Ever dreamt of galloping across a vast expanse of golden grass? Hold your horses, exam warriors! While you might not be on a literal wild ride, mastering the major grasslands of the world is a crucial step in conquering those competitive exams – SSC, UPSC, Railways, and all the state PSCs you set your sights on.
These grassy plains, often called major grasslands, are a recurring theme in geography sections. Often, questions test your knowledge of their names and locations. But fret not, aspirants! This article is your one-stop guide to acing this topic.
We’ll be traversing the globe, unveiling the major grasslands of the world, complete with their locations. By the end of this quick read, you’ll be a grassland guru, ready to conquer those annoying exam questions!
Why should you read this article? Simple – it’s your key to unlocking those precious marks and getting a step closer to your dream career. ✨ Let’s get started!
What are Grasslands?
Ever Seen a Sea of Grass? Welcome to the Grasslands!
Imagine a vast landscape stretching before you, not unlike a rippling emerald ocean. This, my friends, is a grassland – a majestic ecosystem teeming with life where grasses reign supreme.
Closer than the African savannas you might have seen in documentaries, grasslands cover a whopping 40% of India, blanketing the plains of Rajasthan, Maharashtra, and Gujarat.
But what exactly are grasslands?
✅ Read Also: Top 10 Largest Freshwater Lakes in the World with Facts
Grasslands Decoded: A Land of Grasses
A grassland is a vast area of short grass supporting animals and insects. It covers about 25% of the total land surface of the Earth.
Grasslands are important natural ecosystems, known by different names in countries such as Llanos in Venezuela, Veld in South Africa, etc.

These resilient plants have adapted to thrive in areas with moderate rainfall, typically between 25-75 cm annually.
This rainfall isn’t enough to support dense forests, but it’s perfect for a sea of swaying grasses.
According to UNESCO, grassland is defined as “land covered with herbaceous plants with less than 10 per cent tree and shrub cover” and “wooded grassland as 10-40 per cent tree and shrub cover”.
Fun fact: Did you know there are over 4,000 known grass species? That’s a lot of variety for these green giants!
Grasslands: More Than Just Grass
While grasses are the stars of the show, grasslands are teeming with life. They provide vital habitat for various animals, from grazing herbivores like bison and antelope to stealthy predators like cheetahs and wolves.
In India, our grasslands are home to the majestic Asiatic lion, the endangered Great Indian Bustard, and many colourful birds.
Not All Grasslands Are Created Equal: A Glimpse into Diversity
The term “grassland” encompasses a variety of ecosystems, each with its unique character:
- Savannas: Scattered trees dot these tropical grasslands, creating a mosaic of grassland and woodland. Think Kaziranga National Park with its tall elephant grass and grazing rhinos!
- Temperate Grasslands: Think lush green meadows (A field of Grass) – these grasslands experience warm summers and cool winters with moderate rainfall. The famed Shola grasslands of Tamil Nadu fall into this category.
- Steppes: These vast grasslands exist in colder regions with limited rainfall. While not as common in India, they can be found in the Himalayan foothills.
Let’s explore some key characteristic features of grasslands.

Characteristic features of grasslands
Grasslands, those vast expanses carpeted with swaying grasses, are iconic ecosystems teeming with life. But what exactly defines these landscapes? Here’s a breakdown of their key characteristic features:
Dominant Grasses
Unlike forests dominated by trees, grasslands are ruled by grasses and grass-like plants.
These resilient species adapted extensive root systems that efficiently capture moisture, allowing them to thrive in moderate rainfall conditions (typically 25-75 cm annually).
The dominant grasses in a grassland can vary depending on the specific location and climate.
However, some of the most common types of dominant grasses in different grasslands around the world include:
Temperate Grasslands
- North American Prairies: Big bluestem, Indiangrass, switchgrass, little bluestem.
- Eurasian Steppes: Feather grass, needlegrass, fescue.
- South American Pampas: Pampas grass, bunchgrass.
Tropical Grasslands
- African Savannas: Napier grass, Rhodes grass, bunchgrass.
- Australian Savannas: Kangaroo grass, Mitchell grass, Flinders grass.
