Here is a brief description of “Types of Fruits and Their Edible Parts”. Several questions arise from this topic in various competitive exams, such as whether apples are real or false fruit. What are the edible parts of litchi? What is the name of the structural part of the fruit?
Introduction
• Fruits are nutritious and tasty seed-bearing edible structures found in flowering plants.
• Fruits are how flowering plants (angiosperms) disperse their seeds.
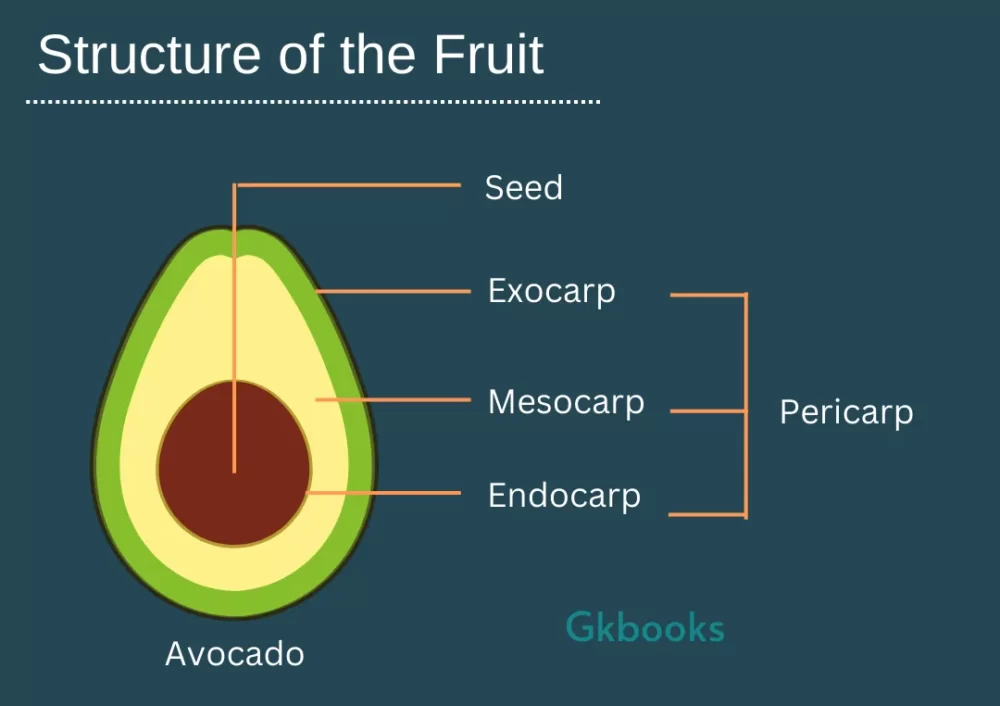
Structure of the Fruit
• Fruit is a mature or ripened ovary, which develops after fertilization.
• The fruit consists of a wall or pericarp and seeds.
• Seed surrounded by pericarp. The pericarp may be dry or fleshy.
• When the thick and fleshy pericarp is differentiated into outer epicarp, middle mesocarp, and inner endocarp.
Seedless Fruits
• Seedlessness is an important characteristic of some fruits of commercial importance.
• Bananas and pineapples are examples of seedless fruits.
• Seedlessness is the result of parthenocarpy.
• If a fruit is formed without fertilisation of the ovary, it is called a parthenocarpic fruit.
• Nowadays induced parthenocarpy is applied for the commercial production of various fruits (eg seedless watermelon).
How do you remember the Endocarp, Mesocarp, and Exocarp?
This is very easy to remember. Check out the tricks below
♦ Exocarp – EX (First 2 Letters) – Exit (Outer Cover)
♦ Mesocarp – M (First letter ) – Middle (In Between Exocarp and Endocarp)
♦ Endocarp – EN (First 2 Letters) – Enter (Inner Side)
Types of Fruits
Based on the fertilization of the flowers, fruit is classified as True Fruits and False Fruits.
• True Fruits: Fruit forms in the flower’s ovary through fertilization. E.g. Strawberry.
• False Fruits: Fruits derived from floral parts other than the ovary. such as calyx, thalamus, corolla, etc. E.g. pear, apple, etc.
Further, In terms of verities and diversities, fruits are classified as Simple, Aggregate, and Multiple.
