Welcome to our guide all about carbohydrates! In this blog, we’ll explore different kinds of Carbohydrates, show examples, and share important facts. Carbs are super important because they give us energy for our bodies. From simple sugars to more complicated starches, there are lots of types of carbs out there.
Each one does something special for us and helps keep us healthy. Whether you’re curious about what’s in your food or want to make better choices, this guide is here to help. Let’s learn together about the world of carbohydrates!
What is Carbohydrate?
Carbohydrates are one of the main types of nutrients found in foods and drinks. They are essential for providing energy to our bodies. Carbohydrates come in two main forms: simple and complex.
Simple carbohydrates are sugars. They can be found in fruits, vegetables, milk, and sweets. These give quick bursts of energy because they are easy to digest.
Complex carbohydrates are starches and fibers. They are found in foods like bread, pasta, rice, and some vegetables. These take longer to digest and provide a steady source of energy.
Our bodies break down carbohydrates into glucose, which is used for energy by our cells, tissues, and organs. Eating a balanced diet with the right amount of carbohydrates helps keep our bodies functioning well.
Definition and Formula of Carbohydrates
Definition
Carbohydrates are biomolecules that consist of carbon (C), hydrogen (H), and oxygen (O) atoms, usually with a hydrogen-to-oxygen atom ratio of 2:1. This structure is what defines carbohydrates.
Carbohydrates are also known as saccharides, which means sugars.
General Formula
The general formula for carbohydrates is ( C_n(H_2O)n ), where ( n ) is the number of carbon atoms. For example, glucose, a simple carbohydrate, has the formula ( C_6H{12}O_6 ).
Sources of Carbohydrates
Carbohydrates can be found in a variety of foods. Here are some common sources:
- Fruits: Apples, bananas, berries, and oranges are rich in natural sugars and fibers.
- Vegetables: Potatoes, corn, and peas have high starch content, while leafy greens provide fiber.
- Grains: Bread, rice, pasta, and cereals are major sources of complex carbohydrates.
- Legumes: Beans, lentils, and chickpeas offer both starch and fiber.
- Dairy Products: Milk, yogurt, and cheese contain lactose, a type of sugar.
- Sugary Foods: Sweets, candies, and sugary drinks are high in simple sugars.
Nutritional Significance of Carbohydrates
- The main function of carbohydrates is to provide energy to our bodies.
- An adult needs about 3000 Kcal of energy each day.
- Out of the 3000 Kcal of energy, 47%, or 1400 Kcal, comes from carbohydrates.
- The daily requirement of carbohydrates is about 405 grams.
- The calorific value of carbohydrates is 4.1 Kcal per gram.
Biological Significance of Carbohydrates
Carbohydrates play an important role in living organisms. Their roles are described below:
Storage Role
- Carbohydrates in plants and animals act as a storage of metabolic fuel.
- For example, starch is present in plants, and glycogen is present in animals as storage forms.
- These storage forms, starch in plants and glycogen in animals, are broken down into glucose units to provide needed energy.
Structural Role
- Carbohydrates such as cellulose, hemicellulose, and lignin provide mechanical and protective functions to plant cell walls.
- They give a definite shape to plant cells and are part of the outer exoskeleton of insects and crustaceans, which is composed of chitin.
- Glycosaminoglycans like hyaluronic acid, heparin, chondroitin sulfate, and dermatan sulfate are part of the extracellular matrix, playing a structural role in both bacteria and animals.
- These are units of acidic sugar and amino sugar.
Communication Role
- Carbohydrates are covalently bound to proteins or lipids to form glycoproteins or glycolipids, which act as hormones and enzymes respectively.
Glycoproteins
- Act as hormones such as TSH (Thyroid-stimulating hormone) and erythropoietin.
- Function as enzymes including phosphatase, lipase, and pepsinogen.
- Serve as receptors and integral membrane proteins.
Glycolipids
- Function as membrane proteins, enzymes, secretory proteins, and immunoglobulins.
Types of Carbohydrate
Carbohydrates are classified into two broad categories: simple carbohydrates and complex carbohydrates.
Simple Carbohydrates
These are called monosaccharides. They consist of single sugar molecules and are quickly digested, providing fast energy. Examples include glucose and fructose.
Complex Carbohydrates
These include oligosaccharides and polysaccharides.
- Oligosaccharides: Made up of a few linked sugar molecules. Examples include raffinose and stachyose.
