Discover the origins of high-level programming languages and their creators on Computer GK. Gain knowledge about the visionaries who shaped the programming landscape. Begin your exploration now!
What is high-level language?
A high-level language is a programming language designed to be easily understood and used by humans.
It uses English-like words and symbols to represent concepts rather than the binary code that computers understand. It provides a level of abstraction that is closer to natural language.
This makes high-level languages much easier to learn and use than low-level ones, closer to the machine code that computers understand. It allows programmers to write code in a more intuitive and readable manner.
High-level languages are characterized by their use of variables, data structures, control structures (such as loops and conditionals), and built-in functions or libraries that simplify everyday programming tasks.
They often have extensive standard libraries that provide pre-written code (such as Python Standard Library) for various operations, reducing the need for manual implementation.
Examples of High-level language
Some of the most popular high-level languages include:
- Python
- Java
- C++
- C#
- JavaScript
- PHP
- Ruby
- Swift
- Kotlin
High-level languages are often used to develop software, web, and mobile applications. They are also used in data science, machine learning, and artificial intelligence.
✅ Types of Application Software in Computers with Examples
High-Level Programming Languages and Their Discoverer
Here is a table of the most common high-level computer languages, along with the year they were created and the names of their discoverers:
| Language | Year | Discoverer |
|---|---|---|
| Fortran | 1957 | John Backus |
| COBOL | 1959 | Grace Hopper |
| Lisp | 1958 | John McCarthy |
| BASIC | 1964 | John Kemeny and Thomas Kurtz |
| Pascal | 1970 | Niklaus Wirth |
| C | 1972 | Dennis Ritchie |
| C++ | 1983 | Bjarne Stroustrup |
| Java | 1995 | James Gosling |
| Python | 1991 | Guido van Rossum |
✅ Generation of Computer 1st to 5th with Examples, Features & Tables
Important Facts about High-level Programming Language
▪ Fortran was the first high-level programming language to be widely used. It was initially developed for scientific and engineering applications, but it is now used for various tasks.
▪ COBOL is another early high-level language that was designed for business applications. It is still widely used today, especially in the financial industry.
▪ Lisp is a very powerful language often used for artificial intelligence and functional programming. Although it is not as widely used as some other languages, it has a loyal following among programmers.
▪ BASIC was one of the first high-level languages for personal computers. It is still a popular language for teaching programming but is not as widely used for commercial applications as other languages.
Plankalkül, created by Konrad Zuse, is often regarded as the first high-level programming language designed for computers. However, due to World War II and other circumstances, Plankalkül was not implemented during Zuse’s time.
▪ Pascal is a structured language designed to be easy to learn and use. It is often used for teaching programming and some commercial applications.
▪ C is a powerful and versatile language used for various tasks, including operating systems, compilers, and embedded systems.
▪ C++ is a successor to C that adds object-oriented features. It is a prevalent language for commercial applications.
▪ Java is a general-purpose language designed to be portable and secure. It is very popular for web development and mobile applications.
▪ Python is a general-purpose language known for its simplicity and readability. It is popular for scripting, data science, and machine learning.
✅ List of Computer Abbreviations with SSC MCQs (Updated List)
Advantages and Disadvantages
Advantages of High-level Language
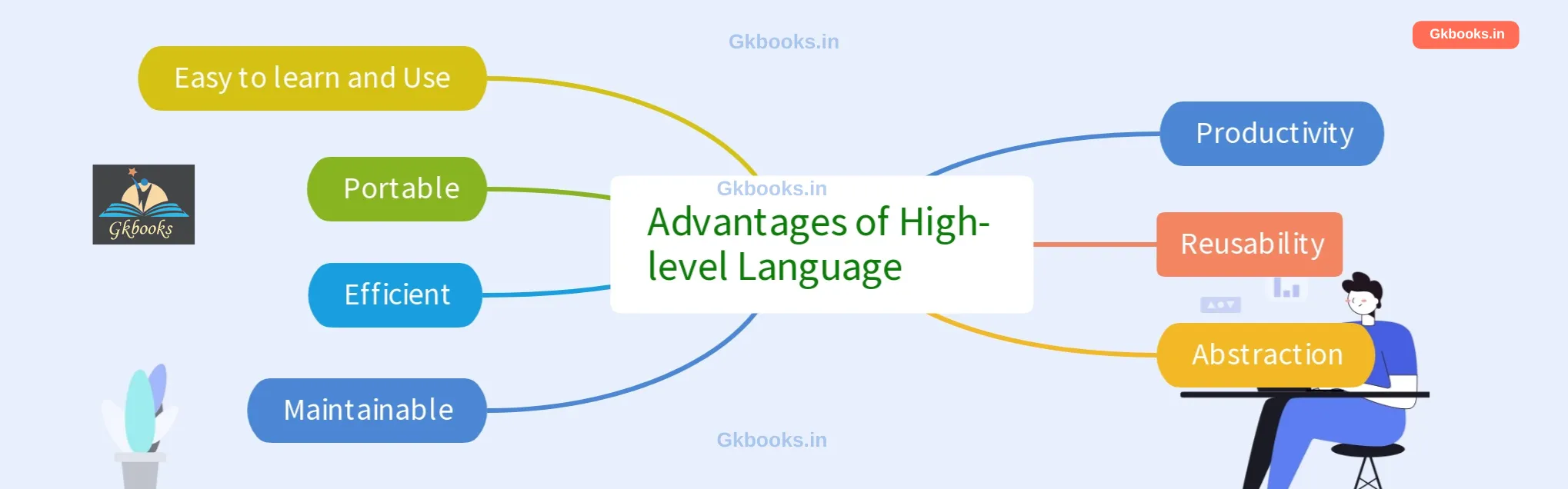
High-level languages offer several advantages over low-level languages. Here are some of the most important advantages:
- Easy to learn and Use: High-level languages use English-like words and symbols, which makes them much easier to learn and use than low-level languages, which use binary code.