These dominant grasses are well-adapted to the fire regimes and grazing pressures typical of grasslands. They have deep root systems that help them store water and nutrients and can grow back quickly after being grazed or burned.
Moderate Rainfall
Grasslands are characterized by moderate rainfall, typically ranging from 25 to 75 centimetres (10 to 30 inches) annually. This is in contrast to deserts, which receive much less rain, and rainforests, which receive significantly more.
Here’s a breakdown of rainfall characteristics in grasslands:
- Moderate Amounts: Grasslands receive enough rain to support grasses and other herbaceous plants, but not enough to sustain the growth of large trees.
- Seasonal Variations: Rainfall in grasslands is often unevenly distributed throughout the year. There may be distinct wet and dry seasons, with most rain falling during a specific period. This seasonality plays a major role in shaping the type of plants and animals found in a particular grassland.
- Unpredictability: Rainfall patterns in grasslands can be somewhat unpredictable, with occasional droughts or periods of heavy rain. This variability pressures the plants and animals that live there, requiring them to adapt to survive in wet and dry conditions.
Temperature
While rainfall is a key factor, temperature also plays a role. Temperate grasslands have colder winters and warmer summers, while tropical grasslands have year-round warmth.
Grasslands come in two main temperature flavours: temperate and tropical, each with distinct characteristics:
Temperate Grasslands
- Seasonal Extremes: These grasslands experience significant swings in temperature throughout the year. Summers can be hot, with highs reaching over 30°C (86°F), while winters can be frigid, dipping below -20°C (-4°F) in some regions.
- Large Seasonal Variation: The temperature difference between summer and winter can be as much as 40°C (72°F) in some temperate grasslands. This wide range necessitates adaptations for the plants and animals that live there.
Tropical Grasslands
- Warm Year-Round: Tropical grasslands experience consistently warm temperatures throughout the year. Averages typically stay above 15°C (59°F) even in the cooler months.
- Wet and Dry Seasons: While warm, tropical grasslands have distinct wet and dry seasons. Rainfall patterns significantly impact temperature fluctuations within these seasons. The dry season can be quite hot, with minimal cloud cover allowing daytime temperatures to soar.
Here’s a table summarizing the key points:
| Feature | Temperate Grasslands | Tropical Grasslands |
|---|---|---|
| Average Temperature | Wide range, with warm summers and cold winters | Warm year-round |
| Seasonal Variation | Large temperature swings between summer and winter | Relatively constant temperatures, with variations due to wet and dry seasons |
| Example Locations | North American Prairies, Eurasian Steppes, South American Pampas | African Savannas, Australian Savannas |
Soil Drainage
Well-drained soils characterize grasslands. This means water percolates through the soil profile relatively quickly, preventing waterlogging that could harm the dominant grasses. Here’s a closer look at the drainage characteristics of grasslands:
Importance of Drainage
- Good drainage is essential for grasslands because most dominant grass species are not adapted to saturated soils.
- Poor drainage can lead to root rot, reduced nutrient uptake, and stunted plant growth.
Soil Texture
- The soil texture plays a major role in drainage. Sandy soils with large pore spaces drain quickly, while clay soils with smaller pores drain more slowly.
- Many grasslands have a mix of sand, silt, and clay particles, creating a balance that allows for good drainage while still retaining some moisture.
Topography
- The slope of the land also affects drainage. Steeper slopes allow water to drain away more readily than flat areas.
- However, some grasslands, like those in low-lying valleys, may have flatter topography and require specific drainage adaptations, such as plants with shallow root systems.
Human Modifications
- In some cases, humans may modify the drainage characteristics of grasslands. For example, drainage ditches or tiles may be installed in some areas to improve drainage for agricultural purposes. However, this can disrupt the natural ecosystem and should be done cautiously.
Seasonal Variations
- Drainage characteristics can vary throughout the year. During periods of heavy rain, even well-drained grasslands may experience temporary waterlogging. However, the soil should recover quickly once the rain subsides.
Soil Organic Matter
- The amount of organic matter in the soil can also affect drainage.
- Soils with high organic matter content tend to drain more slowly than those with low organic matter content.
- However, the benefits of organic matter in terms of nutrient retention and soil health often outweigh the slight drainage impact in grasslands.
