In competitive exams, the subject of computer fundamentals is often overlooked as it typically only comprises a small portion of the test. However, the questions that are asked on this subject are relatively simple and can be easily answered with proper preparation.
To assist you in your studies, we have compiled a collection of detailed notes on the generation of computers. By reviewing these notes, you will be able to gain a deeper understanding of the subject and increase your chances of success in your exam. Don’t overlook the importance of computer fundamentals, take the time to review your notes and give yourself an edge in the exam
Introduction
- In the present era, the term “generation” in computer terminology refers to both hardware and software components of a computer system.
- However, in the past, the term was primarily used to distinguish between different advancements in hardware technology.
- It was used to differentiate between various hardware technologies in the computer industry.
- In the past, when modern computing tools such as graphing calculators, spreadsheets, and computer algebra systems were not yet available, mathematicians and inventors relied on mechanical calculators to ease the computational workload.
- These mechanical calculators were used to perform mathematical operations and were essential tools for performing complex calculations.
▪ 8 Mechanical Calculators Before the Invention of the Modern Computer.
- Abacus (ca. 2700 BC)
- Pascal’s Calculator (1652)
- Stepped Reckoner (1694)
- Arithmometer (1820)
- Comptometer (1887) and Comptograph (1889)
- The Difference Engine (1822)
- Analytical Engine (1834)
- The Millionaire (1893)
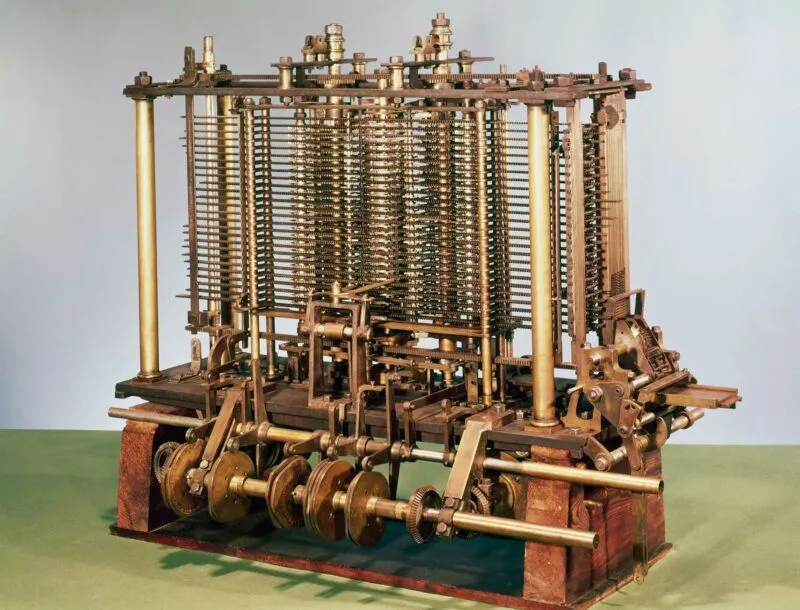
- The early computers were not as technologically advanced as the current ones. However, with time, computers have undergone significant improvements in terms of speed, accuracy, size, and cost.
- This long period of evolution is often classified into different stages known as computer generations. These generations reflect the advancements made in computer technology over time.
Generation of Computer 1st to 5th with examples
- There are five computer generations known to date. Each generation has been discussed in detail along with its period and characteristics.
- First Generation Computers (1940-1956)
- Second Generation Computers (1956-1963)
- Third Generation Computers (1964-1971)
- Fourth Generation Computers (1971-Present)
- Fifth Generation Computers (Present and Beyond)
Let’s take a look at the history of computer generation.
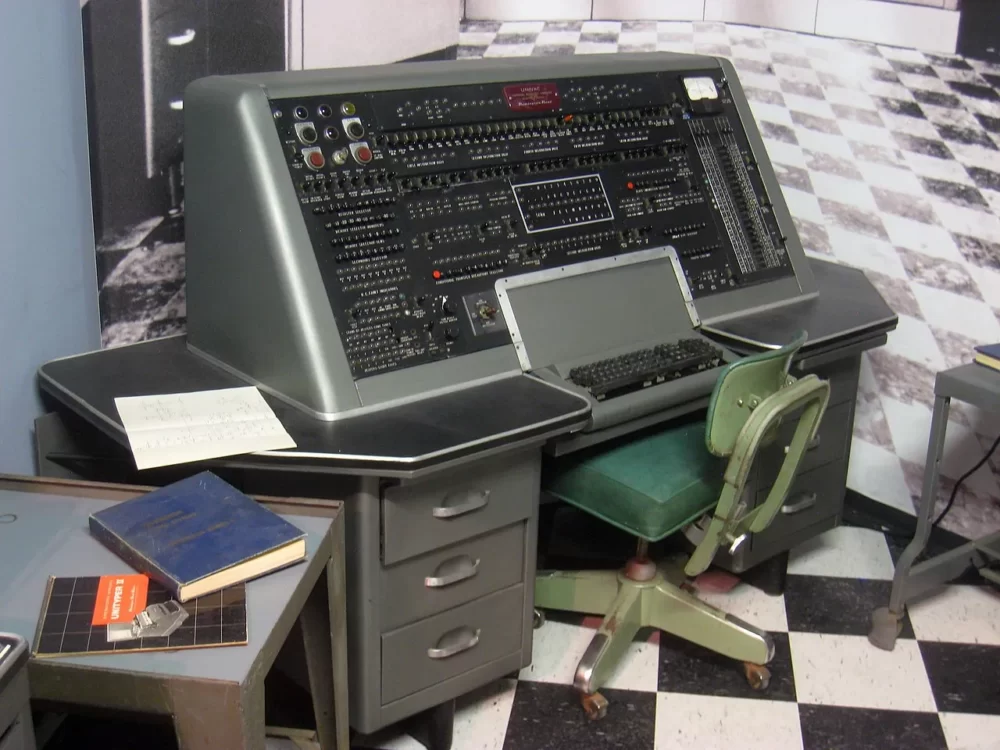
First Generation of Computers (1940-1956)
- The first generation of computers was based on vacuum tubes.
- The period of the first-generation Computer is 1940-1956.
Examples of first-generation computers
- ENIAC
- EDVAC
- UNIVAC
- IBM-750
- UNIVAC-1 (Universal Automatic Computer)