- Polysaccharides: Consist of many linked sugar molecules and provide sustained energy. Examples include starch, cellulose, and glycogen.
Monosaccharides
- The word “monosaccharide” comes from Greek: “monos” means single, and “sacchar” means sugar.
- Monosaccharides are also called simple sugars.
- They are the simplest form of sugar and the most basic units (monomers) of carbohydrates.
- The general formula is ( C_nH_{2n}O_n ).
- Monosaccharides cannot be hydrolyzed into simpler units of polyhydroxy aldehyde or ketone.
- If a monosaccharide contains an aldehyde group (-CHO), it is called an aldose. If it contains a keto group (C=O), it is called a ketose.
- Monosaccharides are the building blocks of disaccharides (such as sucrose and lactose) and polysaccharides (such as cellulose and starch).
Examples of monosaccharides
- Glucose (dextrose)
- Fructose (levulose)
- Galactose
Structure of Carbohydrates – Glucose
- The naturally occurring form of glucose is d-glucose, while l-glucose is produced synthetically in small amounts and has less biological activity.
- Glucose is a monosaccharide that contains six carbon atoms and an aldehyde group (-CHO), making it an aldohexose.
The glucose molecule can exist in two forms:
- Open-chain (acyclic) form
- Ring (cyclic) form

Facts about Glucose
- Molecular Formula: Glucose is a simple sugar with the molecular formula ( C_6H_{12}O_6 ). It is the most abundant monosaccharide in the world.
- Photosynthesis: It is mainly produced by plants and most algae during photosynthesis from water and carbon dioxide, using energy from sunlight.
- Cellulose Production: In plants, glucose is used to make cellulose for cell walls.
- Energy Source: Glucose is the most important source of energy in all organisms.
- Storage: In plants, glucose is stored as starch and amylopectin. In animals, glucose is stored as glycogen.
- Glycogenolysis: In animals, glucose is released from the breakdown of glycogen in a process called glycogenolysis.
- Blood Sugar: Glucose circulates in the blood of animals as blood sugar. It is naturally found in its free state in fruits and other parts of plants.
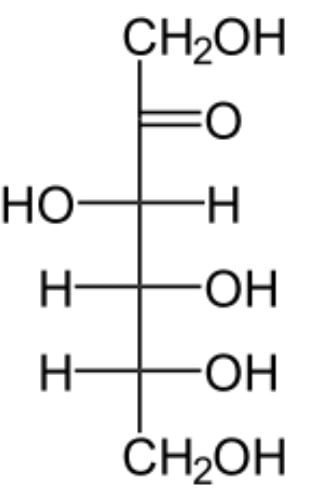
Structure of Carbohydrates – Fructose
- The molecular formula of fructose is C6H12O6.
- It is an important ketohexose.
- It has a Ketone(-CO) functional group.
Facts about Fructose
Here are some interesting facts about fructose:
- Fructose was first discovered back in 1847 by a French chemist named Augustin-Pierre Dubrunfaut. The name “fructose” was later given by an English chemist, William Allen Miller, in 1857.
- Fructose, also known as fruit sugar, is super sweet! In fact, it’s considered the sweetest sugar in the world.
- It’s one of the three main types of simple sugars that we eat, along with glucose and galactose.
- When we eat foods containing fructose, like fruits or sweet treats, our liver changes it into glucose, which is what our bodies use for energy.
- Fructose is really good at dissolving in water. In fact, it’s the most water-soluble sugar there is.
- You can find fructose in lots of different places commercially. It’s extracted from sugarcane, sugar beet, and even corn.
- Ever heard of high-fructose corn syrup? It’s a mix of glucose and fructose, often used in sweetening drinks and foods.
- And when glucose and fructose team up, they form a compound called sucrose. That’s what we commonly know as table sugar, the stuff we sprinkle on cereal or stir into our coffee!

Oligosaccharide
- An oligosaccharide is a polymer of saccharides containing two to ten monosaccharides
- Most of the Oligosaccharides in the cell are found on the cell membrane. These are present on the outer side of the cell.
- These sugar groups come in three sizes: there are the two-sugar ones called disaccharides, the three-sugar ones called trisaccharides, and the four-sugar ones called tetrasaccharides.
Disaccharide
- Disaccharides are formed when two sugars join up. They’re simple sugars that dissolve easily in water. You might have heard of some, like lactose in milk, sucrose in sugar, and maltose in grains.