Overall, the well-drained nature of grassland soils is a key factor that allows these ecosystems to thrive. It promotes healthy plant growth and supports the diverse range of wildlife that depends on grasslands.
Fire as a Force
Fire is a duality in grasslands, acting as both a destructive force and a renewal mechanism. Here’s a breakdown of fire’s role in grasslands:
Destructive Force
- Immediate Impact: Fires can be devastating in the short term, burning aboveground vegetation and creating a blackened landscape. This can displace animals and destroy their habitat.
- Loss of Nutrients: The intense heat of fires can volatilize some nutrients stored in the aboveground biomass, leading to temporary depletion in the soil.
Renewal Mechanism
- Nutrient Cycling: Fire is crucial in nutrient cycling within the grassland ecosystem. By breaking down dead plant material, fire releases nutrients trapped in those tissues, making them more readily available for new plant growth.
- Reduced Competition: Fire can eliminate accumulated dead plant matter and woody shrubs, creating competition for light, water, and nutrients with desired grasses. This creates space and resources for new grasses to flourish.
- Seed Germination: Fire can stimulate the germination of certain grass seeds that have a hard outer shell. The heat from the fire can scarify the seed coat, allowing water to penetrate and trigger germination.
- Maintaining Biodiversity: Regular fires can help maintain the diversity of plant and animal life in a grassland. By preventing the establishment of woody plants, fire creates an open habitat essential for many grassland species.
Natural vs. Prescribed Fires
- Natural Fires: Lightning strikes are a common cause of wildfires in grasslands. These fires can be beneficial but unpredictable and difficult to control.
- Prescribed Fires: Land managers may use controlled fires, called prescribed fires, to manage grasslands. Prescribed fires are set under controlled conditions to achieve specific ecological goals, such as reducing brush encroachment or promoting new growth.
Fire Regimes
- Frequency and Intensity: The impact of fire on a grassland ecosystem depends on the frequency and intensity of fires. Frequent fires of low intensity can be beneficial, while infrequent fires of high intensity can be more destructive.
- Adaptation: Many grassland plants and animals have evolved adaptations to cope with fire. For example, some grasses have underground buds that allow them to sprout quickly after a fire.
Overall, fire is a natural and important force in shaping grasslands. While it can be destructive in the short term, it also plays a vital role in maintaining the health and diversity of these ecosystems.

Diversity of Wildlife
Grasslands may seem like a simple expanse of grass, but they teem with life. These ecosystems provide vital habitat for grazing herbivores like bison, antelope, and India’s Asiatic lions.
Predators like cheetahs and wolves also find their place in the food chain, while a dazzling array of birds fills the skies.
Here’s a look at some of the wildlife groups you might find in a grassland:
- Mammals: Large grazing animals like bison, antelope, zebras, and wildebeest are iconic grassland herbivores. But grasslands are also home to smaller mammals like prairie dogs, meerkats, rabbits, and ground squirrels.
- Birds: Grasslands are a bird haven, with resident and migratory species finding food and shelter here. Birds of prey like hawks, owls, and falcons soar overhead, while smaller birds like larks, sparrows, and buntings flit amongst the grasses.
- Reptiles: Lizards and snakes are common reptiles in grasslands, where they find plenty of prey in insects and small mammals.
- Insects: Grasslands are teeming with insect life, including grasshoppers, crickets, butterflies, bees, and beetles. These insects play an important role in the grassland ecosystem, as pollinators, decomposers, and food for other animals.
The diversity of wildlife in a grassland is not just about the number of species present. It is also about the complex web of interactions between these species. Predators, prey, herbivores, and plants all play a role in keeping the grassland ecosystem healthy and balanced.
✅ Read Also: Country with Capital and Currency 2024 (Updated List)
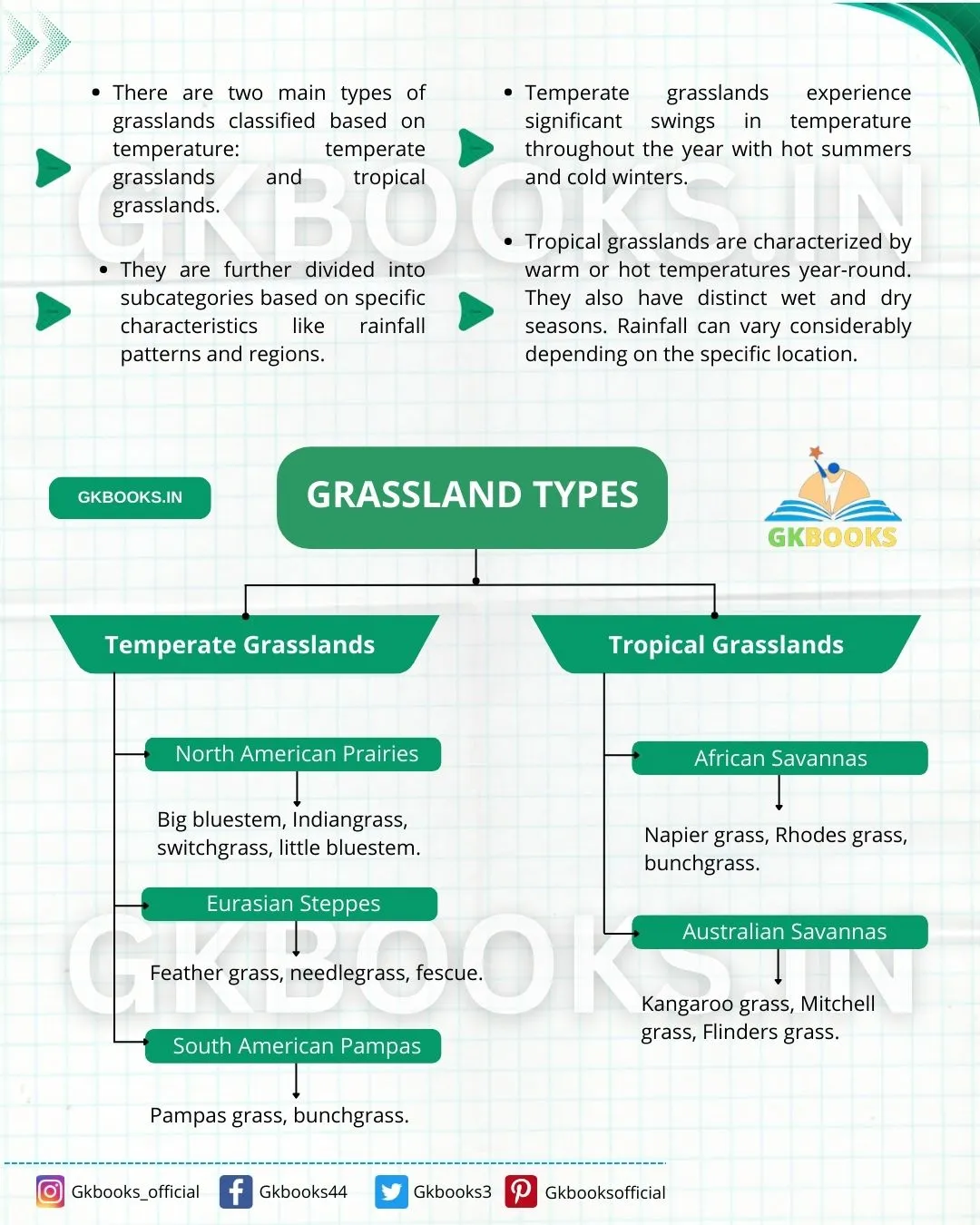
Types of grasslands
There are two main types of grasslands classified based on temperature: temperate grasslands and tropical grasslands.
They are further divided into subcategories based on specific characteristics like rainfall patterns and regions.
Temperate Grasslands
- Temperate grasslands experience significant swings in temperature throughout the year with hot summers and cold winters.
- They receive moderate rainfall from 25 to 75 centimetres (10 to 30 inches) annually.
Subtypes of Temperate Grasslands:
- North American Prairies: In central North America, prairies are known for their tall grasses and wildflowers. Bison, pronghorn antelope, and prairie dogs are some of the iconic animals of the North American prairies.
- Eurasian Steppes: These are vast grasslands stretching across central Asia and Eastern Europe. These grasslands are home to grazing animals like horses, sheep, and saiga antelopes.
- South American Pampas: The pampas are fertile plains in Argentina, Uruguay, and southern Brazil. They are characterized by tall bunchgrasses used extensively for grazing cattle and sheep.
Tropical Grasslands
- Tropical grasslands are characterized by warm or hot temperatures year-round. They also have distinct wet and dry seasons. Rainfall can vary considerably depending on the specific location.
Subtypes of Tropical Grasslands:
- Savannas: Savannas are scattered grasslands with a mix of grasses, shrubs, and acacia trees. They are found in Africa, Australia, and South America. Large herbivores like elephants, zebras, giraffes, and lions are some of the well-known inhabitants of the savannas.
- Wetlands: Wetlands are grasslands that are periodically flooded or saturated with water. They are important habitats for various birds, fish, and amphibians. Some well-known examples of wetlands include the Everglades in Florida and the Pantanal in Brazil.
Tropical Grassland
Let’s explore more details about Tropical Grassland including its key characteristics, definition, and examples.
What is tropical grassland?
Tropical grasslands, also widely known as savannas, are vast stretches of land dominated by grasses and scattered trees. These regions are found in warmer areas of the world, primarily around the equator in Africa, South America, and Australia.
Characteristics of tropical grasslands
Here are some key characteristics of tropical grasslands:
Warm or hot temperatures year-round
- Unlike temperate grasslands, which experience significant seasonal swings in temperature, tropical grasslands have consistent warmth throughout the year.
- Average temperatures typically stay above 15°C (59°F) even in the cooler months.
Distinct wet and dry seasons
- Tropical grasslands experience a dramatic difference in rainfall throughout the year.
- There’s a well-defined wet season with significant rainfall, followed by a long dry season with little to no rain.
- This seasonality significantly impacts the plant and animal life in these regions.
Grasses as the dominant vegetation
- Grasses are the most abundant plants in tropical grasslands.
- The specific types of grasses can vary depending on the location, but they are typically tall and bunch-forming.
- These grasses have adapted to survive the long dry season by having deep root systems that store water and go dormant during drought periods.
Scattered trees and shrubs
- While grasses dominate the landscape, tropical grasslands also have scattered trees and shrubs.
- These trees have adapted to the dry season by developing drought-resistant features such as deep taproots, small leaves, and thick bark.
- Some common tree species in savannas include acacias, baobabs, and sausage trees.
Diverse wildlife
- Tropical grasslands are home to a wide variety of wildlife that has adapted to the seasonal changes and open habitat.
- Large herbivores like elephants, zebras, giraffes, and wildebeest are some of the most iconic animals of the savanna.
- These grazing animals rely on the grasses for food and must migrate or conserve energy during the dry season. Predators like lions, leopards, and cheetahs prey on the herbivores.
Tropical grassland location
Tropical grasslands, also widely known as savannas, are found in warmer areas of the world, primarily around the equator. Here’s a breakdown of the regions with tropical grasslands:
Africa
- The savannas of Africa are among the most famous and iconic tropical grasslands globally.
- They cover a vast expanse, extending from the eastern and southern parts of the continent to the northern Sahel region, bordering the Sahara Desert.
- These savannas harbour an incredible diversity of wildlife, including iconic grazing animals such as zebras, wildebeest, elephants, and giraffes.
- Predators like lions, leopards, and cheetahs also inhabit these savannas, forming intricate ecosystems where prey-predator dynamics play a crucial role.
South America
- South America boasts extensive tropical grasslands, known as llanos in Colombia and Venezuela, and cerrados in Brazil.
- The llanos are expansive, treeless plains subject to seasonal flooding.
- In contrast, the cerrados feature a mosaic landscape of savanna, woodland, and forest.
- Similar to Africa, the wildlife of South American savannas is incredibly diverse.
- Animals such as capybaras, rheas, jaguars, and anacondas are among the many species that inhabit these grasslands, contributing to the rich biodiversity of the region.
Australia
- Australia features a distinctive type of tropical grassland known as savanna woodlands.
- These woodlands are defined by a blend of eucalyptus trees and grasses, adapted to the Australian climate characterized by wet and dry seasons.
- The savannas of Australia are inhabited by a diverse range of wildlife, including iconic marsupials such as kangaroos and wallabies.
- Additionally, birds like emus and kookaburras are also prominent residents of these unique ecosystems.
Example of tropical grassland
There are many examples of tropical grasslands around the world, but here are a few of the most well-known:
The Serengeti in Africa
- This vast savanna in Tanzania and Kenya is one of the most iconic examples of a tropical grassland.
- It is renowned for its annual wildebeest migration, during which millions of animals undertake long-distance journeys searching for water and food.
- The spectacle of the wildebeest migration is a testament to the remarkable resilience and adaptability of wildlife in these grassland ecosystems.
The Masai Mara in Kenya
- This national reserve, bordering the Serengeti, serves as another prime example of an East African savanna.
- It is renowned for its abundant wildlife, which includes iconic species such as lions, elephants, zebras, and giraffes.
- The reserve’s rich biodiversity and stunning landscapes attract visitors from around the world, offering unforgettable safari experiences.
The Llanos in South America
- These vast, seasonally flooded plains in Colombia and Venezuela are home to a unique variety of wildlife.
- Among the notable inhabitants are capybaras, which are the world’s largest rodents, and caimans, large reptiles related to alligators.
- The rich biodiversity of these flooded plains contributes to the region’s ecological importance and attracts nature enthusiasts and researchers alike.
The Pantanal in Brazil
- This wetland biome is a diverse mix of tropical grassland, forest, and flooded areas.
- It is recognized as the world’s largest wetland and is renowned for its incredible biodiversity.
- Notable inhabitants include jaguars, giant otters, and a vast array of birdlife.
- The richness of wildlife in this wetland biome makes it a globally significant area for conservation and ecological research.
The Kakadu National Park in Australia
- This UNESCO World Heritage Site in northern Australia exemplifies a savanna woodland ecosystem.
- It is inhabited by various unique Australian wildlife, such as wallabies and kookaburras.
- Additionally, the area is home to Aboriginal people who are known for their cultural traditions, including playing the didgeridoo.
- The site’s ecological and cultural significance contributes to its designation as a UNESCO World Heritage Site.
Temperate Grassland
Let’s uncover more about Temperate Grasslands, including its key characteristics, definition, and examples.
What is temperate grassland?
- Temperate grasslands are vast regions dominated by grasses with few or no scattered trees.
- Unlike tropical grasslands, temperate grasslands experience significant changes in temperature throughout the year.
- They have hot summers and cold winters, with moderate rainfall, typically ranging from 25 to 75 centimetres (10 to 30 inches) annually.
- These regions are found in mid-latitude areas around the world.
Characteristics of temperate grasslands
Here are some key characteristics of temperate grasslands:
Seasonal temperature variations
- Temperate grasslands undergo significant temperature fluctuations throughout the year.
- Summers can be hot, with temperatures exceeding 30°C (86°F).
- Winters are cold, with temperatures dropping below -20°C (-4°F) in certain areas.
- The wide temperature range necessitates special adaptations for these regions’ flora and fauna.
Moderate rainfall
- Temperate grasslands receive sufficient rainfall to support the growth of grasses and other herbaceous plants.
- However, the rainfall is insufficient to sustain the growth of large trees.
- Rainfall distribution is often uneven and characterized by wet and dry seasons.
- The seasonality of rainfall significantly influences the composition of plant and animal species within temperate grasslands.
Well-drained soils
- Soil in temperate grasslands is well-drained, facilitating rapid water percolation through the soil profile.
- This characteristic is crucial as dominant grass species are generally unsuited to saturated soils.
Grasses as the dominant vegetation
- Grasses dominate the vegetation in temperate grasslands, being the most abundant plants.
- The types of grasses may vary by location, but they are usually tall and form bunches.
- These grasses have adapted to the extreme temperature fluctuations by developing deep root systems, which store water and nutrients.
- They also go dormant during the coldest and hottest parts of the year, aiding their survival.
Large grazing animals
- Temperate grasslands harbour large grazing animals such as bison, pronghorn antelope, and horses.
- These animals have evolved adaptations to cope with seasonal changes, including migrating to warmer areas during winter.
- They also possess thick fur, which acts as insulation against the cold temperatures experienced in the grasslands.
Location of Temperate Grasslands
Here are some of the common temperate grasslands found around the world:
- North American Prairies: Found in central North America, prairies are known for their tall grasses and wildflowers. Bison, pronghorn antelope, and prairie dogs are some of the iconic animals of the North American prairies.
- Eurasian Steppes: Steppes are vast grasslands that stretch across central Asia and Eastern Europe. These grasslands are home to grazing animals like horses, sheep, and saiga antelopes.
- South American Pampas: The pampas are fertile plains in Argentina, Uruguay, and southern Brazil. They are characterized by tall bunchgrasses and are used extensively for grazing cattle and sheep.
Example of Temperate grassland
Temperate grasslands are vast regions of land covered in grasses with few, or scattered trees. These are found throughout the world, including:
- North American Prairies
- South American Pampas
- Eurasian steppes
- Australian grasslands
- New Zealand tussock grasslands
They are characterized by a temperate climate with distinct seasons – hot summers and cold winters. Rainfall varies depending on the region, but it is generally less than in forested areas.
Temperate grasslands are known for their fertile soil, which makes them ideal for grazing animals.
Other types of grasslands are floodplain grasslands, Tundra grasslands, Montane grasslands, and xeric grasslands.
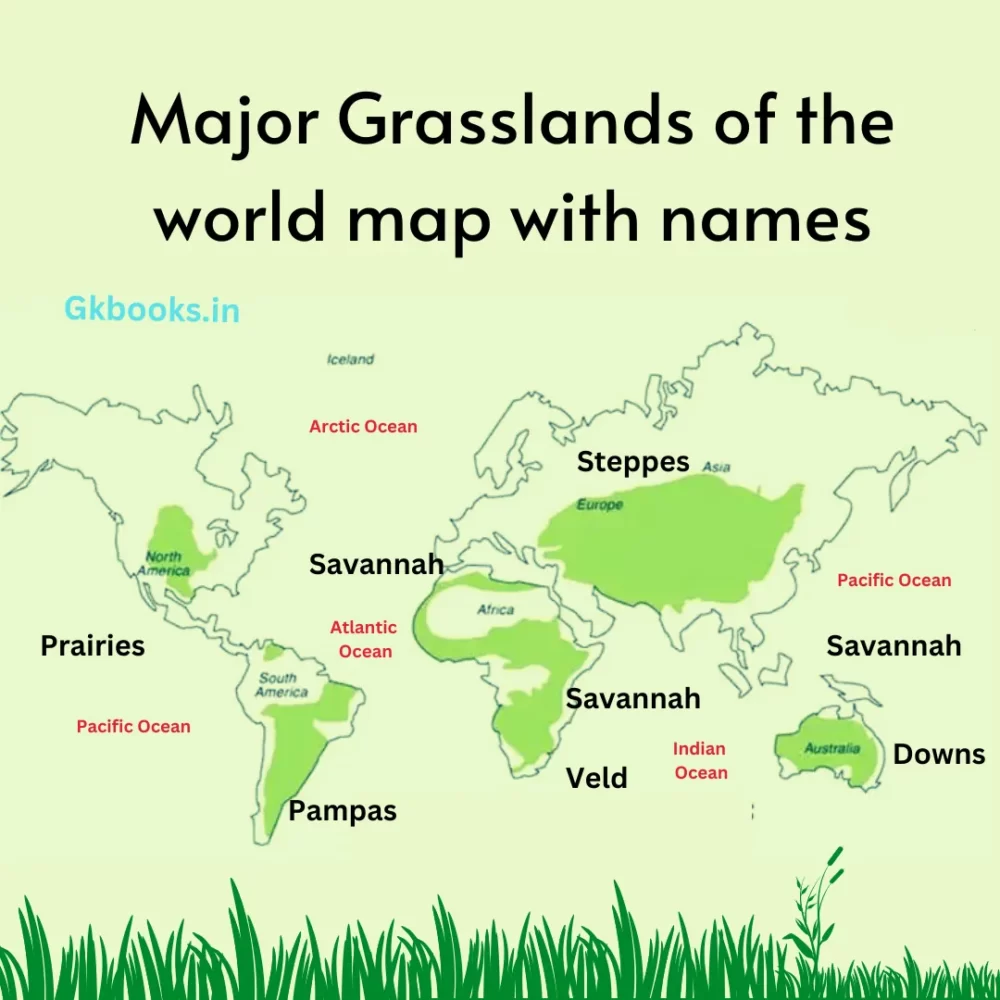
Important grasslands of the world
| Sl. No | Grassland | Region |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Stappes | Europe |
| 2 | Puszta | Hungary |
| 3 | Prairie | North America |
| 4 | Pampas | Argentina |
| 5 | Veld | South Africa |
| 6 | Downs | Australia |
| 7 | Cantebury | NewZealand |
| 8 | Savannah | Africa |
| 9 | Llanos | Venezuela |
Is Taiga a Grassland? ▪ Taiga is a boreal (meaning northern) forest or snow forest found throughout the high northern latitudes, between the tundra and the temperate forest. ▪ Taiga, meaning "land of small sticks" in Russian, derives its name from the collective term for Russia's northern forests, particularly Siberia. ▪ The forest characterized by coniferous forests consisting mostly of pines, spruces, and larches. ▪ It occupies about 17 percent of the Earth's land surface area in a circular belt in the far northern hemisphere. ▪ Although the taiga is a boreal forest, parts of the region, such as the Far East of Russia and the semiarid region of North America (Yukon and Alaska), are considered grasslands.
Significance of Grassland
Grasslands, despite their seemingly simple landscape, are teeming with life. These vast expanses support a remarkable diversity of species:
A Feast for Herbivores
- Grasslands support various plant-eating animals, ranging from iconic species like zebras and wildebeests in the African savanna to grazing herds of bison in North American prairies.
- Other examples of herbivores thriving in grasslands include gazelles, pronghorn antelope, and giraffes, benefiting from the nutritious grasses in these ecosystems.
Temperate Grassland Homes
- While zebras and wildebeests often steal the spotlight, temperate grasslands harbour their fascinating inhabitants.
- Prairie dogs are known for their intricate burrow systems, while badgers exhibit exceptional digging skills.
- Predators such as coyotes and swift foxes play crucial roles in these ecosystems.
- Soaring birds of prey like hawks and eagles thrive in grasslands, preying on the abundant small mammals in these open landscapes.
Hidden Gems of the Tropics
- Tropical grasslands, characterized by shorter grasses, serve as prime hunting grounds for large carnivores such as lions and cheetahs.
- The open habitat provides excellent visibility, enabling these predators to spot prey easily.
- Additionally, various insects, including grasshoppers and locusts, thrive in the warm climate of tropical grasslands.
Beyond the Grasses
- Grasses do not solely define grasslands. Red oat grass, Rhodes grass, and purple needlegrass serve as vital food sources for livestock.
- A diverse array of wildflowers also adorn these landscapes.
- These wildflowers play a crucial role in the ecosystem by providing nectar for pollinators such as butterflies and bees, thus enhancing the biodiversity of grassland habitats.
Cradle of Civilization
- Nomadic and pastoral cultures have inhabited grasslands for millennia.
- These cultures have traditionally relied on the land for grazing their livestock.
- The symbiotic relationship between these communities and the grassland ecosystems has shaped human culture and the landscape over generations.
Environmental Powerhouses
- The root systems of grasses play a crucial role in preventing soil erosion and filtering rainwater.
- This helps protect land and water resources by maintaining soil stability and quality.
- Additionally, healthy grasslands serve as significant carbon sinks, storing large amounts of carbon dioxide.
- This plays a vital role in mitigating climate change by helping to offset greenhouse gas emissions and reduce atmospheric CO2 levels.
By understanding the importance of grasslands, we can ensure their continued health and the rich biodiversity they support.
Major Grasslands of the world map with names
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Answer: Argentina
Answer: South Africa
Answer: Pampas
Answer: Prairies
Answer: Venezuela
Don’t Miss:
- List of Major Grasslands of the World: Detailed Notes
- Major International Summits and Venues, Latest Current Affairs 2024
- International Organizations and Their Headquarters Tricks PDF 2024 with Establishment Year
- List of Countries and their Parliaments Names PDF
- Top 10 Largest Freshwater Lakes in the World with Facts