Main features of the First-Generation Computer
- Based on Vacuum tube technology
- Used machine language only
- Very costly
- Produced a lot of heat
- Consumed Huge size
- Need AC for cooling
- Consumes a lot of electricity
- Unreliable
- Non-portable (Large size)
- Slow Input / Output process

✳️ Read More: Know More About the First Generation of Computers: Full Details, Examples
2nd Generation of Computer (1956-1963)
- Computers of this generation used transistors.
- It supported assembly language as well as high-level programming languages like FORTRAN, and COBOL.
Examples of second-generation computers are
- IBM 1400 series
- IBM 1620
- IBM 7094 series
- CDC 1604
- CDC 3600
- UNIVAC 1107

The main features of the second generation are:
- Transistors-based computer
- It Supported machine and assembly languages.
- Generates less heat as compared to first-generation computers.
- Smaller size as compared to first-generation computers.
- Consumed less electricity as compared to first-generation computers
- Faster than first-generation computers
- Reliable compares to first-generation computers.
- Still very costly
- AC required for cooling

3rd Generation of Computer (1964-1971)
- Third-generation computers are based on Integrated Circuits (ICs).
- It supported remote time-sharing, processing, and multi-programming operating systems.
- Large magnetic core, magnetic tape/disk type memory used in this generation of computers.
- List of High-level languages used in this generation:
– FORTRAN-II
– COBOL
– PASCAL PL/1
– BASIC
– ALGOL-68
Examples of third-generation computer
- UNIVAC 1108
- UNIVAC AC 9000
- IBM-370/168
- IBM-360 series
- Honeywell-6000 series
- PDP (Personal Data Processor)
- TDC-316

The main features of the third generation are:
- Based on Integrated Circuits (ICs).
- More reliable than 1st and 2nd generations.
- More Smaller sizes.
- Produced less heat compared to previous generations.
- Faster than vacuum tubes and Transistor-based computers.
- Lesser maintenance
- Costly
- AC required
- Consumed lesser electricity
- Supported high-level language
4th Generation Computers (1971-1980)
- Fourth-generation computers are based on Very Large Scale Integrated (VLSI) circuits.
- This generation of computers, supported time-sharing, real-time networks, and distributed operating systems were used.
- All the high-level languages like C, C++, DBASE, etc., were used in this generation.
- Fourth-generation computers were built between 1971 to 1980.
- It uses semiconductor memory such as RAM (Random Access Memory) and ROM (Read Only Memory) etc.
Examples of Fourth generation computers
- Apple Macintosh
- IBM PC
- DEC 10
- STAR 1000
- PDP 11
- CRAY-1 (Super Computer)
- CRAY-X-MP (Super Computer)