- Most common examples of Disaccharides: Lactose, Sucrose, Maltose
- General formula of – Cn(H2O)n-1
✓ Sucrose = Glucose + Fructose ✓ Maltose = Glucose + Glucose ✓ Lactose = Glucose + Galactose
Trisaccharide
- Trisaccharides are like a team of three sugars linked together. They’re often found in plants like sugarbeets.
- Examples of Trisaccharides are raffinose, Robinose, and Manotriose.
✓ Raffinose = Glucose + Galactose + Fructose
Tetrasaccharide
- Tetrasaccharides have four sugars sticking together. One example is stachyose, found in plants like beans.
- Example – Stachyose, Scorodose
Polysaccharides
- Polysaccharides consist of more than 10 monosaccharide units joined together by glycosidic linkages.
- It is a polymer of α glucose and consists of two components-Amylose and Amylopectin.
- During the formation of Polysaccharides the water molecules are released:
- n(C6H12O6) (C6H10O5)n + nH2O
- The general formula of Polysaccharide – (C6H10O5)n
- Examples of Polysaccharides – Starch, Dextrins, Inulin, Cellulose
Types of Polysaccharides
Homopolysaccharides
- It is made up of a single kind of monosaccharide.
- Examples: Starch, Glycogen, Cellulose, Chitin, Inulin
- Starch is the main storage polysaccharide in plants. It is composed of α-D- glucose units.
- Cellulose is also one of the polysaccharides that are mostly found in plants. It is composed of β-D- glucose units joined by a glycosidic linkage between C1 of one glucose unit and C4 of the next glucose unit.
Heteropolysaccharides
- Made up of more than one type of Monosaccharides.
- Examples: Pectin, Peptidoglycan, Agar-agar
Test for Carbohydrates
Testing for carbohydrates is an important part of understanding the composition of various foods. One simple test involves using Benedict’s solution. To perform this test, you first need to prepare a sample of the food you want to test. Then, mix the sample with water to create a solution. Next, add some Benedict’s solution to the mixture and heat it gently. If carbohydrates are present, the solution will change color, indicating the presence of reducing sugars. This test is commonly used in laboratories and kitchens to identify the presence of carbohydrates in foods like fruits, bread, and pasta.
Carbohydrate Deficiency Diseases
Carbohydrate deficiency diseases occur when the body lacks an adequate amount of carbohydrates, which are essential for energy production and overall health. These conditions can lead to various symptoms and health issues. Here are some common carbohydrate deficiency diseases:
- Diabetes: A chronic condition where the body cannot properly regulate blood sugar levels due to insufficient insulin production or insulin resistance. It affects how the body processes carbohydrates.
- Galactosemia: A rare genetic disorder in which the body cannot break down galactose (a type of sugar found in milk). This can lead to serious health problems if not managed properly.
- Ketosis: When the body doesn’t have enough carbohydrates to use as fuel, it starts breaking down fats for energy. This process produces ketones, which can accumulate and cause ketosis. While mild ketosis is normal during fasting or low-carb diets, severe ketosis can be harmful.
- Hunter Syndrome: Also known as mucopolysaccharidosis II (MPS II), this inherited disorder affects the breakdown of complex carbohydrates called glycosaminoglycans. It leads to various physical and developmental issues.
- Hurler Syndrome: Another type of mucopolysaccharidosis (MPS I), Hurler syndrome results from the deficiency of an enzyme needed to break down glycosaminoglycans. It affects multiple organs and tissues.
- Mucopolysaccharidoses: A group of rare genetic disorders characterized by the accumulation of glycosaminoglycans in various tissues. Symptoms vary depending on the specific type of MPS.
- Mucolipidosis: A group of inherited metabolic disorders that affect the breakdown of carbohydrates and lipids. It can lead to developmental delays, skeletal abnormalities, and other health issues.
- Pompe Disease: A rare genetic disorder caused by the deficiency of an enzyme called acid alpha-glucosidase. It results in the buildup of glycogen (a type of carbohydrate) in various tissues, affecting muscle function.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Answer: monosaccharides, oligosaccharides, and polysaccharides.
Answer: Complex carbohydrates
Answer: Simple carbohydrates and Complex carbohydrates.
Answer: The main function of carbohydrates is to provide energy to our bodies.
Answer: 4.1 kcal/g
Answer: Fructose
Answer: Glucose