• Simple fruit: Simple fruits are either fleshy (such as gooseberry, tomato, etc.) or dry (such as coconut, walnut, etc.)
• Aggregate fruit: Fruit that develops from merging several ovaries separated in a single flower. E.g. Raspberry.
• Multiple fruit or collective fruits: It is formed from a cluster of flowers (known as inflorescence). Each flower in the inflorescence produces a fruit, but they mature into a single mass. e.g. Pineapple, Mulberry, etc.

Fruits and their Edible Parts
Simple Fruits
| Sl.No | Simple Fruits | Scientific Name | Type | Edible Parts |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Watermelon | Luffa aegyptiaca | Pepo | Mesocarp and endocarp |
| 2 | Sweet orange | Punica granatum | Pepo | Endocarpic juicy hair |
| 3 | Muskmelon | Cucumis melo | Pepo | Mesocarp and endocarp |
| 4 | Bottle gourd | Lagenaria siceraria | Pepo | Mesocarp and endocarp |
| 5 | Long Melon | Citrus sinensis | Pepo | Entire fruit |
| 6 | Smooth Gourd | Cucumis sativus | Pepo | Mesocarp and endocarp |
| 7 | Wheat | Triticum aestivum | Cryopis | Endosperm and Embryo |
| 8 | Maize | Zea mays | Cryopis | Endosperm and Embryo |
| 9 | Rice | Oryza sativa | Cryopis | Endosperm and Embryo |
| 10 | Strawberry | Fragaria ananassa | Etaerio of achenes | Fleshy Thalamus and Seeds |
| 11 | Lotus | Nelumbo nucifera | Etaerio of achenes | Fleshy Thalamus and Seeds |
| 12 | Jack Fruit | Artocarpus heterophyllus | Sorosis | Fleshy axis, bracts, perianth and seeds |
| 13 | Tomato | Solanum lycopersicum | Berry | Pericarp & Placenta |
| 14 | Litchi | Litchi chinensis | Nut | Fleshy aril |
| 15 | Banana | Musa paradisiaca | Berry | Mesocarp & Endocarp |
| 16 | Brinjal | Solanum melongena | Berry | Pericarp and Placenta |
| 17 | Coconut | Cocos nucifera | Drupe | Endosperm, Testa, Cotyeldon and embryo |
| 18 | Almond | Prunus dulcis | Drupe | Seeds |
| 19 | Cashew nut | Anacardium occidentale | Nut | Cotyledons and fleshy pedicel |
| 20 | Water chestnut | Eleocharis dulcis | Nut | Cotyledons and aril |
| 21 | Bean | Phaseolus vulgaris | Legume | Seeds on ripening |
| 22 | Pea | Pisum sativum | Legume | Seeds on ripening |
| 23 | Tamarind | Tamarindus indica | Lomentum | Mesocarp |
| 24 | Lady’s finger | Abelmoschus esculentus | Capsule | Pericarp and seeds (entire fruit) |
| 25 | Groundnut | Arachis hypogaea | Lomentum | Seed |
| 26 | Mango | Mangifera indica | Drupe | Fleshy Mesocarp |
| 27 | Walnut | Juglans regia | Drupe | Cotyledons |
Aggregate fruits
| Sl.No | Fruits | Scientific Name | Type | Edible Parts |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Strawberry | Fragaria ananassa | Etaerio of achenes | Fleshy Thalamus and Seeds |
| 2 | Lotus | Nelumbo nucifera | Etaerio of achenes | Thalamus and Seeds |
| 3 | Raspberry | Rubus idaeus | Etaerio of drupes | Thalamus |
| 4 | Custard apple | Anona squamosa | Etaerio of berries | Mesocarp |
Composite fruits
| Sl. No | Fruits | Scientific Name | Type | Edible Parts |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Pine Apple | Ananas sativus | Sorosis | Peduncle, bracts, perianth |
| 2 | Jack Fruit | Artocarpus heterophyllus | Sorosis | Fleshy axis, bracts, perianth and seeds |
| 3 | Mulberry | Morus alba | Sorosis | Fleshy axis and Succulent perianth |
| 4 | Fig | Ficus carica | Syconus | Peduncle and Seeds |
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Answer: Fleshy aril
Answer: Mesocarp
Answer: Juicy placental hairs
Answer: Apple
Answer: Banana