▪ The Apple Macintosh was introduced on January 24, 1984 by former Apple CEO Steve Jobs. ▪ It was equipped with a 9-inch black and white display, an 8MHz Motorola 68000 processor, 128KB of RAM, a 3.5-inch floppy drive.
The main features of fourth-generation computers
- Based on VLSI technology
- Very cheap
- Use of Personal Computers
- Very small size
- Semiconductor memory (ROM, RAM)
- Pipeline processing
- Portable and reliable
- No AC required
- The concept of the internet was introduced.
5th Generation of Computer (1980 to till date)
- Fifth-generation computers are based on Ultra Large Scale Integration (ULSI) technology.
- This generation supports Parallel processing hardware and AI (Artificial Intelligence) software.
- All the high-level languages like C and C++, Java, .Net, etc., are used in this generation.
- Since it supports AI technology, it can understand natural language or human language.
Examples of fifth-generation Computers
- Desktop
- Laptop
- Notebook
- Ultrabook
- Chromebook
The main features and Characteristics of fifth-generation computers
- Based on ULSI (Ultra Large Scale Integration) technology
- True artificial intelligence
- Multimedia features
- Development of Natural language processing
- More user-friendly interface
- Advancement in Parallel Processing
- Advancement in Superconductor technology
- Faster Solid State Drive (SSD) memory, It is faster than Hard Disk Drives (HDD).
- Availability of very powerful and compact computers at cheaper rates.
Comparing Computer Generations: A Comprehensive Overview
| Generation of Computer | Main Electronic Component | Programming Language | Main Memory | Example |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1st Generation | Vacuum tube | Machine Language | Magnetic tapes and magnetic drums | IBM 750, IBM 701, ENIAC, UNIVAC |
| 2nd Generation | Transistor | Machine language and assembly language | Magnetic core and magnetic tape/disk | IBM 1400 series, IBM 7090 and 7094, UNIVAC 1107, CDC 3600 |
| 3rd Generation | Integrated circuits (ICs) | High-level language | Large magnetic core, magnetic tape/disk | IBM 360, IBM 370, PDP, B6500, UNIVAC 1108, UNIVAC AC 9000 |
| 4th Generation | Very large-scale integration (VLSI) | semiconductor memory (such as RAM, ROM, etc.) | High-level language | IBM PC, STAR 1000, Apple Macintosh, Alter 8800 |
| 5th Generation | Ultra Large-Scale Integration (ULSI), Aartificial intelligence (AI) | Faster Solid State Drive (SSD) memory | Understand natural language or human language | Notebook, Desktops, laptops, tablets, smartphones |
Frequently Asked Questions
Fifth-generation computers are based on Ultra Large Scale Integration (ULSI) technology.
Fifth-generation computers are based on Ultra Large Scale Integration (ULSI) technology.
Some examples of first-generation computers are ENIAC, EDVAC, UNIVAC
• Notebooks
• Desktop PCs of Pentium
• Workstations of SUN.
• IBM SP/2.
• IBM 1400 series
• IBM 1620
• IBM 7094 series
• CDC 1604
• CDC 3600
• UNIVAC 1108
• Transistors-based computer
• It Supports machine and assembly languages.
• Generates less heat as compared to first-generation computers
• Smaller size as compared to first-generation computers
• Consumed less electricity as compared to first-generation computers
• Faster than first-generation computers
• Reliable compares to the first generation computers.
• Still very costly
• AC required for cooling
1949-1965
Discover More Computer Awareness:
6 Types of Network Topologies With Diagram: Computer Awareness
Unveiling DeepSouth: The World’s First Human Brain-Scale Supercomputer
Exploring the First Generation of Computers: Full Details, Examples
Computer Storage Devices and Their Storage Capacity: Computer Awareness
High-Level Programming Languages and their Discoverer: Computer GK
Guided Media in Computer Network: Types, Applications, Advantages, Disadvantages