Have you ever wondered how many different types of computers there are? From personal computers to laptops to tablets, there is a computer out there for everyone.
In today’s technology-driven era, computers have become essential tools, seamlessly integrating into every aspect of our lives. From powering businesses to shaping our entertainment, these versatile machines have revolutionized how we communicate, learn, and work.
Understanding the diverse types of computers and their applications is crucial for navigating the digital landscape effectively. Whether you’re an aspiring tech enthusiast or preparing for competitive exams like UPSC, RRB NTPC, SSC, or other state-level exams, this comprehensive guide will equip you with the knowledge you need to excel in the digital realm.
In this blog post, we will look at the different types of computers and their functions. Some sample questions are answered at the end of the article to give you an idea of the types of questions that come from this topic.
Introduction
- The abacus was the first calculating tool and was one of the first inventions that led to the first computer. In the present era, there has been a great change in computer technology. Today we can choose computers with different features according to our work.
- For example, Weather forecasting requires supercomputers.
What is a Computer?
- A computer is a digital electronic device that takes data from the user and converts the data into meaningful information. It automatically carries the function through a sequence of arithmetic or logical operations (calculations).
Read Also: Exploring the First Generation of Computers: Full Details, Examples
What are the 7 Types of Computers?
Based on size usage and applications computers can be classified into 7 categories: Such as:
- PC (Personal Computer)
- Supercomputer
- Mainframe computer
- Minicomputer
- Workstation
- Servers
- Embedded Systems
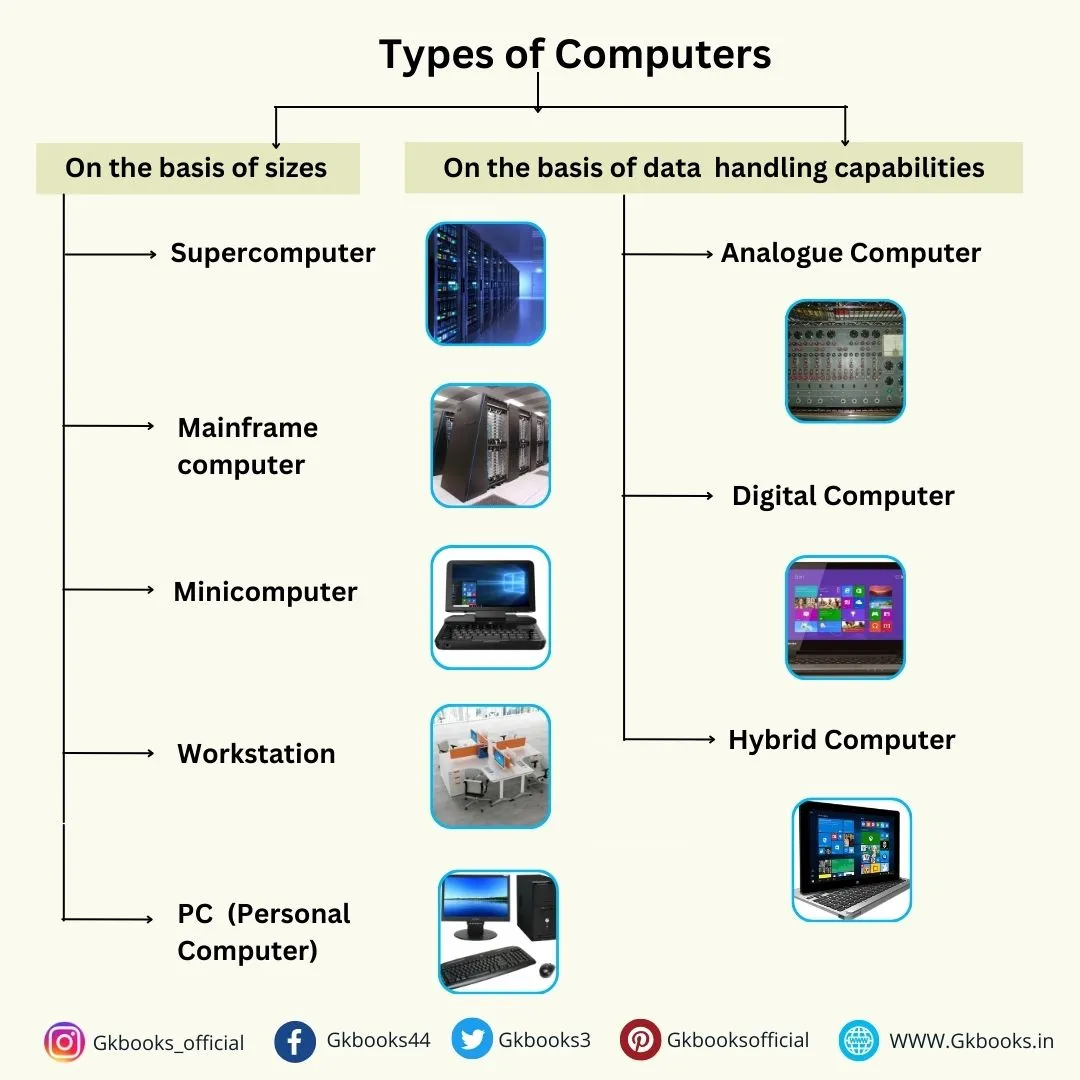
Also, Computers can be classified in two ways based on their different types and sizes and their data-handling capabilities.
