs on List of Optical Instruments
Answer: Dutch tradesman Antoni Van Leeuwenhoek.
Answer: In 1590, Two Dutch spectacle-makers and a father-and-son team, Hans and Zacharias Janssen created the first microscope.
Answer: scientist Robert Hooke
Answer: Two Dutch spectacle-makers Hans and Zacharias Janssen [because they use a two-lens system]
Answer: Microscope
Answer: Telescopes, cameras, lasers, glasses, binoculars (most of the advanced optical instrument uses a combination of concave and convex lenses)
Answer: Magnifying glasses, Eyeglasses, Cameras, Microscopes
Answer: kaleidoscope and Periscopes
Answer: Cameras work very similarly to how the human eye works.
Answer: The Compound Microscope
Answer: Optical Flat(It is used in conjunction with a monochromatic light to measure the difference between two surfaces)
Answer: A periscope is based on the Laws of Reflection
Answer: Ernst Ruska
Answer: Ernst Ruska and Max Knoll
Explore More Topics on Physics: