Uncover the rich history, compositions, features, functions, and key points of Regional Rural Banks in India. This article provides a comprehensive list and valuable information about these banks. Start exploring now!
Empowering Rural India: A Guide to Regional Rural Banks (RRBs)
Established in 1975, RRBs are a unique banking initiative in India specifically designed to serve the financial needs of rural populations.
What are RRBs?
RRBs are government-backed scheduled commercial banks with a regional focus. Unlike traditional banks concentrated in urban areas, RRBs have a widespread branch network in villages and smaller towns.
Why are RRBs Important?
Before RRBs, access to essential banking services like savings accounts, loans, and money transfers was limited in rural India. RRBs bridge this gap by providing the following:
- Financial Inclusion: Opening bank accounts in rural areas, fostering financial literacy, and empowering communities.
- Agricultural Support: Offering loans tailored to farmers’ needs, such as crop and equipment financing.
- Microfinance: Providing small loans to entrepreneurs, helping them grow their businesses and create jobs.
Beyond Banking
Many RRBs are now offering additional services like:
- Government Scheme Disbursement: Facilitating easy access to government benefits for rural residents.
- Digital Banking Solutions: Promoting mobile banking and online transactions in rural areas.
How Many Regional Rural Banks Serve India? (Updated for 2024)
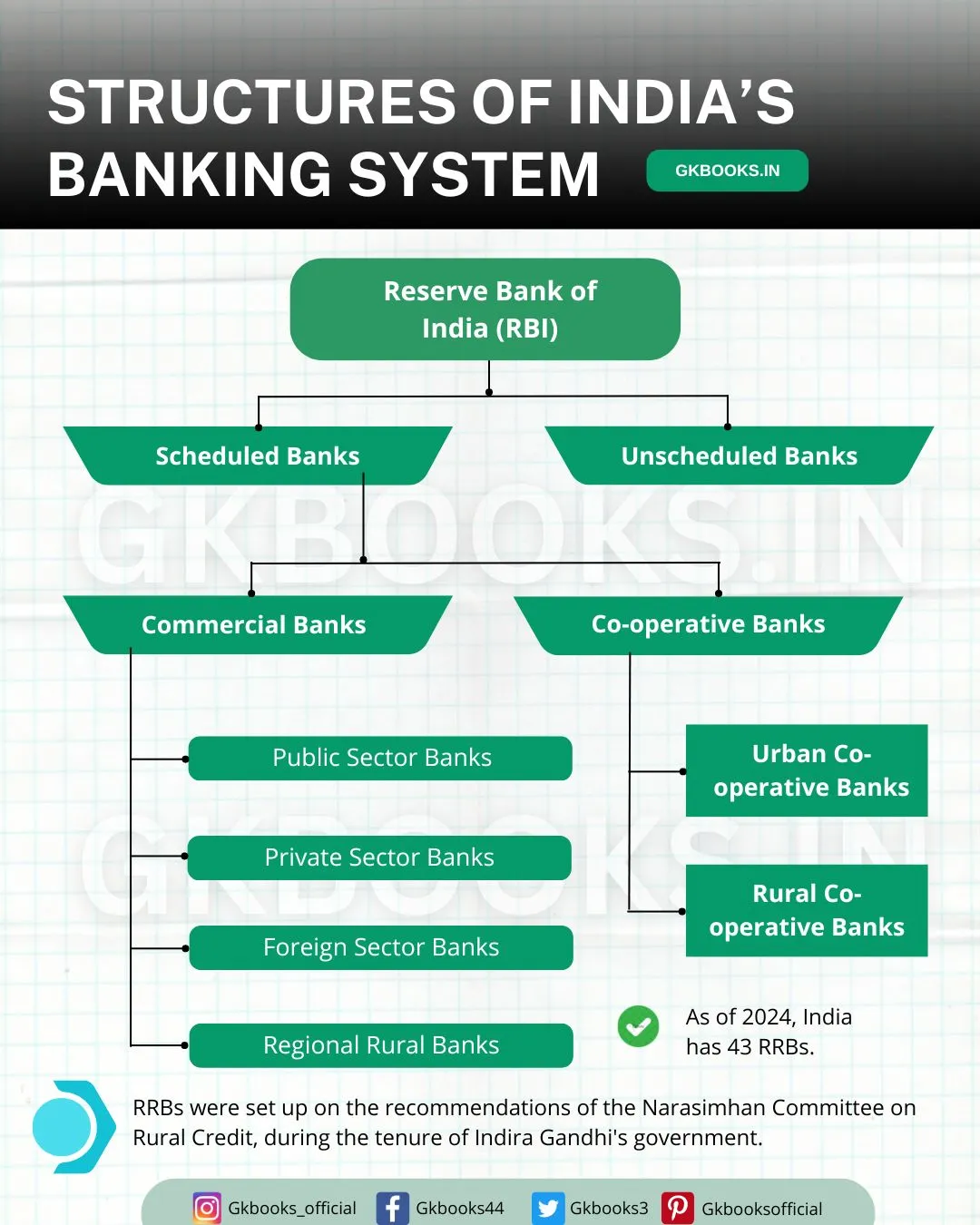
As of 2024, 43 Regional Rural Banks (RRBs) are functioning across India. These banks play a vital role in bridging the gap between conventional banking and rural communities.
These 43 Regional Rural Banks (RRBs) are spread across 26 States and 3 Union Territories in India, collectively running 21,856 branches.
They are backed by 12 Scheduled Commercial Banks (SCBs) and cater to 28.3 crore depositors and 2.6 crore borrowers.
RRBs aim to support small-scale farmers, artisans, and others in rural areas, fostering financial inclusivity throughout the nation.
Merger of Regional Rural Banks (RRBs) in India: What You Need to Know
The question of Regional Rural Bank (RRB) mergers in India has been a topic of discussion for several years. Here’s a breakdown of the situation and its implications:
What are RRB Mergers?
RRBs are government-backed banks serving rural communities. To optimize operations and strengthen their financial standing, some RRBs undergo mergers, consolidating multiple banks into one entity.
Past Consolidation and Current Status
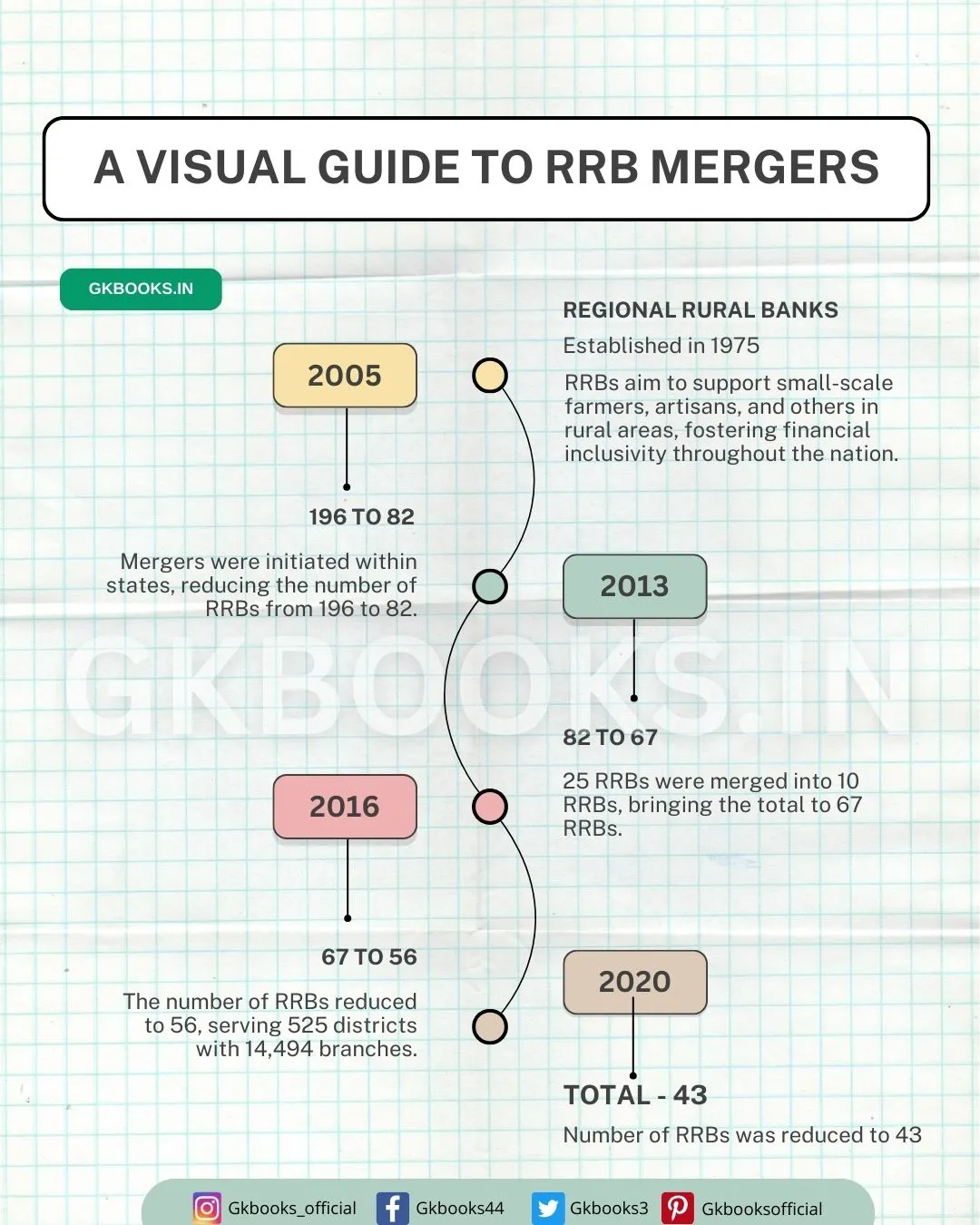
Several RRB mergers have taken place over the years. Since 2020, there have been 43 RRBs in India, down from a higher number in the past.
Here’s the timeline of the process of amalgamation of Regional Rural Banks (RRBs):
- 2005: Mergers were initiated within states, reducing the number of RRBs from 196 to 82.
- January 2013: 25 RRBs were merged into 10 RRBs, bringing the total to 67 RRBs.
- March 2016: The number of RRBs reduced to 56, serving 525 districts with 14,494 branches.
- From April 1, 2020: Following a roadmap by NABARD, consultations with stakeholders, and considering factors like efficiency and financial health, the number of RRBs was reduced to 43
Why Mergers? (Possible Reasons)
- Enhanced Efficiency: Mergers can streamline operations, reduce administrative costs, and create a more robust banking network in rural areas.
- Improved Financial Strength: A larger entity may have better access to resources and capital, allowing for better loan offerings and services for rural communities.
Expected Outcomes of Mergers
- Enhanced Efficiency: Streamlined operations and resource allocation will lead to cost savings and improved service delivery.
- Stronger Financial Footing: Larger RRBs may have better access to capital and resources, enabling them to offer a wider range of financial products and services to rural communities.
- Increased Credit Flow: Consolidation might allow RRBs to provide larger loans to support agricultural growth and rural businesses.
List of regional rural banks in India
| Sl. No. | Name of Regional Rural Bank | Sponsor Bank | State |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Andhra Pradesh Grameena Vikas Bank | State Bank of India | Telangana |
| 2 | Andhra Pragathi Grameena Bank | Canara Bank | Andhra Pradesh |
| 3 | Arunachal Pradesh Rural Bank | State Bank of India | Arunachal Pradesh |
| 4 | Aryavart Bank | Bank of India | Uttar Pradesh |
| 5 | Assam Gramin Vikash Bank | Punjab National Bank | Assam |
| 6 | Bangiya Gramin Vikash Bank | Punjab National Bank | West Bengal |
| 7 | Baroda Gujarat Gramin Bank | Bank of Baroda | Gujarat |
| 8 | Baroda Rajasthan Kshetriya Gramin Bank | Bank of Baroda | Rajasthan |
| 9 | Baroda UP Bank | Bank of Baroda | Uttar Pradesh |
| 10 | Chaitanya Godavari Grameena Bank | Union Bank of India | Andhra Pradesh |
| 11 | Chhattisgarh Rajya Gramin Bank | State Bank of India | Chhattisgarh |
| 12 | Dakshin Bihar Gramin Bank | Punjab National Bank | Bihar |
| 13 | Ellaquai Dehati Bank | State Bank of India | Jammu & Kashmir |
| 14 | Himachal Pradesh Gramin Bank | Punjab National Bank | Himachal Pradesh |
| 15 | J&K Grameen Bank | J&K Bank Ltd. | Jammu & Kashmir |
| 16 | Jharkhand Rajya Gramin Bank | State Bank of India | Jharkhand |
| 17 | Karnataka Gramin Bank | Canara Bank | Karnataka |
| 18 | Karnataka Vikas Grameena Bank | Canara Bank | Karnataka |
| 19 | Kerala Gramin Bank | Canara Bank | Kerala |
| 20 | Madhya Pradesh Gramin Bank | Bank of India | Madhya Pradesh |
| 21 | Madhyanchal Gramin Bank | State Bank of India | Madhya Pradesh |
| 22 | Maharashtra Gramin Bank | Bank of Maharashtra | Maharashtra |
| 23 | Manipur Rural Bank | Punjab National Bank | Manipur |
| 24 | Meghalaya Rural Bank | State Bank of India | Meghalaya |
| 25 | Mizoram Rural Bank | State Bank of India | Mizoram |
| 26 | Nagaland Rural Bank | State Bank of India | Nagaland |
| 27 | Odisha Gramya Bank | Indian Overseas Bank | Odisha |
| 28 | Paschim Banga Gramin Bank | UCO Bank | West Bengal |
| 29 | Prathama UP Gramin Bank | Punjab National Bank | Uttar Pradesh |
| 30 | Puduvai Bharthiar Grama Bank | Indian Bank | Puducherry |
| 31 | Punjab Gramin Bank | Punjab National Bank | Punjab |
| 32 | Rajasthan Marudhara Gramin Bank | State Bank of India | Rajasthan |
| 33 | Saptagiri Grameena Bank | Indian Bank | Andhra Pradesh |
| 34 | Sarva Haryana Gramin Bank | Punjab National Bank | Haryana |
| 35 | Saurashtra Gramin Bank | State Bank of India | Gujarat |
| 36 | Tamil Nadu Grama Bank | Indian Bank | Tamil Nadu |
| 37 | Telangana Grameena Bank | State Bank of India | Telangana |
| 38 | Tripura Gramin Bank | Punjab National Bank | Tripura |
| 39 | Utkal Grameen Bank | State Bank of India | Odisha |
| 40 | Uttar Banga Kshetriya Gramin Bank | Central Bank of India | West Bengal |
| 41 | Uttar Bihar Gramin Bank | Central Bank of India | Bihar |
| 42 | Uttarakhand Gramin Bank | State Bank of India | Uttarakhand |
| 43 | Vidharbha Konkan Gramin Bank | Bank of India | Maharashtra |
State-wise List of Regional Rural Banks in India
Andhra Pradesh
| Name of RRB | Sponsor Bank | Head Office |
|---|---|---|
| Andhra Pragathi Grameena Bank | Syndicate Bank | Kadapa |
| Chaitanya Godavari Grameena Bank | Andhra Bank | Guntur |
| Andhra Pradesh Grameena Vikas Bank | State Bank of India | Kadapa |
| Saptagiri Grameena Bank | Indian Bank | Chittor |
Arunachal Pradesh
| Name of RRB | Sponsor Bank | Head Office |
|---|---|---|
| Arunachal Pradesh Rural Bank | State Bank of India | Naharlagun |
Assam
| Name of RRB | Sponsor Bank | Head Office |
|---|---|---|
| Assam Gramin Vikash Bank | United Bank of India | Guwahati |
| Langpi Dehangi Rural Bank | State Bank of India | Diphu |
Bihar
| Name of RRB | Sponsor Bank | Head Office |
|---|---|---|
| Uttar Bihar Gramin Bank | Central Bank of India | Muzaffarpur |
| Bihar Gramin Bank | UCO Bank | Patna |
| Madhya Bihar Gramin Bank | Punjab National Bank | Patna |
Chhattisgarh
| Name of RRB | Sponsor Bank | Head Office |
|---|---|---|
| Chhattisgarh Rajya Gramin Bank | State Bank of India | Raipur |
Gujarat
| Name of RRB | Sponsor Bank | Head Office |
|---|---|---|
| Baroda Gujarat Gramin Bank | Bank of Baroda | Bharuch |
| Dena Gujarat Gramin Bank | Dena Bank | Gandhinagar |
| Saurashtra Gramin Bank | State Bank of India | Rajkot |
Haryana
| Name of RRB | Sponsor Bank | Head Office |
|---|---|---|
| Sarva Haryana Gramin Bank | Punjab National Bank | Rohtak |
Himachal Pradesh
| Name of RRB | Sponsor Bank | Head Office |
|---|---|---|
| Himachal Pradesh Gramin Bank | Punjab National Bank | Mandi |
Jammu and Kashmir
| Name of RRB | Sponsor Bank | Head Office |
|---|---|---|
| Ellaquai Dehati Bank | State Bank of India | Srinagar |
| J&K Grameen Bank | J&K Bank Ltd. | Jammu |
Jharkhand
| Name of RRB | Sponsor Bank | Head Office |
|---|---|---|
| Vananchal Gramin Bank | State Bank of India | Ranchi |
| Jharkhand Gramin Bank | Bank of India | Ranchi |
Karnataka
| Name of RRB | Sponsor Bank | Head Office |
|---|---|---|
| Pragathi Krishna Gramin Bank | Canara Bank | Ballari |
| Kaveri Gramin Bank | State Bank of India | Mysuru |
| Karnataka Vikas Grameena Bank | Syndicate Bank | Dharwad |
Kerala
| Name of RRB | Sponsor Bank | Head Office |
|---|---|---|
| Kerala Gramin Bank | Canara Bank | Mallapuram |
Madhya Pradesh
| Name of RRB | Sponsor Bank | Head Office |
|---|---|---|
| Narmada Jhabua Gramin Bank | Bank of India | Indore |
| Central Madhya Pradesh Gramin Bank | Central Bank of India | Indore |
| Madhyanchal Gramin Bank | State Bank of India | Sagar |
Maharashtra
| Name of RRB | Sponsor Bank | Head Office |
|---|---|---|
| Vidarbha Konkan Gramin Bank | Bank of India | Nagpur |
| Maharashtra Gramin Bank | Bank of Maharashtra | Aurangabad |
Manipur
| Name of RRB | Sponsor Bank | Head Office |
|---|---|---|
| Manipur Rural Bank | United Bank of India | Imphal |
Meghalaya
| Name of RRB | Sponsor Bank | Head Office |
|---|---|---|
| Meghalaya Rural Bank | State Bank of India | Shillong |
Uttar Pradesh
| Name of RRB | Sponsor Bank | Head Office |
|---|---|---|
| Gramin Bank of Aryavart | Bank of India | Lucknow |
| Allahabad UP Gramin Bank | Allahabad Bank | Banda |
| Baroda Uttar Pradesh Gramin Bank | Bank of Baroda | Raebareli |
| Kashi Gomti Samyut Gramin Bank | Union Bank of India | Varanasi |
| Sarva UP Gramin Bank | Punjab National Bank | Meerut |
| Prathama UP Gramin Bank | Syndicate Bank | Moradabad |
| Purvanchal Bank | State Bank of India | Gorakhpur |
Mizoram
| Name of RRB | Sponsor Bank | Head Office |
|---|---|---|
| Mizoram Rural Bank | State Bank of India | Aizawl |
Tamil Nadu
| Name of RRB | Sponsor Bank | Head Office |
|---|---|---|
| Pallavan Grama Bank | Indian Bank | Salem |
| Pandyan Grama Bank | Indian Overseas Bank | Virudhunagar |
Nagaland
| Name of RRB | Sponsor Bank | Head Office |
|---|---|---|
| Nagaland Rural Bank | State Bank of India | Kohima |
Odisha
| Name of RRB | Sponsor Bank | Head Office |
|---|---|---|
| Utkal Grameen Bank | State Bank of India | Bolangir |
| Odisha Gramya Bank | Indian Overseas Bank | Bhubaneshwar |
Tripura
| Name of RRB | Sponsor Bank | Head Office |
|---|---|---|
| Tripura Gramin Bank | United Bank of India | Agartala |
Uttarakhand
| Name of RRB | Sponsor Bank | Head Office |
|---|---|---|
| Uttarakhand Gramin Bank | State Bank of India | Dehradun |
Puducherry
| Name of RRB | Sponsor Bank | Head Office |
|---|---|---|
| Puduvai Bharathiar Grama Bank | Indian Bank | Puducherry |
Telangana
| Name of RRB | Sponsor Bank | Head Office |
|---|---|---|
| Telangana Grameena Bank | State Bank of India | Hyderabad |
Punjab
| Name of RRB | Sponsor Bank | Head Office |
|---|---|---|
| Punjab Gramin Bank | Punjab National Bank | Kapurthala |
| Malwa Gramin Bank | State Bank of India | Sangrur |
| Sutlej Gramin Bank | Bhatinda |
Rajasthan
| Name of RRB | Sponsor Bank | Head Office |
|---|---|---|
| Baroda Rajasthan Kshetriya Gramin Bank | Bank of Baroda | Ajmer |
| Rajasthan Marudhara Gramin Bank | State Bank of India | Jodhpur |
West Bengal
| Name of RRB | Sponsor Bank | Head Office |
|---|---|---|
| Bangiya Gramin Vikash Bank | United Bank of India | Murshidabad |
| Paschim Banga Gramin Bank | UCO Bank | Howrah |
| Uttarbanga Kshetriya Gramin Bank | Central Bank of India | Coochbehar |
The Functions of Regional Rural Banks (RRBs) in India
Regional Rural Banks (RRBs) are the backbone of financial inclusion in India, catering specifically to the needs of rural and semi-urban populations. But what exactly do they do?
Essential Banking Services for All
- Opening Savings Accounts: RRBs empower rural communities by making saving money safely and securely easier.
- Granting Loans: Farmers, small businesses, and individuals can access loans tailored to their needs, fuelling agricultural growth and local entrepreneurship.
- Money Transfers & Cash Deposits: RRBs ensure convenient money transfer options and cash deposit facilities, bringing vital financial services closer to home.
Beyond Traditional Banking
- Government Scheme Disbursement: RRBs streamline the process of receiving government benefits like pensions and MGNREGA wages for rural residents.
- Digital Banking Solutions: Many RRBs also offer para-banking services like mobile banking, locker facilities, debit and credit cards, internet banking, and UPI services, making banking services accessible even in remote locations.
Unique Advantages of RRBs
Unlike large commercial banks, RRBs deeply understand local needs and challenges. They offer:
- Localized Support: Staff who speak the local language and are familiar with regional agricultural and business practices.
- Flexible Loan Options: Loan products are designed specifically for rural borrowers, considering factors like seasonal income and crop cycles.
Financial Empowerment for Rural India
RRBs play a pivotal role in bridging the financial divide in India. By providing essential banking services, fostering financial literacy, and supporting local economic development, RRBs are catalysts for a more inclusive and prosperous rural future.
A Look Back at the History of Regional Rural Banks (RRBs) in India
In 1975, India undertook a vital step to bridge the financial gap between urban and rural areas. This journey began with the establishment of Regional Rural Banks (RRBs).
The Narasimham Committee and a Nation’s Need
The 1970s saw a growing need for financial inclusion in rural India, where over 70% of the population resided. Recognizing this gap, the Narasimham Committee, formed under the Indira Gandhi government, recommended the establishment of RRBs.
Birth of a Banking Revolution (October 2nd, 1975)
Following the committee’s recommendations, the first five RRBs were established on October 2nd, 1975. This marked a historic moment, laying the foundation for a nationwide network dedicated to serving the financial needs of rural communities.
From Humble Beginnings to Widespread Presence
Initially, RRBs faced challenges in terms of infrastructure and operational efficiency. However, they expanded their reach over time, establishing branches across rural and semi-urban regions.
The Evolving Role of RRBs
Today, RRBs play a vital role in rural India’s financial landscape. They go beyond basic banking services, offering loans tailored to agriculture, microfinance options for entrepreneurs, and even facilitating government benefit disbursements.
The First Five Regional Rural Banks of India
1975 marked a turning point for rural finance in India, establishing the first five Regional Rural Banks (RRBs) on October 2nd. These institutions paved the way for a more inclusive financial landscape, bringing essential banking services to the doorsteps of rural communities.
Leading the Charge: Prothama Bank
The distinction of being India’s first RRB goes to Prothama Bank, headquartered in Moradabad, Uttar Pradesh.
Sponsored by Syndicate Bank, Prothama Bank began its journey with an authorized capital of Rs. 5 crore, serving as a model for future RRBs.
The Founding Five
Here’s a glimpse into the other four RRBs that were established alongside Prothama Bank:
| Sl. No. | Name of Regional Rural Bank | Sponsor Bank | State |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Prathama Bank | Syndicate Bank | Moradabad, Uttar Pradesh |
| 2 | Gaur Gramin Bank | UCO Bank | Sahajadpur, West Bengal |
| 3 | Gorakhpur Kshetriya Gramin Bank | State Bank of India | Gorakhpur, Uttar Pradesh |
| 4 | Haryana Kshetriya Gramin Bank | Punjab National Bank | Haryana |
| 5 | Jaipur-Nagaur Anchalik Gramin Bank | UCO Bank | Jaipur, Rajasthan |
A Legacy of Empowerment
These first five RRBs laid the groundwork for a nationwide network of RRBs that continue to play a vital role in rural India’s financial development. They serve as a testament to India’s commitment to bridging the urban-rural divide and empowering communities through financial inclusion.
Understanding Regional Rural Bank (RRB) Ownership
A Partnership for Progress
Regional Rural Banks (RRBs) in India operate under a unique ownership structure designed to leverage the strengths of various stakeholders. Here’s a breakdown of who owns RRBs:
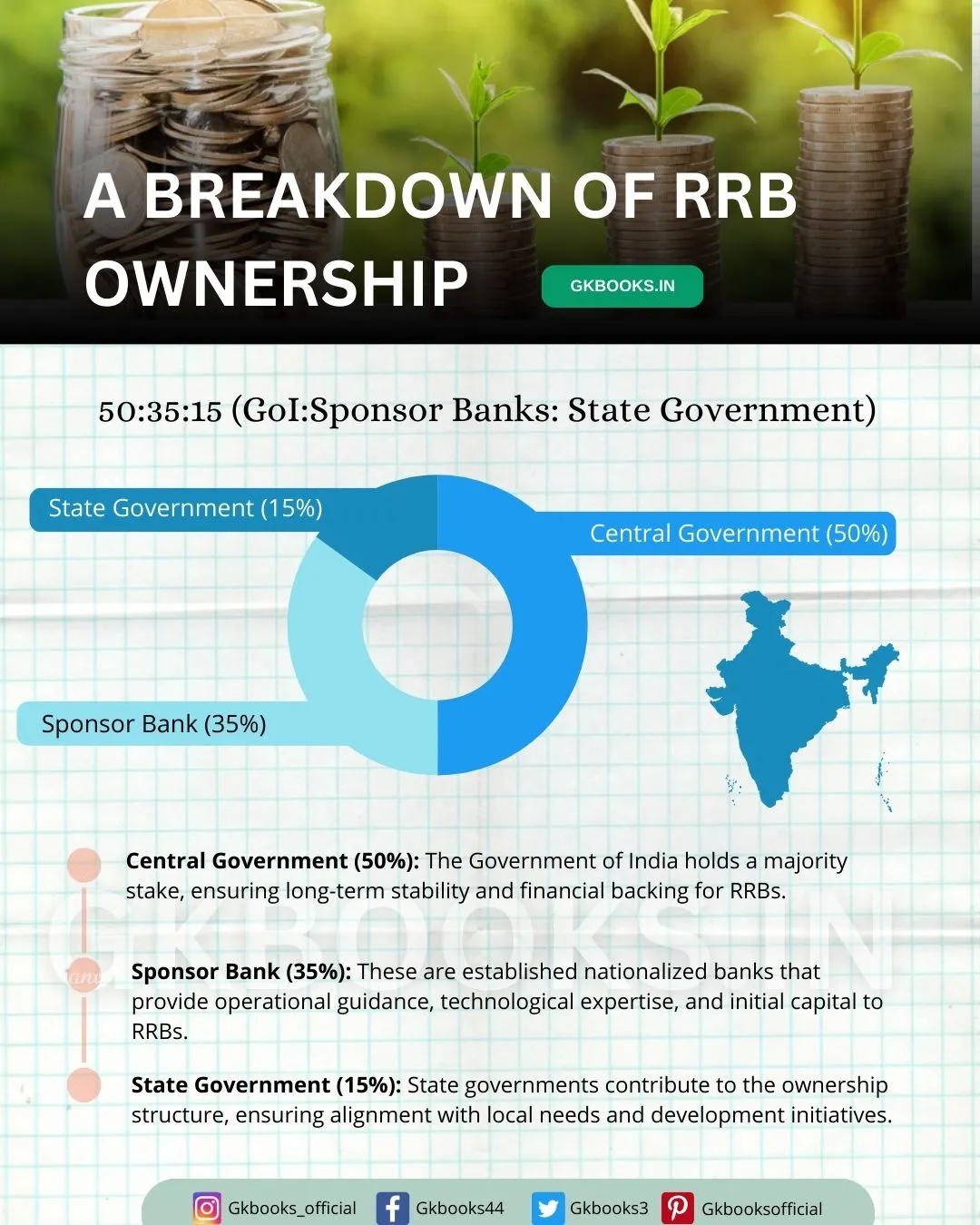
- Central Government (50%): The Government of India holds a majority stake, ensuring long-term stability and financial backing for RRBs.
- Sponsor Bank (35%): These are established nationalized banks that provide operational guidance, technological expertise, and initial capital to RRBs.
- State Government (15%): State governments contribute to the ownership structure, ensuring alignment with local needs and development initiatives.
Why This Tripartite Model?
This ownership structure fosters a collaborative approach:
- Government Support: Provides financial security and facilitates policy implementation for rural financial inclusion.
- Banking Expertise: Sponsor banks offer operational knowledge and best practices, ensuring efficient banking operations.
- Local Understanding: State government involvement ensures RRBs cater to the specific needs and priorities of their regions.
The Core Objectives of Regional Rural Banks (RRBs)
Regional Rural Banks (RRBs) are vital in bridging the financial gap between urban and rural India. But what are their primary goals? Let’s explore the key objectives of RRBs:
Financial Inclusion for All
- Expanding Banking Services: RRBs bring essential banking facilities like account opening, money transfers, and cash deposits to rural areas, empowering communities to manage their finances securely.
- Tailored Loan Products: Understanding the unique needs of rural borrowers, RRBs offer loans for agriculture, small businesses, and micro-enterprises, fostering entrepreneurship and local economic growth.
Supporting Agricultural Development
- Financing for Farmers: Small and marginal farmers, the backbone of Indian agriculture, often lack access to credit. RRBs provide loans for seeds, fertilizers, equipment, and irrigation, enabling them to improve yields and income.
- Financial Literacy Programs: Many RRBs conduct awareness programs to educate farmers about financial management and loan options, empowering them to make informed financial decisions.
Uplifting Rural Communities
- Meeting Diverse Needs: Beyond agriculture, RRBs cater to the credit requirements of rural artisans, self-employed individuals, and small businesses, promoting local economic diversification.
- Government Scheme Disbursement: RRBs streamline access to government benefits like pensions and MGNREGA wages for rural residents.
Digital banking solutions
Modern RRBs are leveraging technology to promote digital banking solutions like mobile and Internet banking, making banking services even more accessible in remote locations.
The Impact of RRBs
By focusing on financial inclusion, agricultural development, and overall rural upliftment, RRBs contribute significantly to India’s economic and social progress.
Features and Benefits of Regional Rural Bank
Regional Rural Banks (RRBs) are a unique banking initiative in India specifically designed to serve the financial needs of rural populations. But what sets them apart? Here’s a breakdown of their key features and the benefits they offer:
Rural Focus
- Unlike traditional banks concentrated in urban areas, RRBs have a widespread network of branches in villages and smaller towns, ensuring easy access to banking services for rural communities.
Customized Financial Solutions
RRBs understand the specific needs of rural borrowers. They offer loans for:
- Agriculture: Supporting farmers with loans for seeds, fertilizers, equipment, and irrigation.
- Microfinance: Providing small loans to entrepreneurs for starting or expanding businesses.
- Artisanal Enterprises: Catering to the credit requirements of rural artisans and craftspeople.
Supporting Local Development
RRBs contribute to rural economic growth by:
- Financial Inclusion: Expanding access to banking services like savings accounts and money transfers, empowering rural residents to manage their finances effectively.
- Priority Sector Lending: Directing a significant portion of their credit towards agriculture and other priority sectors crucial for rural development.
Strong Backing
Sponsored by established nationalized banks, RRBs benefit from:
- Financial Stability: The backing of a larger bank ensures access to resources and financial expertise.
- Operational Efficiency: Sponsor banks provide guidance and best practices for smooth banking operations.