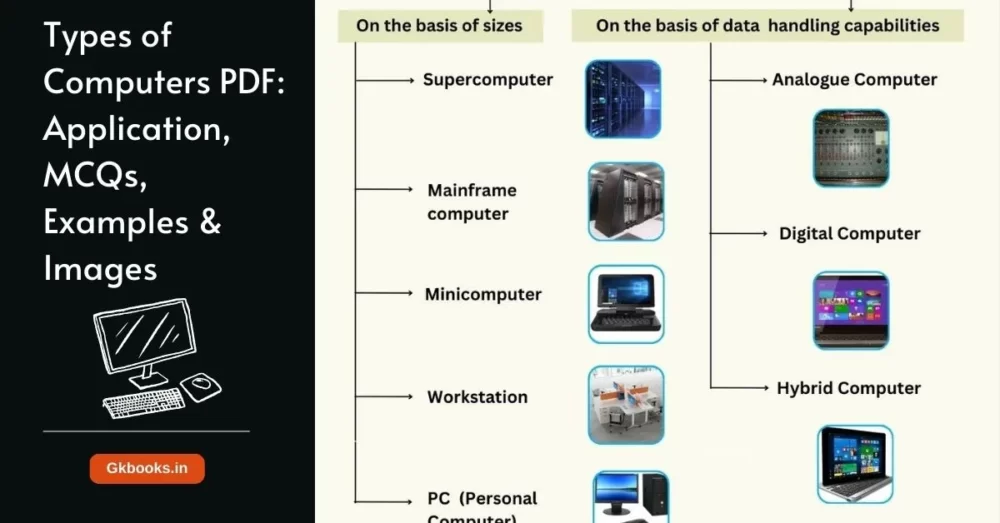
Types of Computers on the basis of sizes
• On the basis of size, there are five types of computers:
- Supercomputer
- Mainframe computer
- Minicomputer
- Workstation
- PC (Personal Computer)
Types of computers on the basis of data handling capabilities
• There are three types of computers in terms of data handling capabilities.
- Analogue Computer
- Digital Computer
- Hybrid Computer
Read Also: Unraveling the Fascinating History of Computer Invention
Details about all the types of computers
Supercomputer
- They are the biggest and fastest computers(in terms of speed of processing data).
- They are designed to handle large amounts of data, such as processing trillions of instructions in one second.
- A supercomputer consists of thousands of interconnected processors that help execute user instructions very quickly.
- The first supercomputer was built by Roger Cray in 1976.
Characteristics of supercomputers
- Data processing speed is very fast.
- These are Very expensive
- It can perform up to ten trillion distinct calculations each second.
- Super Computers are used in large organizations to manage a huge amount of data, such as the Stock market.
- It is used in various scientific research and development to analyze data obtained from the exploration of solar systems, satellites, etc.
- Supercomputers perform resource-intensive calculations that general-purpose computers cannot handle. They often run engineering and computational science applications, such as the following:
What are supercomputers used for?
Supercomputers are widely used in the following fields.
- Weather forecasting: To predict extreme storms and floods’ impact and affected areas.
- Oil and gas exploration: To collect huge quantities of geophysical seismic data to aid in finding oil reserves.
- Molecular modelling: For calculating and analyzing the structures and properties of chemical compounds and crystals.
- Physical simulations: Physical simulations like modelling supernovas and the birth of the universe.
- Aerodynamics: Used in designing cars with the lowest air drag coefficient.
- Nuclear fusion: Research to develop a nuclear fusion reactor that extracts energy from plasma reactions.
- Medical research: To develop new cancer drugs, understand genetic factors that contribute to opioid addiction, and find treatments for COVID-19.
- Next-generation materials identification: To find new materials for manufacturing.
- Cryptanalysis: Analyzing ciphertexts, cyphers, and cryptosystems to understand how they work and identify ways to defeat them.
Mainframe computer
- A mainframe computer is not as large as a supercomputer.
- It has higher processing power than some classes of computers such as minicomputers, servers, workstations, and personal computers.
- Mainframe computers are designed to support hundreds or thousands of users at the same time.
- It also supports multiple programs simultaneously. So, they can carry out different processes simultaneously.
- A mainframe computer is ideal for large organizations like banking, telecom sectors, etc., which generally process a high volume of data.
Characteristics of mainframe computers
- It is also an expensive computer.
- It has a high storage capacity and great performance.
- It can quickly process a huge amount of data (like data involved in the banking sector).
- It runs smoothly for a long period of time.
- Its lifespan is also long.