- Portable: High-level languages are designed to be portable, meaning they can be run on different types of computers. This makes them ideal for developing software that needs to be used on various platforms.
- Efficient (for programmer time): High-level languages can help programmers write more compact code by abstracting away the details of the underlying hardware. This allows programmers to focus on the program’s logic and can improve development speed. It’s important to note that high-level languages might not always be the most efficient in terms of raw execution speed compared to low-level languages.
- Maintainable: High-level languages often use more abstract concepts, which makes it easier to understand and modify the code, leading to better maintainability.
- Productivity: High-level languages allow programmers to write code that is easier to read, write, and debug, leading to greater productivity.
- Reusability: High-level languages often come with libraries of pre-written code that programmers can reuse, saving them a lot of time and effort.
Overall, high-level languages offer several advantages over low-level languages. They are easier to learn and use, more portable, maintainable, and promote programmer productivity and code reusability. However, they can be slower and less flexible than low-level languages.
Disadvantages of High-level Languages
High-level languages, while powerful, come with some drawbacks compared to low-level languages:
- Slower execution speed: High-level languages need translation into machine code before execution. This translation process can add overhead, slowing down the program compared to directly written machine code.
- Less flexibility: Designed for a wider range of tasks, high-level languages might offer less flexibility for extreme optimization. This can impact execution speed for very specific tasks.
- More complex code: The syntax of high-level languages can be more intricate than low-level ones. This can make the code harder to read and understand, potentially extending debugging time.
- More memory usage: High-level languages often require storing translated code, leading to increased memory usage compared to low-level languages. This can be a concern for devices with limited memory.
- Less control over hardware: Abstraction is a benefit of high-level languages but also reduces direct control over the hardware. This can be a disadvantage in situations where fine-grained hardware control is necessary.
- Debugging challenges: While modern debuggers help, the translated code from high-level languages can still be more complex, posing debugging challenges compared to low-level code that directly maps to machine operations.
- Portability considerations: High-level languages themselves can be portable across different systems. However, the runtime environment they rely on (interpreters or compilers) might not be as portable, potentially limiting use on specific platforms.
High-level languages are the dominant choice for most programming due to their ease of use, portability (to a degree), and efficiency balance. However, understanding these limitations helps you choose the right tool for the job, especially when performance or hardware interaction becomes critical.
Difference between High-level language and Low-level language
The following table summarizes the differences between high-level language and low-level language:
| Features | High-Level Language | Low-Level Language |
|---|---|---|
| Abstraction | Provides a high level of abstraction, closer to human language. | Provides a low level of abstraction, closer to machine code. |
| Readability | More readable and understandable by humans. | Less readable and understandable by humans. |
| Portability | Portable across different platforms and operating systems. | Less portable, often specific to a particular computer architecture. |
| Development Time | Requires less time and effort for development. | Requires more time and effort for development. |
| Memory Management | Automatic memory management (garbage collection) is usually provided. | Manual memory management is required. |
| Code Efficiency | Generally less efficient in terms of execution speed and memory usage. | More efficient in terms of execution speed and memory usage. |
| Error Handling | Better error handling and debugging capabilities. | Limited error handling and debugging capabilities. |
| Programming Skills | Requires less technical knowledge and expertise. | Requires more technical knowledge and expertise. |
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Dennis Ritchie developed the high-level programming language C at Bell Laboratories in the early 1970s.
A compiler is a software application that converts a program written in a high-level language into the machine language understood by a computer.
A high-level programming language is designed to be moderately easy for humans to read and write. It is typically more relative to human languages than machine languages and uses abstractions to represent concepts that are difficult to express in machine code.