Evolving with Technology
- Many RRBs promote digital banking solutions like mobile banking and Internet banking, making banking services even more accessible in remote locations.
The Regulatory Framework for Regional Rural Banks (RRBs) in India
Regional Rural Banks (RRBs) in India play a vital role in financial inclusion for rural communities. But who ensures they operate effectively and responsibly? Here’s a breakdown of the regulatory framework:
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI): The Overarching Authority
As the central bank of India, the RBI holds the ultimate authority over the entire banking system, including RRBs.
The RBI’s role encompasses:
- Licensing and Authorization: Granting licenses to RRBs and approving their establishment.
- Prudential Regulation: Setting guidelines for RRBs on capital adequacy, liquidity, and risk management practices to ensure financial stability.
- Monetary Policy: Implementing monetary policies that indirectly impact RRBs’ lending rates and overall economic environment.
✅ Related Post: RBI Governors List from 1935 to 2024: Name, Eligibility, Powers, Tenure Complete Guide
NABARD: The Dedicated Rural Financial Supervisor
The National Bank for Agriculture and Rural Development (NABARD) is a specialized regulator for RRBs (and Rural Cooperative Banks).
NABARD’s focus areas include:
- Conducting Inspections: Regularly evaluate RRBs’ financial health, adherence to regulations, and corporate governance practices.
- Promoting Financial Inclusion: Encouraging RRBs to expand their reach and develop financial products tailored to meet the needs of rural populations.
- Supervising Rural Credit Delivery: Ensuring RRBs allocate a significant portion of their credit towards priority sectors like agriculture and allied activities.
The Benefits of Dual Regulation
This two-pronged approach fosters a robust regulatory framework for RRBs:
- Stability and Oversight: The RBI’s overarching role ensures financial stability and adherence to broader banking regulations.
- Rural Focus: NABARD’s specialized expertise promotes financial inclusion and credit delivery specifically targeted towards rural development.
Key points about regional rural banks in India
- Regional Rural Banks (RRBs) are government-owned scheduled commercial banks in India.
- As the name suggests, Regional Rural Banks operate at a regional level in rural areas.
- They are owned by the Government of India (Ministry of Finance), a Sponsored Bank, and the concerned State Government in a ratio of 50:35:15 respectively.
- During the tenure of Indira Gandhi’s government, RRBs were set up on the recommendations of the Narasimhan Committee on Rural Credit.
- As of 2024, 43 Regional Rural Banks are operating across India.
- Prathama Bank, headquartered in Moradabad, Uttar Pradesh, is India’s first regional rural bank.
- Uttar Pradesh has the highest number of RRBs in India.
- The National Bank for Agriculture and Rural Development (NABARD) regulates regional rural and apex cooperative banks throughout India.
Regional Rural Banks (RRBs) in India: A Summary
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Established | 2 October, 1975 |
| Purpose | Provide financial inclusion and banking services to rural communities in India. |
| Ownership | 🔸 Central Government (50%) 🔸 Sponsor Bank (35%) 🔸 State Government (15%) |
| Regulatory Bodies | 🔸Reserve Bank of India (RBI) 🔸National Bank for Agriculture and Rural Development (NABARD) |
| Key Functions | 🔸Offer savings accounts, loans (agriculture, microfinance, etc.), money transfers, and other banking services. 🔸Promote financial inclusion in rural areas. 🔸 Support agricultural development and rural businesses. |
| Benefits | 🔸 Increased access to banking services for rural communities. 🔸 Financial support for farmers, small businesses, and entrepreneurs in rural areas. 🔸Contributes to rural economic development. |
| Recent Developments | 🔸 Consolidation of RRBs to improve efficiency and financial health. 🔸 Increased focus on digital banking solutions for wider reach. |
| Number of RRBs (as of 2024) | 43 |
| Branch Network | Over 21,800 branches across rural and semi-urban areas in India. |
| Target Clientele | Small and marginal farmers, agricultural laborers, artisans, micro-entrepreneurs, and residents in rural areas. |
FAQs on Regional Rural Banks
In RRBs, a 15% stake is held by the state government, 50% by the central government, and 35% by the sponsor bank.
The authorized capital of each RRB is to be Rs five crore.
Answer: 43 (As of 2024)
Like other public sector Banks, RRBs are established by the Government of India and are scheduled & notified by the Reserve Bank of India.
It provides basic banking facilities in rural areas like locker facilities, debit and credit cards, mobile banking, internet banking, and UPI services.
Regional Rural Banks were set up in 1975.
Regional Rural Banks were set up based on the recommendations of the Narasimham Committee.
The Prathama Grameen Bank was the first bank established on 02nd October 1975.
Regional Rural Banks (RRBs) operate under the supervision of NABARD (National Bank for Agriculture and Rural Development)
Regional Rural Banks have been termed as small man’s banks.
Source:
- Wikipedia
- Indian Economy Nitin Singhania (Text Book)