Read Also: Computer Storage Devices and Their Storage Capacity
Minicomputer
- A minicomputer is a class of small general-purpose computers developed in the mid-1960s.
- A minicomputer is a medium size multiprocessing computer.
- In this type of computer, there are two or more processors.
- It supports up to 200 users at a time.
- Minicomputers are used in different work like billing, accounting, inventory management, etc.
- It is smaller than a mainframe computer but larger in comparison to the microcomputer.
Characteristics of a minicomputer
- Its weight is low.
- Because of its low weight, it is easy to carry anywhere.
- It is less expensive than a mainframe computer.
- Faster than Workstation.
Workstation
- A workstation is a special-purpose computer system designed for technical or scientific applications.
- It consists of a fast microprocessor, with a large amount of RAM and a high-speed graphic adapter.
- They are usually connected to local area networks and run multi-user operating systems.
- It is generally used to perform a specific task with great accuracy.
Characteristics of Workstation
- It is expensive compared to personal computers.
- They are exclusively designed for complex tasks.
- It provides large storage capacity, better graphics, and a more powerful CPU when compared to a PC.
- Some workstations are designed or certified for use only with a specific application such as AutoCAD, Avid Express Studio HD, or 3D Studio Max.
PC (Personal Computer)
- A personal computer (PC) is also known as a multi-purpose microcomputer.
- Its price, capacity, and size make it feasible for individual use.
- The user can operate personal computers without needing experts or technicians.
- It comprises a microprocessor as a central processing unit (CPU), memory, input, and output.
Example of Personal Computer
Examples of Personal computers are Laptops and desktop computers.
- Desktop computer: A personal computer is designed to be in one location and fits on or under a desk.
- Laptop computer (or notebook): A laptop computer is a battery-powered portable personal computer that is small enough to rest on the user’s lap and can be carried from one place to another.
Characteristics of personal computer
- It is relatively cheaper than other computers.
- It is designed for personal or individual use.
- Time-sharing features like mini and mainframe computers are unavailable in these types.
- Suitable for personal work such as making an assignment, watching a movie, or at the office for office work, etc.
- Easy to use.
- It uses a limited number of software.
- It is the smallest in size.
Read Also: Characteristics of Computer Systems: Computer Awareness
Analogue Computer
- It is specifically designed to process analogue data.
- Continuous data that changes continuously and cannot have discrete values is called analogue data.
- Analog computer is used where we do not need exact or approximate values like speed, temperature, pressure, etc.
- It can receive data directly from measuring instruments without converting them to numbers and codes.
- It measures continuous changes in physical quantities. It outputs the reading on a dial or scale, like speedometers, mercury thermometers, etc.
Digital Computer
- A digital electronic computer is a computer machine that is both an electronic computer and a digital computer.
- It takes raw data as an input and processes it with programs stored in its memory to produce the final output.
- It only understands binary inputs 0 and 1, so the raw input data is converted into 0 and 1 by the computer and then processed by the computer to produce the result or final output.
- All modern computers like smartphones, laptops, and desktops are digital computers.
Hybrid Computer
- A hybrid computer exhibits characteristics of both analogue and digital computers.
- It is a combination of both analog and digital computers.
Characteristics of Hybrid Computer
- Hybrid computers are fast like analog computers and have memory and accuracy like a digital computer.
- It has the ability to process both continuous and discrete data.
- It converts the input analog signals to digital form before processing the input data.
- It is widely used in specialized applications where the processing of both analog and digital data is required.
Example of Hybrid computers
- A petrol pump fuel meter that converts fuel flow measurements into quantity and price is an example of a hybrid computer.
- Hycomp 250 was the first desktop hybrid computing system, released by Packard Bell in 1961.
Read Also: Basic Components of Computer System
Sample Questions on Types of Computers
Q1. What are the types of computers based on data handling capabilities?
A. 5
B. 3
C. 2
D. 1
Answer: B. 3 (Analog Computer, Digital Computer, Hybrid Computer)
Question 2. Which computer can deal with analog data?
A. Analog Computer
B. Digital Computer
C. both a and b
D. None of the above
Answer: Analog computer
Question 3. Which of the following is also known as a Microcomputer?
A. Supercomputer
B. Minicomputer
C. Workstation
D. Personal computer
Answer: Personal computer
Question 4. Which of the following computers is designed for personal use only?
A. Minicomputer
B. Personal computer
C. Analogue computer
D. All of the above
Answer: Personal computer
Question 5. Modern computers, like laptops, Desktops are examples of ……….. computers.
A. Hybrid
B. Analogue
C. Digital
D. Supercomputer
Answer: Digital
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) on types of computers
Answer: There are 4 main types of computers such as supercomputers. Mainframe computer. Minicomputer. Microcomputer.
Answer: Personal computers are of two types – desktop and laptop computers.
Answer: Supercomputers are used to handle large amounts of data such as weather forecasting, molecular modelling, and aerodynamics.
Answer: Personal Computers
Answer: Hybrid Computer
More Computer Awareness for You